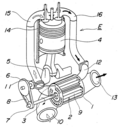
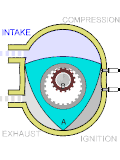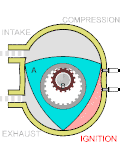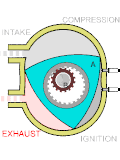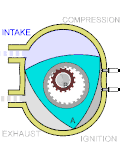
Exhaust pulse pressure charging (EPPC) is a system for supercharging two-stroke diesel engines of the loop-scavenge type. Loop-scavenge engines cannot...
2 KB (225 words) - 19:11, 14 November 2024
as the maximum that a system's pump can reliably produce. Exhaust pulse pressure charging Expansion chamber Scalar quantity Shekhar, Ravi; Singh Dhugga...
6 KB (626 words) - 21:36, 27 December 2024
Kiki Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan - United States Patent 4563997. Exhaust pulse pressure charging Inertial supercharging effect Kadenacy effect Ferrari 126C...
7 KB (731 words) - 03:32, 11 October 2024
the exhaust system can be optimised ("tuned") to maximise the power output of the engine. Tuned exhausts are designed so that reflected pressure waves...
8 KB (915 words) - 00:55, 11 September 2023
Turbocharger (redirect from Turbo charging)
media related to Turbochargers. Boost gauge Engine downsizing Exhaust pulse pressure charging Hot vee turbocharged engine Nice, Karim (4 December 2000)....
33 KB (3,483 words) - 16:49, 3 June 2025
in pressure decreases and the exhaust velocity decreases. This forms the medium-pressure body component of the exhaust pulse The remaining exhaust gas...
11 KB (1,571 words) - 11:39, 1 May 2025
Kadenacy effect (category Exhaust systems)
supercharger or turbocharger. Exhaust pulse pressure charging Inertial supercharging effect Pressure wave supercharger Supercharger Pulse-jets website Archived...
2 KB (212 words) - 00:00, 1 March 2025
maximized to create the most power in each cycle. Exhaust pulse pressure charging Kadenacy effect Pressure wave supercharger Supercharger "Inertia Supercharging...
4 KB (567 words) - 04:26, 16 April 2025
Pressure charger may refer to: Exhaust pulse pressure charging Supercharger Turbocharger This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title...
128 bytes (43 words) - 19:49, 29 December 2019
system of exhaust pulse pressure charging whereby surplus air in the exhaust manifold was forced back into the cylinder by the exhaust pulse from a neighbouring...
12 KB (1,438 words) - 15:51, 26 December 2024
engines had exhaust pulse pressure charging and developed 1,200 horsepower (895 kW) at 625 rpm. There were no valves, and inlet and exhaust were via ports...
15 KB (1,420 words) - 10:20, 16 May 2025
Oxygen sensor (redirect from Exhaust gas oxygen sensor)
specific area. Exhaust gas analyzer Digifant engine management system Jetronic Motronic Oxygen saturation Winkler test for dissolved oxygen Pulse oximetry "What...
30 KB (4,236 words) - 19:23, 24 May 2025
Trionic T5.5 (section Basic charging pressure)
basic charging pressure it shall be noted that the pressure decreases at high RPM and increases at low outside temperatures. Charging pressure regulation...
21 KB (3,500 words) - 00:37, 11 March 2024
Muffler (redirect from Exhaust silencer)
distinct pulses of exhaust gas that exit through the exhaust pipes and the muffler. For example, a four-cylinder engine will have four high-pressure pulses for...
8 KB (786 words) - 02:22, 16 October 2024
Two-stroke engine (redirect from Exhaust port)
engines, his had a separate charging cylinder. The crankcase-scavenged engine, employing the area below the piston as a charging pump, is generally credited...
29 KB (3,786 words) - 15:30, 3 June 2025
the pressure at the output of the intake runner is reduced. This low pressure pulse runs to the input end, where it is converted into an over-pressure pulse...
17 KB (2,315 words) - 14:46, 7 March 2025
Internal combustion engine (redirect from Charge (engine))
irreversibly due to the leftover pressure—in excess of back pressure, the gauge pressure on the exhaust port. Exhaust: The exhaust valve remains open while the...
101 KB (13,117 words) - 01:41, 4 June 2025
Environment Ericsson Portable PC Ethics and Public Policy Center Exhaust pulse pressure charging This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the...
368 bytes (63 words) - 10:30, 12 April 2017
increased pressure at the charging side of the turbo. This is achieved as an excess amount of fuel/air mixture escapes through the exhaust valves and...
12 KB (1,814 words) - 12:07, 1 May 2025
an exhaust stroke and a charging stroke. As the power piston remained withdrawn during exhaust and charging, it was practical to provide exhaust and...
20 KB (2,557 words) - 21:40, 28 April 2025
Rocket engine (section Exhaust noise)
expulsion of an exhaust fluid that has been accelerated to high speed through a propelling nozzle. The fluid is usually a gas created by high pressure (150-to-4...
101 KB (11,734 words) - 13:38, 30 May 2025
adjusted exhaust camshaft timing, increased cross-section high-pressure injectors, 1.2 bar (17.4 psi) (value only valid for Audi S3(8P)) boost pressure K04...
132 KB (15,983 words) - 16:19, 25 April 2025
Horsepower", when both intake & exhaust are open simultaneously, the much-higher-pressure exhaust pushes the intake-charge back, out from the cylinder, polluting...
30 KB (3,853 words) - 00:10, 23 May 2025
Twincharger (redirect from Twin charging)
uses two separate chambers to better harness energy from alternating exhaust gas pulses. The chambers' nozzles may also be of different sizes, to better balance...
15 KB (1,487 words) - 14:50, 14 February 2025
HRP8 stationary diesel. The engines used Crossley's system of exhaust pulse pressure charging and developed 1,200 horsepower (895 kW) at 625 rpm, though...
19 KB (1,418 words) - 05:59, 25 October 2024
Otto cycle (section Process 1–0 exhaust stroke)
cylinder, from 0 to 1, at atmospheric pressure (constant pressure) through the open intake valve, while the exhaust valve is closed during this process...
24 KB (4,251 words) - 12:47, 26 April 2025
dimensions are calculated to maintain a design chamber pressure, while producing thrust from the exhaust gases. Once ignited, a simple solid rocket motor cannot...
44 KB (5,414 words) - 22:21, 28 April 2025
Nuclear pulse propulsion or external pulsed plasma propulsion is a hypothetical method of spacecraft propulsion that uses nuclear explosions for thrust...
27 KB (2,925 words) - 20:25, 25 May 2025
Energy-efficient driving (redirect from Pulse and glide)
kilometres per hour (37 mph), approximately 33% of the energy goes into exhaust and 29% is used to cool the engine; engine friction takes another 11%....
34 KB (4,112 words) - 16:29, 26 May 2025
engines operate better with a low-pressure exhaust system. Higher exhaust back pressure reduces mean effective pressure, more severely in peripheral intake...
136 KB (16,656 words) - 20:34, 1 June 2025