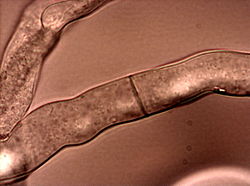
A conidium (/kəˈnɪdiəm, koʊ-/ kə-NID-ee-əm, koh-; pl.: conidia), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (pl.: chlamydoconidia),...
15 KB (1,778 words) - 03:21, 25 May 2025
conidium production, the conidiogenous cell elongates before producing another conidium atop a small denticle (a narrow projection bearing a conidium...
8 KB (766 words) - 16:10, 24 May 2025
various stages of the shot hole disease: brown spots on the leaf with conidium holders in the middle (center) that eventually fall off, leaving BB-sized...
4 KB (496 words) - 12:34, 13 September 2023
place of the ovary, which will release C. sorghi's conidium in a honeydew like substance. These conidium have limited dispersal and rely on the wind and...
9 KB (1,058 words) - 14:13, 23 May 2025
Ascospore/Ascus Basidiospore/Basidium/Teliospore anamorph/asexual: Sporangium Conidium Chlamydospore Oidium Pycniospore Other Hypha Haustorium Mycelium Cell wall...
53 KB (5,591 words) - 17:45, 22 May 2025
dendritic cell A well-resolved dendritic cell drags a conidium through a distance of up to 9 μm. The conidium, however, is not phagocytosed by the cell. The...
35 KB (4,110 words) - 15:04, 8 May 2025
inaequalis) and the horse chestnut disease Guignardia aesculi. Basidiocarp Conidium "ascocarp (fruiting structure of fungi)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved...
7 KB (739 words) - 23:37, 27 February 2025
Candida yeast. Chlamydospores of the yeast Candida albicans Fungi portal Conidium Resting spore Zygospore Staib, P; Morschhäuser, J (2007). "Chlamydospore...
3 KB (288 words) - 21:20, 6 January 2025
0 μm. The conidia are formed in branching chains in which the youngest conidium is situated at the top. Cladosporium sphaerospermum also produces ramoconidia...
17 KB (1,901 words) - 22:03, 29 May 2025
members of the zygomycete order Entomophthorales. The evolution of the conidium from the sporangiospore is the main defining difference between zygomycetes...
29 KB (3,400 words) - 16:59, 14 May 2025
have arisen independently many times just within the Agaricales. Ascocarp Conidium "MykoWeb: Evolution & Morphology in the Homobasidiomycetes". www.mykoweb...
5 KB (548 words) - 08:10, 14 November 2024
Acervulus morphology. cu: cuticle, co: conidium, cf: conidiophore, ps: pseudo-parenchymatic stroma, hi: hypha....
969 bytes (79 words) - 00:54, 20 August 2023
containing the asci and ascospores. ascoconidium Plural ascoconidia. A conidium that is formed directly from an ascospore. ascogenous Also ascogenic. Producing...
228 KB (20,293 words) - 07:50, 14 May 2025
synchronously in a sticky mass. Agar colonies are smooth and pinkish, conidium producing collars ("phialides") arising directly on hyphae, and slimy,...
3 KB (325 words) - 17:01, 12 October 2023
cycle is initiated (i.e. fertilization occurs) when a cell, usually a conidium, of opposite mating type contacts a part of the trichogyne (see Figure)...
36 KB (4,688 words) - 10:30, 21 April 2025
vary greatly between species, ranging from fewer than 20 to over 100 per conidium. The arms of the conidia show considerable variation among different Psammina...
14 KB (1,437 words) - 20:16, 22 January 2025
endospores that cause a pyogenic (pus-causing) inflammation. Fungi portal Conidium Sun SH, Sekhon SS, Huppert M (1979). "Electron microscopic studies of saprobic...
2 KB (176 words) - 05:44, 31 December 2024
third[clarification needed] cell) at one end (the pore[clarification needed] end of the conidium). Curvularia can be distinguished from the species Bipolaris and Drechslera...
5 KB (492 words) - 12:29, 11 August 2024
occurs, the respective nuclei can pass through the fused CATs from one conidium to the other. These are events of fungal vegetative growth (asexual reproduction)...
2 KB (303 words) - 18:43, 6 December 2023
Magnaporthe grisea Conidium and conidiogenous cell Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Fungi Division: Ascomycota Class: Sordariomycetes...
37 KB (3,537 words) - 01:17, 25 May 2025
affects sapling graftings in nurseries. Coryneum perniciosum, one of the two conidium-like side forms of this fungus, occurs on all decayed, ligneous parts of...
91 KB (10,690 words) - 05:02, 26 May 2025
indistinguishable from vegetative hyphae until production of the first conidium. Conidium development is distinctive and was first described by Ingold in 1956...
22 KB (2,476 words) - 22:39, 21 March 2025
the apex and along the sides; e.g. conidia of Trichothecium. adiaspore Conidium of Emmonsia parva. A large spore that increases notably in size, but does...
151 KB (13,044 words) - 21:32, 2 June 2025
cycle is initiated (i.e. fertilization occurs) when a cell (usually a conidium) of opposite mating type contacts a part of the trichogyne (see Figure)...
22 KB (2,708 words) - 17:26, 26 March 2025
a macroconidium through the surface of a honeydew drop and a secondary conidium of an oval to pearlike shape is formed, to which the contents of the original...
51 KB (5,918 words) - 04:24, 26 May 2025
triggered by rainfall, or even just a sudden drop in humidity. When the conidium lands on a leaf, it will wait until the nighttime dew, and then germinate...
16 KB (1,706 words) - 05:21, 3 February 2025
infect free living amoeba. Infection begins when a conidium comes in contact with an amoeba. The conidium produces a penetration tube to invade the host and...
4 KB (348 words) - 10:12, 4 October 2022
dispersal of male gametes, two or more female gametes may be attracted to one conidium, or male gamete. The presence of karyogamy further supports the possibility...
10 KB (1,494 words) - 01:25, 1 August 2024
resting nearby. If no hosts are available for infection, a smaller secondary conidium may develop. Once on a fly, the conidia germinate within a few hours and...
6 KB (656 words) - 17:31, 23 May 2024
temperature, relative humidity, leaf wetness and leaf age on Spilocaea oleagina conidium germination on olive leaves". European Journal of Plant Pathology. 120...
11 KB (1,427 words) - 11:37, 20 March 2025