In chemistry, an acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several...
36 KB (5,025 words) - 18:48, 24 July 2025
chemical reaction: acid + base ↽ − − ⇀ conjugate base + conjugate acid {\displaystyle {\text{acid}}+{\text{base}}\;{\ce {<=>}}\;{\text{conjugate base}}+{\text{conjugate...
13 KB (1,310 words) - 14:02, 17 May 2025
The Brønsted–Lowry theory (also called proton theory of acids and bases) is an acid–base reaction theory which was developed independently in 1923 by physical...
16 KB (1,949 words) - 16:30, 29 May 2025
di-t-butylpyridine and tiny proton. Acid Base (chemistry) Acid–base reaction Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory Chiral Lewis acid Frustrated Lewis pair Gutmann–Beckett...
22 KB (2,771 words) - 02:54, 24 June 2025
the context of acid–base reactions. The chemical species HA is an acid that dissociates into A−, called the conjugate base of the acid, and a hydrogen...
103 KB (11,534 words) - 07:28, 2 June 2025
otherwise specified, acid–base reactions are assumed to involve the transfer of a proton (H+) from an acid to a base. Hydronium ions are acids according to all...
47 KB (5,960 words) - 01:33, 5 July 2025
(titrant). A pH indicator is used to monitor the progress of the acid–base reaction and a titration curve can be constructed. This differs from other...
24 KB (2,650 words) - 21:07, 28 June 2025
according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Ca(OH)2...
26 KB (3,035 words) - 02:15, 29 June 2025
Neutralization (chemistry) (redirect from Acid-Base neutralization)
differences) is a chemical reaction in which acid and a base react with an equivalent quantity of each other. In a reaction in water, neutralization results...
17 KB (2,128 words) - 01:06, 10 June 2025
Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, an acid–base reaction involves a transfer of protons (H+) from one species (the acid) to another (the base). When a proton...
66 KB (8,048 words) - 01:14, 16 June 2025
In acid catalysis and base catalysis, a chemical reaction is catalyzed by an acid or a base. By Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, the acid is the proton...
7 KB (888 words) - 08:18, 24 May 2025
the acid. The alkali salt acts as a base catalyst, and other bases can be used instead. Several reviews have been written. Clear from the reaction mechanism...
4 KB (431 words) - 11:02, 25 May 2025
Baking powder (section Acid-base reactions)
by releasing carbon dioxide gas into a batter or dough through an acid–base reaction, causing bubbles in the wet mixture to expand and thus leavening the...
48 KB (5,339 words) - 12:51, 18 July 2025
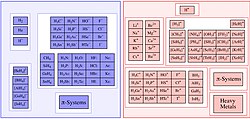
HSAB theory (redirect from Hard Acid)
"hard and soft (Lewis) acids and bases". HSAB is widely used in chemistry for explaining the stability of compounds, reaction mechanisms and pathways...
19 KB (2,118 words) - 10:59, 24 May 2025
moderate strength (pKa of conjugate acid around 10-13) N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA, also called Hünig's Base), pKa = 10.75 1,8-Diazabicycloundec-7-ene...
3 KB (354 words) - 02:44, 22 March 2024
Acid–base imbalance is an abnormality of the human body's normal balance of acids and bases that causes the plasma pH to deviate out of the normal range...
9 KB (778 words) - 14:36, 20 November 2024
Acid–base extraction is a subclass of liquid–liquid extractions and involves the separation of chemical species from other acidic or basic compounds....
18 KB (2,146 words) - 11:05, 12 July 2025
forms the strong acid sulfuric acid with water: SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 This reaction is important in the manufacturing of sulfuric acid. Chlorine(I) oxide...
5 KB (592 words) - 21:19, 19 May 2025
-ic acid and -ate for a conjugate acid and its conjugate base, respectively. For example, the conjugate base of acetic acid is acetate. Carbonic acid, which...
28 KB (2,760 words) - 20:00, 19 June 2025
of a chemical reaction is the point at which chemically equivalent quantities of reactants have been mixed. For an acid-base reaction the equivalence...
8 KB (1,118 words) - 08:14, 21 May 2024
The Suzuki reaction or Suzuki coupling is an organic reaction that uses a palladium complex catalyst to cross-couple a boronic acid to an organohalide...
35 KB (3,984 words) - 17:56, 24 May 2025
Superacid (redirect from Super Acid)
(according to the original definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which has a Hammett acidity function...
13 KB (1,519 words) - 16:49, 23 July 2025
Chemical equation (redirect from Unbalanced reaction)
radiation. Similarly, if a reaction requires a certain medium with certain specific characteristics, then the name of the acid or base that is used as a medium...
24 KB (3,519 words) - 12:52, 19 May 2025
compound containing an acidic α-proton. The Mannich reaction is a condensation reaction.: 140 The mechanism of the Mannich reaction starts with the formation...
10 KB (915 words) - 18:55, 17 July 2025
final step of the reaction, the acid and alkoxide ions formed exchange a proton. In the presence of a very high concentration of base, the aldehyde first...
8 KB (929 words) - 01:53, 14 November 2024
Dissociation constant (section Acid–base reactions)
constant, and it may be necessary to see the reaction or the equilibrium expression to know which is meant. Acid dissociation constants are sometimes expressed...
20 KB (3,119 words) - 16:09, 18 December 2024
Deprotonation (category Acid–base chemistry)
cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction. The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when...
5 KB (643 words) - 23:17, 4 February 2024
organic acids. A few common examples include: Lactic acid Acetic acid Formic acid Citric acid Oxalic acid Uric acid Malic acid Tartaric acid Butyric acid Folic...
10 KB (1,203 words) - 20:01, 24 May 2025
salts formed from the acid–base reaction with hydrochloric acid are known as hydrochlorides. For example, compare the free base hydroxylamine (NH2OH)...
7 KB (875 words) - 19:07, 25 April 2025
measure of acidity than the pH. A strong acid is an acid that dissociates according to the reaction HA + S ⇌ SH+ + A− where S represents a solvent molecule...
19 KB (2,474 words) - 21:52, 17 April 2025