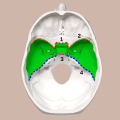
A cranial fossa is formed by the floor of the cranial cavity. There are three distinct cranial fossae: Anterior cranial fossa (fossa cranii anterior),...
3 KB (142 words) - 18:45, 18 May 2024
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid...
6 KB (563 words) - 14:57, 31 January 2024
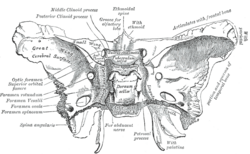
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper...
8 KB (979 words) - 23:56, 15 October 2023
hypophyseal fossa (the depression in the sphenoid bone). Some examples include: In the skull: Cranial fossa Anterior cranial fossa Middle cranial fossa Interpeduncular...
3 KB (263 words) - 03:25, 9 August 2024
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the...
5 KB (595 words) - 04:36, 6 December 2024
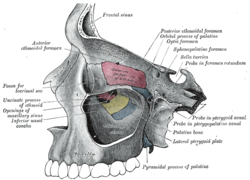
communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina. It has the following boundaries:...
4 KB (356 words) - 22:01, 21 July 2023
spread into the infratemporal fossa. This can be surgically removed through the middle cranial fossa. The infratemporal fossa can also be used to approach...
8 KB (864 words) - 15:04, 9 July 2023
Base of skull (redirect from Cranial base)
Trigeminal ganglion Middle cranial fossa Anterior cranial fossa Middle meningeal artery Cribriform plate Posterior cranial fossa Nasociliary nerve Hypoglossal...
3 KB (219 words) - 09:31, 25 February 2025
Sella turcica (redirect from Pituiary fossa)
hypophyseal fossa. The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa...
5 KB (561 words) - 17:11, 13 March 2025
Skull (redirect from Cranial bone)
its fossae, the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae changes rapidly. The anterior cranial fossa changes especially during the first trimester...
41 KB (4,616 words) - 23:05, 17 May 2025
Skull fracture (section Cranial burst fracture)
of orbits in the anterior cranial fossa, and the areas between the mastoid and dural sinuses in the posterior cranial fossa. Children with a simple skull...
22 KB (2,808 words) - 04:49, 18 October 2024
the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through its own canaliculus to reach the infratemporal fossa. Cell bodies...
5 KB (517 words) - 22:09, 18 December 2024
lacerum. The anterior surface forms the posterior part of the middle cranial fossa of the base of the skull, and is continuous with the inner surface of...
13 KB (1,819 words) - 01:19, 14 September 2024
hypophysial veins. This depends upon the area of the cranial cavity: in the anterior cranial fossa the anterior meningeal artery (branch from the ethmoidal...
15 KB (1,713 words) - 18:50, 4 May 2025
Epidural hematoma (redirect from Hematoma, epidural, cranial)
the time it occurs. In the case of epidural hematoma in the posterior cranial fossa, tonsillar herniation causes Cushing's triad: hypertension, bradycardia...
17 KB (1,746 words) - 23:18, 11 November 2024
Vagus nerve (redirect from Tenth cranial nerve)
pain, and temperature of the outer ear, the dura of the posterior cranial fossa and the mucosa of the larynx The motor division of the glossopharyngeal...
31 KB (3,601 words) - 12:18, 11 May 2025
Facial nerve (redirect from Cranial nerve VII)
and sensory parts of the facial nerve join and traverse the posterior cranial fossa before entering the petrous temporal bone via the internal auditory...
19 KB (2,273 words) - 14:16, 29 August 2024
surgicala approaches are described to achieve decompression: Middle cranial fossa approach Translabarynthine approach "Total decompression" can also be...
11 KB (1,355 words) - 02:04, 15 April 2025
known as mastoid ecchymosis, is an indication of fracture of middle cranial fossa of the skull. These fractures may be associated with underlying brain...
3 KB (173 words) - 17:07, 16 February 2025
subarcuate fossa is a shallow depression upon the internal surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone forming the wall of the posterior cranial fossa. The...
4 KB (327 words) - 15:34, 18 May 2024
Posterior fossa may refer to: Posterior cranial fossa, an area of the head PHACES Syndrome, a condition of the posterior cranial fossa Posterior intercondyloid...
232 bytes (62 words) - 12:06, 10 January 2019
carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into (the middle cranial fossa of) the cranial cavity. Observing the trajectory of the canal from exterior...
8 KB (774 words) - 16:31, 21 March 2025
the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. It allows for the passage of the maxillary nerve (V2)...
4 KB (435 words) - 20:43, 15 May 2024
petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear. The opening to the meatus is called the porus acusticus...
5 KB (523 words) - 20:12, 1 May 2024
pharyngotympanic tube, superior jugular bulb, posterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa, carotid canal, abducens nerve, sigmoid sinus) to which they...
5 KB (545 words) - 18:19, 30 October 2024
sphenoid, closed by sphenoidal conchae. This forms the floor of the middle cranial fossa. It presents (starting from the front): foramen rotundum foramen ovale...
16 KB (1,812 words) - 14:27, 17 March 2025
Craniosynostosis (redirect from Cranial synostosis)
elements of metopic suture closure involve a low volume of the anterior cranial fossa, the metopic ridging and hypotelorism. These problems are all addressed...
72 KB (7,727 words) - 21:00, 24 February 2025
Diploe Cranial base Internal surface of cranial base Sphenopetrosal fissure Petro-occipital fissure Anterior cranial fossa Middle cranial fossa Posterior...
50 KB (4,111 words) - 20:02, 4 April 2025
85%. They are most often associated with fractures of the anterior cranial fossa. Raccoon eyes may also be a sign of disseminated neuroblastoma, amyloidosis...
4 KB (374 words) - 10:14, 18 August 2024
that enters the middle cranial fossa through either the foramen spinosum or foramen ovale to innervate the meninges of this fossa as well as the mastoid...
2 KB (142 words) - 16:18, 8 May 2024