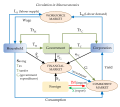
Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand in an economy is more than aggregate supply. It involves inflation rising as real gross domestic product...
4 KB (477 words) - 02:28, 28 January 2025
the demand-pull theory is the theory that inflation occurs when demand for goods and services exceeds existing supplies. According to the demand pull theory...
2 KB (193 words) - 20:14, 6 July 2025
different price Demand curve, a graphical representation of a demand schedule Demand pull theory, the theory that inflation occurs when demand for goods and...
884 bytes (156 words) - 01:34, 9 June 2021
Stagflation (section Demand-pull stagflation theory)
Middle East crises for the benefit of pecuniary interests. Demand-pull stagflation theory explores the idea that stagflation can result exclusively from...
43 KB (5,088 words) - 17:53, 5 July 2025
Price revolution (section Quantity theory of money)
is linked with the demand-pull explanation of the price revolution. This "demand-pull" theory states that an increase in the demand for money and the growth...
32 KB (4,305 words) - 23:14, 8 May 2025
Cost-push inflation (redirect from Cost push theory (economics))
to increase prices of their outputs. It is contrasted with the theory of demand-pull inflation. Both accounts of inflation have at various times been...
5 KB (505 words) - 15:09, 19 April 2025
argues that the primary risk once the economy reaches full employment is demand-pull inflation, which acts as the only constraint on spending. MMT also argues...
66 KB (7,214 words) - 22:28, 15 July 2025
In economics, general equilibrium theory attempts to explain the behavior of supply, demand, and prices in a whole economy with several or many interacting...
50 KB (6,213 words) - 04:56, 10 March 2025
In economics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is...
21 KB (2,867 words) - 02:14, 30 January 2025
demand Expectations Adaptive Rational Financial crisis Growth Inflation Demand-pull Cost-push Interest rate Investment Liquidity trap Measures of national...
5 KB (538 words) - 20:00, 6 July 2025
Diving helmet (redirect from Lightweight demand helmet)
incorporate a demand valve so the helmet only delivers breathing gas when the diver inhales. Free-flow helmets use much larger quantities of gas than demand helmets...
69 KB (7,951 words) - 16:17, 26 June 2025
concurred with the latter theory, suggesting that "demand creates its own supply" and developing a comprehensive theory of effective demand. According to Keynesian...
8 KB (1,030 words) - 02:13, 4 December 2024
Triangle model (category Economic theories stubs)
three root causes: built-in inflation, demand-pull inflation, and cost-push inflation. Unlike the earliest theories of the Phillips Curve, the triangle model...
1 KB (99 words) - 15:18, 16 July 2025
Keynesian economics (redirect from Keynesian theory)
economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic...
108 KB (13,333 words) - 04:44, 12 July 2025
Macroeconomics (redirect from Macro-economic theory)
called Keynesianism or Keynesian theory.: 526 In Keynes' theory, aggregate demand - by Keynes called "effective demand" - was key to determining output...
66 KB (7,913 words) - 18:47, 23 May 2025
Post-Keynesian economics (redirect from Post-Keynesian economic theory)
extended beyond the theory of aggregate employment to theories of income distribution, growth, trade and development in which money demand plays a key role...
22 KB (2,240 words) - 21:11, 24 May 2025
market. According to this theory, the determination of wages is the intersection of the demand and supply labor. The demand of labor is derived from marginal...
37 KB (4,756 words) - 07:58, 15 July 2025
Chartalism (category Macroeconomic theories)
they issue, creating demand for it. Georg Friedrich Knapp, a German economist, invented the term "chartalism" in his State Theory of Money, which was published...
10 KB (1,195 words) - 05:45, 14 July 2025
will not be punished even if they yield to a particular demand. One study found that madman theory is frequently counterproductive, but that it can be effective...
22 KB (2,162 words) - 09:22, 17 June 2025
IS–LM model (category General equilibrium theory)
Modern Macroeconomic Theory. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 49–90. ISBN 978-0-631-13158-8. Mankiw, Nicholas Gregory (2022). "Aggregate Demand I+II". Macroeconomics...
29 KB (3,742 words) - 10:17, 1 July 2025
Milton Friedman's 1956 restatement of the quantity theory of money. Friedman argued that the demand for money could be described as depending on a small...
30 KB (3,379 words) - 20:22, 13 July 2025
Keynesian theory. This situation occurs when the demand for money is infinitely elastic with respect to the interest rate. A typical money-demand function...
20 KB (2,841 words) - 02:33, 12 July 2025
Endogenous growth theory holds that economic growth is primarily the result of endogenous and not external forces. Endogenous growth theory holds that investment...
13 KB (1,464 words) - 19:55, 14 October 2024
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (category General equilibrium theory)
forecasting purposes. DSGE econometric modelling applies general equilibrium theory and microeconomic principles in a tractable manner to postulate economic...
51 KB (5,995 words) - 02:13, 5 May 2025
Maynard Keynes—come to the same conclusions in macroeconomics and the theories of demand and supply. Like Keynes, they were inspired by the works of Knut Wicksell...
8 KB (924 words) - 09:46, 30 October 2024
Accelerator effect (redirect from Accelerator theory)
Keynesian theory began to dominate the field of economics. John Maynard Keynes first introduced the idea in his seminal work "The General Theory of Employment...
10 KB (1,403 words) - 23:43, 30 June 2025
inflation is too high. Keynesian theory posits that removing spending from the economy will reduce levels of aggregate demand and contract the economy, thus...
21 KB (2,623 words) - 12:28, 24 June 2025
current inflation rate equals the sum of demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation. "Demand-pull inflation" refers to the effects of...
3 KB (441 words) - 17:32, 13 July 2025
DeLong concludes that there is little evidence to support the convergence theory. The key assumption of the Solow–Swan growth model is that capital is subject...
35 KB (4,945 words) - 22:02, 12 July 2025
Liquidity preference (redirect from Liquidity preference theory of interest)
In macroeconomic theory, liquidity preference is the demand for money, considered as liquidity. The concept was first developed by John Maynard Keynes...
10 KB (1,213 words) - 06:26, 28 June 2025