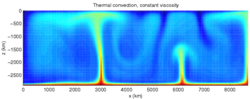
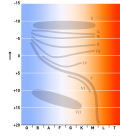
A convection zone, convective zone or convective region of a star is a layer which is unstable due to convection. Energy is primarily or partially transported...
7 KB (837 words) - 11:35, 21 March 2025
Sun (section Convective zone)
sinks to the base of the convection zone, where it again picks up heat from the top of the radiative zone and the convective cycle continues. At the photosphere...
173 KB (19,378 words) - 15:47, 16 June 2025
than by convection. Energy travels through the radiative zone in the form of electromagnetic radiation as photons. Matter in a radiative zone is so dense...
11 KB (1,732 words) - 11:35, 21 March 2025
the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place...
57 KB (7,033 words) - 21:49, 24 May 2025
needed] Convective overshoot also occurs at the boundaries of convective zones in stars. An example of this is at the base of the convection zone in the...
4 KB (528 words) - 08:53, 4 January 2025
not the case, then the plasma becomes unstable and convection will occur, forming a convection zone. This can occur, for example, in regions where very...
148 KB (16,421 words) - 22:25, 19 June 2025
entirely radiative with convective zones near the surface. With decreasing stellar mass, the proportion of the star forming a convective envelope steadily increases...
61 KB (6,829 words) - 11:13, 18 June 2025
) Near the base of the Sun's convection zone, the convection is adiabatic, but near the surface of the Sun, convection is not adiabatic. A more realistic...
29 KB (3,899 words) - 08:19, 13 June 2025
identify candidate cluster members. Given the lack of a significant outer convection zone, theory predicts the absence of a magnetic dynamo in earlier A stars...
65 KB (8,115 words) - 08:44, 13 June 2025
Convection (or convective heat transfer) is the transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. Although often discussed as a...
10 KB (1,283 words) - 05:55, 19 June 2025
dwarf. Such stars will not become red giants as the whole star is a convection zone and it will not develop a degenerate helium core with a shell burning...
50 KB (6,439 words) - 10:38, 17 June 2025
temperature classes. Type-B stars do not have a corona and lack a convection zone in their outer atmosphere. They have a higher mass loss rate than smaller...
12 KB (1,369 words) - 06:50, 16 June 2025
in contrast to the Sun, which has a radiation zone centered on the core with an overlying convection zone. The energy flux from Vega has been precisely...
98 KB (10,326 words) - 20:15, 20 June 2025
rotating outer convective zone. This causes the region to have a very large shear as the rotation rate changes very rapidly. The convective exterior rotates...
4 KB (510 words) - 11:36, 21 March 2025
Recurrent Micronova Supernova Structure Core Convection zone Microturbulence Oscillations Radiation zone Atmosphere Photosphere Starspot Chromosphere...
14 KB (1,695 words) - 21:03, 7 June 2025
core to the outer edge of the radiative zone at about 170,000 years. From there they cross into the convective zone (the remaining 25% of distance from the...
14 KB (1,893 words) - 21:12, 15 April 2025
Altair (A7), Sirius A (A1), and Vega (A0). A-type stars do not have convective zones and thus are not expected to harbor magnetic dynamos. As a consequence...
12 KB (1,060 words) - 12:37, 19 June 2025
A. (1985). "Numerical simulations of stellar convective dynamos III. At the base of the convection zone". Solar Physics. 125 (1–2): 137–150. Bibcode:1985GApFD...
13 KB (1,618 words) - 10:40, 29 April 2025
flux that convective energy transfer becomes more important than does radiative transfer. As a result, the core region becomes a convection zone, which stirs...
38 KB (4,498 words) - 08:26, 24 May 2025
observation, granules are convection cells in the Sun's photosphere. They are caused by currents of plasma in the Sun's convective zone, directly below the...
3 KB (320 words) - 19:15, 5 May 2025
the volume of a star, lying above the stellar core, radiation zone and convection zone. The stellar atmosphere is divided into several regions of distinct...
7 KB (822 words) - 13:23, 9 June 2025
Hayashi track (section Forbidden zone)
convection zone, cannot explain the shape of the red-giant branch. He therefore replaced the model by including the effects of thick convection zones...
24 KB (3,724 words) - 23:23, 15 March 2025
and brown dwarfs, which do not have a radiative core and only have a convection zone, have demonstrated that they maintain large-scale, solar-strength magnetic...
8 KB (885 words) - 14:34, 26 May 2025
discovery. The convection zone of the Sun, the region beneath the photosphere in which energy is transported primarily by convection, is sensitive to...
39 KB (4,716 words) - 22:42, 7 June 2025
solar dynamo. Although it roughly coincides with the base of the solar convection zone — also inferred through helioseismology — it is conceptually distinct...
51 KB (5,445 words) - 01:38, 26 November 2024
main sequence stars have no radiation zone; the dominant energy transport mechanism throughout the star is convection. The simplest commonly used model of...
15 KB (2,089 words) - 21:20, 1 October 2024
Asteroseismology (section Surface convection)
the base of a surface convection zone is sharp and the convective timescales slower than the pulsation timescales, the convective flows react too slowly...
18 KB (2,290 words) - 07:53, 18 March 2025
reproduced here: AD dynamic When RLOF happens to a star with a deep convection zone. Mass transfer happens rapidly on the dynamical time scale of the star...
14 KB (1,957 words) - 08:42, 19 March 2025
Recurrent Micronova Supernova Structure Core Convection zone Microturbulence Oscillations Radiation zone Atmosphere Photosphere Starspot Chromosphere...
11 KB (1,312 words) - 00:13, 16 June 2025
little immediate change at the surface. Red supergiants develop deep convection zones reaching from the surface over halfway to the core and these cause...
34 KB (4,293 words) - 21:26, 19 June 2025