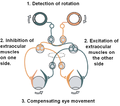
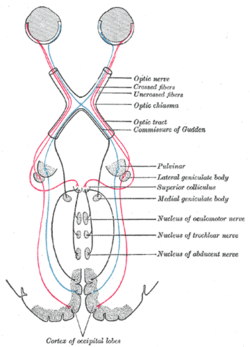
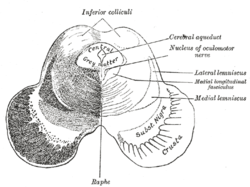
Conjugate eye movement refers to motor coordination of the eyes that allows for bilateral fixation on a single object. A conjugate eye movement is a movement...
4 KB (586 words) - 04:00, 14 September 2024
Gaze (physiology) (redirect from Conjugate lateral gaze)
the world Paramedian pontine reticular formation Conjugate eye movement "Neural Control of Saccadic Eye Movements -- Neuroscience -- NCBI Bookshelf". Retrieved...
4 KB (459 words) - 03:59, 14 September 2024
ophthalmoplegia. Symptoms of conjugate gaze palsies include the impairment of gaze in various directions and different types of movement, depending on the type...
15 KB (1,706 words) - 16:39, 17 March 2024
originates in the frontal eye field (Brodmann area 8) and terminates in the midbrain. Its fibers mediate conjugate eye movement. The corticomesencephalic...
5 KB (477 words) - 08:17, 8 October 2024
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (category Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction)
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) is a disorder of conjugate lateral gaze in which the affected eye shows impairment of adduction. When an attempt is made...
5 KB (375 words) - 14:17, 25 May 2025
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals (including humans) and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of...
70 KB (8,508 words) - 01:12, 9 June 2025
gyrus and is involved in the control of saccadic, contralateral and conjugate eye movement. This area receives its main inputs from both the occipital cortex...
52 KB (6,136 words) - 14:13, 23 May 2025
mandible condyle cone cell confluence of the sinuses conjoint tendon conjugate eye movement conjunctiva connective tissue conoid consensual reflex constrictor...
55 KB (4,485 words) - 13:36, 13 February 2025
prepositus results in inability to hold gaze upon a visual target; conjugate eye movement is unaffected. It may be conceptually regarded as a vestibular nucleus...
5 KB (450 words) - 21:33, 23 May 2025
Vergence (redirect from Convergence (eye))
This is the only eye movement that is not conjugate, but instead adducts the eye. Convergence is one of three processes an eye does to properly focus...
12 KB (1,371 words) - 10:22, 11 May 2024
responsible for saccadic eye movements for the purpose of visual field perception and awareness, as well as for voluntary eye movement. The FEF communicates...
7 KB (674 words) - 00:13, 25 January 2025
A horizontal gaze palsy is a subtype of gaze palsy in which conjugate, horizontal eye movements are limited by neurologic deficits. Horizontal gaze palsies...
10 KB (976 words) - 22:52, 1 July 2024
medical conditions, such as movement disorders. This neurological phenomenon is characterized by a sustained dystonic, conjugate, involuntary upward deviation...
10 KB (883 words) - 01:03, 16 September 2024
Nystagmus (redirect from Involuntary eye movement)
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. People can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or...
39 KB (4,189 words) - 19:22, 13 May 2025
One and a half syndrome (category Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction)
by "a conjugate horizontal gaze palsy in one direction and an internuclear ophthalmoplegia in the other". Nystagmus is also present when the eye on the...
5 KB (384 words) - 22:12, 25 May 2025
Extraocular muscles (redirect from Eye muscles)
muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye. The other muscle, the levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid...
28 KB (2,345 words) - 16:38, 21 April 2025
Vestibulo-ocular reflex (redirect from Doll's eye reflex)
reflex (VOR) is a reflex that acts to stabilize gaze during head movement, with eye movement due to activation of the vestibular system, it is also known...
26 KB (3,328 words) - 05:38, 5 February 2025
Fixation (visual) (redirect from Fixational eye movement)
and fastest of the fixational eye movements. Like saccades in general, microsaccades are usually binocular, and conjugate movements with comparable amplitudes...
24 KB (2,887 words) - 02:35, 1 June 2025
In physical organic chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers...
35 KB (4,303 words) - 09:26, 15 May 2025
Opsoclonus (category Eye stubs)
nonrhythmic eye movement. Opsoclonus consists of rapid, involuntary, multivectorial (horizontal and vertical), unpredictable, conjugate fast eye movements...
3 KB (203 words) - 06:36, 8 July 2024
Strabismus (redirect from Crossed eye)
Strabismus is an eye disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is pointed at an object...
48 KB (5,101 words) - 22:15, 29 May 2025
control eye movement in general. Cortical control of eye movement (saccades, smooth pursuit, accommodation) involves conjugate gaze, not unilateral eye movement...
15 KB (1,751 words) - 11:00, 25 May 2025
non-deviating eye, both eye will produce a conjugate movement in the direction of the prism apex. However unlike a normal response, the fellow deviated eye will...
8 KB (910 words) - 19:26, 14 May 2025
reticular formation. The PPRF mediates horizontal conjugate gaze (i.e. simultaneous horizontal movement of both eyes) by projecting to both: the ipsilateral...
8 KB (849 words) - 13:55, 24 May 2025
Oculometer (category Eye care)
Oculometer is a device that tracks eye movement. The oculometer computes eye movement by tracking corneal reflection relative to the center of the pupil...
17 KB (2,168 words) - 06:48, 28 May 2025
Parinaud's syndrome (redirect from Sunset eye sign)
medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF). It is a group of abnormalities of eye movement and pupil dysfunction and is named for Henri Parinaud (1844–1905), considered...
8 KB (762 words) - 02:58, 12 March 2023
Presbyopia (redirect from Old Eye)
insufficiency of optical accommodation associated with the aging of the eye; it results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close...
22 KB (2,278 words) - 07:03, 4 June 2025
anisometropia, etc.) Eye movement coordination Accommodative and vergence stress Glare Flickering lights Allergy Close viewing distance Dry-eye Fatigue Upward...
9 KB (819 words) - 09:36, 30 May 2025
Amblyopia (redirect from Lazy eye syndrome)
called lazy eye, is a disorder of sight in which the brain fails to fully process input from one eye and over time favors the other eye. It results in...
40 KB (4,265 words) - 23:12, 2 June 2025
Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement. The MLF interconnects interneurons of each abducens nucleus with motor...
11 KB (1,041 words) - 05:18, 7 January 2025