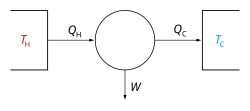
A heat engine is a system that transfers thermal energy to do mechanical or electrical work. While originally conceived in the context of mechanical energy...
28 KB (3,858 words) - 21:27, 4 March 2025
A Carnot heat engine is a theoretical heat engine that operates on the Carnot cycle. The basic model for this engine was developed by Nicolas Léonard...
26 KB (3,335 words) - 17:30, 28 January 2025
A Stirling engine is a heat engine that is operated by the cyclic expansion and contraction of air or other gas (the working fluid) by exposing it to...
96 KB (11,281 words) - 04:15, 5 May 2025
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature...
19 KB (2,457 words) - 22:00, 29 April 2025
and mixing. Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common...
42 KB (5,106 words) - 13:15, 2 May 2025
Thermoacoustic engines (sometimes called "TA engines") are thermoacoustic devices which use high-amplitude sound waves to pump heat from one place to another...
14 KB (1,677 words) - 09:02, 3 April 2025
Carnot cycle (redirect from Engine cycle)
upper limit on the efficiency of any classical thermodynamic engine during the conversion of heat into work, or conversely, the efficiency of a refrigeration...
25 KB (3,240 words) - 21:02, 4 March 2025
force of heat and the laws of heat which may be deduced therefrom". The Mechanical Theory of Heat, with its Applications to the Steam-Engine and to the...
92 KB (12,978 words) - 10:12, 8 April 2025
Second law of thermodynamics (redirect from Heat engine statement)
Carnot, who in 1824 showed that the efficiency of conversion of heat to work in a heat engine has an upper limit. The first rigorous definition of the second...
107 KB (15,472 words) - 01:32, 4 May 2025
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure...
80 KB (9,884 words) - 13:56, 1 May 2025
quantum heat engine is a device that generates power from the heat flow between hot and cold reservoirs. The operation mechanism of the engine can be described...
36 KB (5,134 words) - 13:03, 15 March 2025
Thermodynamics (redirect from Heat generation)
a discourse on heat, power, energy and engine efficiency. The book outlined the basic energetic relations between the Carnot engine, the Carnot cycle...
48 KB (5,843 words) - 03:10, 28 March 2025
Cogeneration (redirect from Clean Heat & Power)
Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Cogeneration...
62 KB (6,977 words) - 23:32, 6 May 2025
Stirling engine range from mechanical propulsion to heating and cooling to electrical generation systems. A Stirling engine is a heat engine operating...
43 KB (5,023 words) - 01:31, 31 December 2024
A hot air engine (historically called an air engine or caloric engine) is any heat engine that uses the expansion and contraction of air under the influence...
13 KB (1,760 words) - 01:48, 29 March 2024
Thermal efficiency (section Heat engines)
such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the ratio...
22 KB (3,338 words) - 09:05, 15 January 2025
This timeline of heat engine technology describes how heat engines have been known since antiquity but have been made into increasingly useful devices...
20 KB (2,616 words) - 22:52, 14 April 2025
Carnot's theorem (thermodynamics) (redirect from Reversible engine)
efficiency that any heat engine can obtain. Carnot's theorem states that all heat engines operating between the same two thermal or heat reservoirs cannot...
17 KB (2,536 words) - 01:05, 7 January 2025
combustion engine cooling uses either air or liquid to remove the waste heat from an internal combustion engine. For small or special purpose engines, cooling...
29 KB (3,815 words) - 01:05, 29 April 2025
An external combustion engine (EC engine) is a reciprocating heat engine where a working fluid, contained internally, is heated by combustion in an external...
3 KB (292 words) - 18:42, 7 June 2024
Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives...
26 KB (3,675 words) - 07:07, 7 March 2025
History of thermodynamics (redirect from Theory of heat)
30 feet, and is thus often considered the first true steam engine. The phenomenon of heat conduction is immediately grasped in everyday life. The fact...
34 KB (3,780 words) - 15:53, 31 March 2025
Brayton cycle (redirect from Brayton engine)
heat engines that have air or some other gas as their working fluid. It is characterized by isentropic compression and expansion, and isobaric heat addition...
23 KB (3,024 words) - 16:07, 29 January 2025
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol c) of a substance is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance...
55 KB (8,537 words) - 22:17, 8 April 2025
Atkinson cycle (redirect from Modified atkinson cycle engine)
The Atkinson-cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine invented by James Atkinson in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency...
20 KB (2,557 words) - 21:40, 28 April 2025
A rocket engine is a reaction engine, producing thrust in accordance with Newton's third law by ejecting reaction mass rearward, usually a high-speed...
101 KB (11,723 words) - 04:43, 8 May 2025
Thermodynamic cycle (redirect from Heat cycle)
may convert heat from a warm source into useful work, and dispose of the remaining heat to a cold sink, thereby acting as a heat engine. Conversely,...
19 KB (2,956 words) - 02:05, 11 April 2025
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion...
101 KB (13,117 words) - 21:52, 1 May 2025
efficiency of heat engines, p. 1 (2007) by James R. Senf: "Heat engines are made to provide mechanical energy from thermal energy." "Understanding Heat Exchangers...
66 KB (8,475 words) - 23:27, 3 April 2025
Rankine cycle (redirect from Rankine cycle engine)
certain heat engines, such as steam turbines or reciprocating steam engines, allow mechanical work to be extracted from a fluid as it moves between a heat source...
19 KB (2,301 words) - 16:52, 16 April 2025