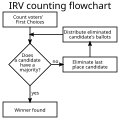
Instant-runoff voting (IRV; US: ranked-choice voting (RCV), AU: preferential voting, UK/NZ: alternative vote) is a single-winner ranked voting election...
81 KB (8,953 words) - 19:42, 9 May 2025
not strictly defined, but most often refers to instant-runoff voting (IRV) or single transferable vote (STV), the main difference being whether only one...
129 KB (10,844 words) - 21:50, 3 May 2025
Maine use the Instant-runoff voting system, the ranked-choice voting (RCV) system, which unlike TRS does not require multiple rounds of voting.) The French...
43 KB (4,899 words) - 15:59, 4 May 2025
voting systems vary dramatically in how preferences are tabulated and counted, which gives them very different properties. In instant-runoff voting (IRV)...
27 KB (3,325 words) - 02:51, 16 May 2025
Instant-runoff voting (IRV) is a ranked voting method used in single-winner elections. IRV is also known outside the US as the alternative vote (AV) or...
70 KB (6,676 words) - 09:52, 11 April 2025
Runoff voting can refer to: election methods where candidates are eliminated based on comparison of votes tallies: Two-round system, a voting system where...
802 bytes (147 words) - 03:57, 24 March 2025
Electoral system (redirect from Voting systems)
in the United States have begun to adopt instant-runoff voting. In 2020 a referendum adopting approval voting in St. Louis passed with 70% support. In...
57 KB (7,248 words) - 05:52, 16 May 2025
other ranked-vote systems – such as single transferable voting (STV), instant-runoff voting (IRV), Coombs' method, and Baldwin's method – allow for many...
18 KB (2,263 words) - 18:12, 3 May 2025
Condorcet winner criterion (redirect from Majority preferential voting)
Plurality voting Instant-runoff voting Borda count Approval Voting Coombs' rule Bucklin voting (and the closely related median voting) Score Voting With plurality...
18 KB (2,303 words) - 23:42, 28 February 2025
Spoiler effect (redirect from Vote-splitting)
severity of spoiler effects depends substantially on the voting method. Instant-runoff voting (IRV), the two-round system (TRS), and especially first-past-the-post...
48 KB (4,987 words) - 05:34, 30 April 2025
a hybrid between (rated) score voting and (ranked) instant runoff voting. The first movement to implement STAR voting was centered in Oregon, with chapters...
17 KB (1,859 words) - 22:57, 28 February 2025
vote (TCP). The TCP is the electoral penultimate result for an electoral division where preferences have been distributed using instant-runoff voting...
89 KB (3,342 words) - 08:44, 9 May 2025
literature) Instant-runoff voting and single transferable vote, referred to as "preferential voting" in Australia by way of conflation Bucklin voting, similarly...
1 KB (125 words) - 14:16, 5 May 2025
later-no-harm (most methods) or monotonicity (such as instant-runoff voting) will encourage bullet voting or truncation in some situations. In systems that...
18 KB (2,156 words) - 16:19, 30 April 2025
preferential voting systems, such as instant runoff voting, as well as the two-round system of runoffs and less tested methods such as approval voting and Condorcet...
72 KB (7,262 words) - 11:02, 9 May 2025
Multiple transferable voting, sometimes called block preferential or block instant-runoff voting, is a winner-take-all system for electing several representatives...
5 KB (582 words) - 23:41, 22 June 2024
Participation criterion (section Instant-runoff voting)
no-show paradoxes is the use of instant-runoff (often called ranked-choice voting in the United States). In instant-runoff voting, a no-show paradox can occur...
26 KB (2,598 words) - 07:29, 4 April 2025
Electoral system of Australia (redirect from Australian preferential voting system)
features including compulsory enrolment; compulsory voting; majority-preferential instant-runoff voting in single-member seats to elect the lower house,...
118 KB (11,068 words) - 07:22, 12 May 2025
one does exist, include instant-runoff voting (often called ranked-choice in the United States), First-past-the-post voting, and the two-round system...
4 KB (5,955 words) - 08:22, 26 February 2025
winner-take-all elections using block plurality voting or block instant-runoff voting. Cumulative voting is commonly-used in corporate governance, where...
17 KB (2,145 words) - 23:06, 9 January 2025
systems – such as first-past-the-post (FPTP), instant-runoff voting (IRV), and block voting – one party or voting bloc can take all seats in a district. The...
134 KB (16,158 words) - 11:49, 10 May 2025
rules like the two-round system, plurality-with-primaries, and instant-runoff voting (IRV). In a center squeeze, the majority-preferred and socially...
48 KB (4,970 words) - 20:37, 3 May 2025
Condorcet method (redirect from Condorcet voting)
is one. Not all single winner, ranked voting systems are Condorcet methods. For example, instant-runoff voting and the Borda count are not Condorcet methods...
71 KB (9,462 words) - 16:03, 8 May 2025
List of electoral systems (redirect from List of voting systems)
"Estimating the Margin of Victory for Instant-runoff Voting". Proceedings of the 2011 Conference on Electronic Voting Technology/Workshop on Trustworthy Elections...
22 KB (746 words) - 01:04, 4 May 2025
Best-is-worst paradox (section Instant-runoff voting)
are sometimes called best-is-worst paradoxes, and can occur in instant-runoff voting and minimax. Methods that satisfy reversal symmetry include the...
11 KB (935 words) - 01:27, 22 April 2025
one vote. Alternatives to First-past-the-post voting include approval voting, two-round, proportional representation, and instant-runoff voting. With...
30 KB (3,765 words) - 18:38, 11 April 2025
preferences (optional preferential voting) for Senate elections but full preferential voting is still used in the instant-runoff voting system used to elect members...
7 KB (935 words) - 18:51, 28 April 2025
Independence of clones criterion (redirect from Clone (voting))
affect the results and cause vote splitting. For example, the center squeeze pathology that affects instant-runoff voting means that several similar (but...
31 KB (2,665 words) - 22:58, 11 November 2024
Exhaustive ballot (redirect from Exhaustive voting)
is necessary to vote only once, instant-runoff voting has been used for large-scale elections in many places. Like instant-runoff voting, the exhaustive...
21 KB (3,243 words) - 06:11, 5 May 2025
Multiple districts paradox (redirect from Consistency criterion for voting systems)
Condorcet methods and instant-runoff (or ranked-choice) voting. Rules that are not susceptible to it include all positional voting rules (such as first-preference...
31 KB (2,316 words) - 23:45, 21 April 2025