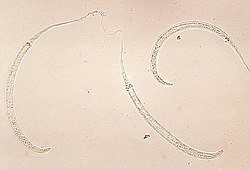
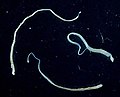
Intestinal capillariasis is a disease in the group of helminthiasis diseases caused by the nematode Capillaria philippinensis. Symptoms in infested humans...
3 KB (196 words) - 09:37, 5 September 2024
Capillariasis is a disease caused by nematodes in the genus Capillaria. The two principal forms of the disease are: Intestinal capillariasis, caused by...
595 bytes (49 words) - 01:24, 2 May 2024
Capillaria philippinensis is a parasitic nematode which causes intestinal capillariasis. This sometimes fatal disease was first discovered in Northern...
9 KB (956 words) - 20:19, 31 March 2025
(link) CS1 maint: others (link) "About Parasites | CDC DPD". 2020-01-28. "Intestinal Protozoal Diseases: eMedicine Pediatrics: General Medicine". Retrieved...
12 KB (1,047 words) - 21:01, 31 May 2025
mammalian gut.[citation needed] Anisakids pose a risk to human health through intestinal infection with worms from the eating of underprocessed fish and through...
24 KB (2,573 words) - 22:38, 29 May 2025
seatworm, is a parasitic worm. It is a nematode (roundworm) and a common intestinal parasite or helminth, especially in humans. The medical condition associated...
25 KB (2,054 words) - 06:24, 25 May 2025
Adenophorea Trichinella spiralis Trichinosis Trichuris trichiura (Trichuriasis / Whipworm) Capillaria philippinensis Intestinal capillariasis C. hepatica...
25 KB (2,369 words) - 20:35, 25 May 2025
in temperate zones, and is one of the most common cestodes (a type of intestinal worm or helminth) infecting humans, especially children. As its name implies...
10 KB (1,382 words) - 19:22, 9 May 2025
albendazole is sufficient to treat intestinal infestations by A. duodenale or Necator americanus. Intestinal capillariasis, as an alternative to mebendazole...
66 KB (5,493 words) - 10:25, 25 May 2025
Fasciolopsis (redirect from Intestinal fluke)
(/ˌfæsioʊˈlɒpsɪs, fəˌsaɪ-/) is a genus of trematodes. They are also known as giant intestinal flukes. Only one species is recognised: Fasciolopsis buski. It is a notable...
12 KB (1,303 words) - 15:39, 24 May 2025
Ascariasis (section Intestinal blockage)
infiltrates with radiographic shadowing. The worms can occasionally cause intestinal blockage when large numbers get tangled into a bolus or they may migrate...
34 KB (3,419 words) - 17:25, 24 May 2025
symptoms commonly include bloody sputum, cough, fever, abdominal discomfort, intestinal ulcer(s), as well as a less commonly missed passing of the quite long...
18 KB (2,049 words) - 09:49, 14 April 2025
it attaches to the intestinal wall, and matures into an adult and begins reproduction. Adults live in the lumen of the intestinal wall, where they cause...
19 KB (2,192 words) - 14:22, 17 October 2023
the deeper tissues of other animals (through to the lungs and then the intestinal tract), humans are incidental hosts and the larvae are only able to penetrate...
8 KB (817 words) - 22:16, 23 January 2025
tapeworms which will reside in the small intestine. The adults attach to the intestinal mucosa by means of the two bilateral grooves (bothria) of their scolices...
16 KB (1,687 words) - 20:36, 29 May 2025
Adenophorea Trichinella spiralis Trichinosis Trichuris trichiura (Trichuriasis / Whipworm) Capillaria philippinensis Intestinal capillariasis C. hepatica...
8 KB (917 words) - 00:55, 27 February 2025
since around 1900. All 6,000 species of Cestoda are parasites, mainly intestinal; their definitive hosts are vertebrates, both terrestrial and marine,...
38 KB (3,760 words) - 13:00, 25 May 2025
Adenophorea Trichinella spiralis Trichinosis Trichuris trichiura (Trichuriasis / Whipworm) Capillaria philippinensis Intestinal capillariasis C. hepatica...
46 KB (5,151 words) - 01:43, 28 May 2025
in feces. When this happens, H. nana oncosphere larvae encyst in the intestinal wall and develop into cysticercoids and then adults. These infections...
14 KB (1,788 words) - 05:29, 22 January 2025
Schistosoma mansoni (redirect from Intestinal schistosomiasis)
blood vessels (mesenteric veins) near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis (similar to S. japonicum, S. mekongi, S. guineensis, and...
57 KB (6,887 words) - 19:12, 23 May 2025
tapeworm belonging to the order Cyclophyllidea and genus Taenia. It is an intestinal parasite in humans causing taeniasis (a type of helminthiasis) and cysticercosis...
19 KB (2,203 words) - 04:02, 21 April 2025
Adenophorea Trichinella spiralis Trichinosis Trichuris trichiura (Trichuriasis / Whipworm) Capillaria philippinensis Intestinal capillariasis C. hepatica...
51 KB (5,808 words) - 21:25, 26 May 2025
then coughed up and swallowed into the gut, where they parasitise the intestinal mucosa of the duodenum and jejunum. In the small intestine, they molt...
25 KB (3,074 words) - 20:47, 10 January 2025
adult female produces batches of live larvae, which bore through the intestinal wall, enters the blood (to feed on it) and lymphatic system, and are carried...
18 KB (2,279 words) - 15:01, 5 February 2025
results from an infection by the trematode Fasciolopsis buski, the largest intestinal fluke of humans, growing up to 7.5 cm (3.0 in) long. Most infections are...
8 KB (862 words) - 22:00, 6 February 2025
Helminthiasis (redirect from Intestinal worm infection)
neurocysticercosis. In extreme cases of intestinal infestation, the mass and volume of the worms may cause the outer layers of the intestinal wall, such as the muscular...
62 KB (5,361 words) - 15:42, 23 May 2025
Adenophorea Trichinella spiralis Trichinosis Trichuris trichiura (Trichuriasis / Whipworm) Capillaria philippinensis Intestinal capillariasis C. hepatica...
7 KB (747 words) - 22:19, 23 January 2025
The larvae then migrate to the small intestine, and burrow into the intestinal mucosa, where they molt four times before becoming adults. Thirty to 34...
46 KB (4,912 words) - 18:50, 24 May 2025
1960s, kilawin consumption of the gudgeon fish contributed to the intestinal capillariasis epidemic where there were 1,884 cases and 110 deaths. Dinakdakan –...
11 KB (956 words) - 18:00, 3 March 2025
Schistosomiasis (section Intestinal schistosomiasis)
rectum. In intestinal schistosomiasis, eggs become lodged in the intestinal wall during their migration from the mesenteric venules to the intestinal lumen...
96 KB (10,104 words) - 19:20, 22 May 2025