A cell envelope antibiotic is an antibacterial that acts primarily at the level of the cell envelope.[citation needed] Examples include cycloserine, penicillin...
721 bytes (47 words) - 09:18, 9 June 2024
The cell envelope comprises the inner cell membrane and the cell wall of a bacterium. In Gram-negative bacteria an outer membrane is also included. This...
9 KB (1,169 words) - 03:12, 12 May 2024
prokaryotic cell has three regions: Enclosing the cell is the cell envelope, generally consisting of a plasma membrane covered by a cell wall which, for...
59 KB (6,143 words) - 20:34, 23 May 2025
antimicrobial tolerance is transient, and not inherited. Antibiotic tolerant persister cells are not antibiotic resistant mutants. Resistance is caused by newly...
17 KB (1,870 words) - 23:22, 25 May 2025
differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner (cytoplasmic) membrane...
27 KB (2,777 words) - 00:08, 11 June 2025
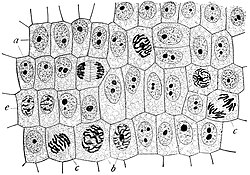
cell shape, Gram staining is a rapid method used to differentiate bacterial species. Such staining, together with growth requirement and antibiotic susceptibility...
24 KB (2,652 words) - 13:18, 10 June 2025
HIV (section Entry to the cell)
the viral envelope. The envelope protein, encoded by the HIV env gene, allows the virus to attach to target cells and fuse the viral envelope with the...
124 KB (14,240 words) - 02:31, 14 June 2025
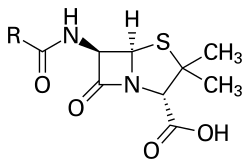
Penicillin (section Antibiotics created from 6-APA)
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens...
100 KB (10,792 words) - 05:23, 9 June 2025
Trimethoprim/polymyxin B (category Combination antibiotics)
Trimethoprim/polymyxin B Combination of Polymyxin B Cell envelope antibiotic Trimethoprim Nucleic acid inhibitor antibiotic Clinical data Trade names Polytrim Routes...
3 KB (157 words) - 13:19, 27 December 2024
opportunities. These antibiotics act via permeabilising the bacterial cell membrane, or neutralising its toxicity to cause cell death in bacteria. Its...
29 KB (3,445 words) - 18:53, 28 May 2025
Staphylococcus aureus (section Antibiotic resistance)
matrix favor the formation of persister cells, which are highly antibiotic-resistant, dormant bacterial cells. S. aureus biofilms also have high resistance...
127 KB (13,914 words) - 02:02, 2 June 2025
Cegelski L (October 2015). "Bacterial cell wall composition and the influence of antibiotics by cell-wall and whole-cell NMR". Philosophical Transactions of...
43 KB (4,789 words) - 05:17, 25 May 2025
Teixobactin (category Polypeptide antibiotics)
a new class of antibiotics, and harms bacteria by binding to lipid II and lipid III, important precursor molecules for forming the cell wall. Teixobactin...
18 KB (1,578 words) - 19:47, 20 October 2024
Virus (section Cytopathic effects on the host cell)
subunits called capsomeres.: 40 Viruses can have a lipid "envelope" derived from the host cell membrane. The capsid is made from proteins encoded by the...
155 KB (18,324 words) - 19:17, 13 June 2025
conjugation, subsequently arming the antibiotic resistant genes' recipient against antibiotics. The rapid spread of antibiotic resistance genes in this manner...
128 KB (13,959 words) - 12:33, 22 May 2025
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (redirect from Genes Involved in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm-Specific Resistance to Antibiotics)
feature that contributes to antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa is the low permeability of the bacterial cellular envelopes. In addition to this intrinsic...
95 KB (10,281 words) - 18:18, 13 June 2025
is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli and Salmonella with a common...
63 KB (7,180 words) - 06:05, 2 June 2025
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall made of peptidoglycan (50–90% of cell envelope), and as a result are stained purple by crystal...
27 KB (2,815 words) - 12:19, 11 June 2025
Darobactin (category Polypeptide antibiotics)
Gram-negative bacteria have a characteristic architecture for the cell envelope, with an inner membrane, an outer membrane, and a periplasmic space...
6 KB (494 words) - 00:07, 18 September 2024
Polymyxin B (category Polymyxin antibiotics)
Polymyxin B, sold under the brand name Poly-Rx among others, is an antibiotic used to treat meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections...
12 KB (1,078 words) - 06:24, 6 May 2025
Plasmid (category Prokaryotic cell anatomy)
In the first step after transforming the host cells with the plasmid, a media with specific antibiotic could be used to select for bacteria that contain...
73 KB (8,310 words) - 05:49, 9 June 2025
A list of antibiotic resistant bacteria is provided below. These bacteria have shown antibiotic resistance (or antimicrobial resistance). Clostridioides...
30 KB (3,434 words) - 15:53, 25 May 2025
Genetic transformation (redirect from Cell transformation, viral)
resistance to an antibiotic that the bacteria are otherwise sensitive to. The mixture of treated cells is cultured on media that contain the antibiotic so that...
55 KB (6,818 words) - 22:30, 1 April 2025
single-cell organisms that do not have a cell nucleus (their DNA floats in the cytoplasm), and eukaryotes, which have DNA surrounded by a nuclear envelope....
7 KB (727 words) - 15:50, 2 June 2025
Respiratory syncytial virus (section Antibiotics)
single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derived from the large cells known as syncytia that form when infected cells fuse. RSV is a common cause of respiratory hospitalization...
98 KB (9,655 words) - 22:04, 29 May 2025
Thermomicrobia (section Cell envelope structure)
diderm cell envelope structure. However, their cell envelope composition are atypical compared to typical Gram-negative bacteria. Cell envelope of Thermomicrobium...
23 KB (2,143 words) - 17:43, 6 June 2025
genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus...
22 KB (2,419 words) - 03:04, 2 January 2025
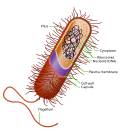
Prokaryote (redirect from Prokaryotic cell)
(/proʊˈkærioʊt, -ət/; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word...
45 KB (4,313 words) - 19:41, 11 June 2025
Anthrax (section Antibiotics)
If infection occurs, treatment is with antibiotics and possibly antitoxin. The type and number of antibiotics used depend on the type of infection. Antitoxin...
101 KB (10,467 words) - 19:58, 29 May 2025
Porin (protein) (section Antibiotic resistance)
have originated from general porins. The channels are found in the cell envelope and help facilitate solute transfer. They have similar characteristics...
17 KB (2,151 words) - 15:07, 1 October 2024