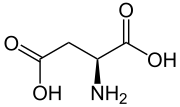
L-Aspartic-4-semialdehyde is an α-amino acid derivative of aspartate. It is an important intermediate in the aspartate pathway, which is a metabolic pathway...
6 KB (624 words) - 18:06, 20 April 2025
L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde:NADP+ oxidoreductase (phosphorylating). Other names in common use include aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase, aspartic semialdehyde...
5 KB (481 words) - 15:00, 19 April 2024
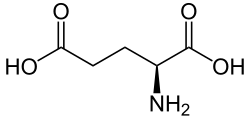
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of...
19 KB (1,714 words) - 08:32, 24 May 2025
2-amino-3,7-dideoxy-D-threo-hept-6-ulosonate synthase condenses L-Aspartic-4-semialdehyde with a sugar to form 2-amino-3,7-dideoxy-D-threo-hept-6-ulosonate...
5 KB (581 words) - 23:53, 20 May 2025
Tyrosine (redirect from L-Tyrosine)
which is greater than the negative charge of the only negatively charged aspartic and glutamic acids. Phosphorylated proteins keep these same properties—which...
26 KB (2,535 words) - 19:55, 2 June 2025
Dihydrodipicolinate synthase (redirect from L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing; (4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(2S)-dipicolinate-forming))
L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), dapA (gene)) is an enzyme with the systematic name L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde...
6 KB (616 words) - 07:12, 5 November 2023
C4H7NO3 (molar mass: 117.104 g/mol) may refer to: Aceturic acid L-Aspartic-4-semialdehyde This set index page lists chemical structure articles associated...
275 bytes (54 words) - 12:01, 1 January 2023
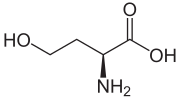
Homoserine (redirect from L-homoserine)
[clarification needed] It forms by two reductions of aspartic acid via the intermediacy of aspartate semialdehyde. Specifically, the enzyme homoserine dehydrogenase...
7 KB (650 words) - 02:09, 28 May 2025
Arginine (redirect from L-Arginine L-malate)
theoretical risks." A meta-analysis showed that L-arginine reduces blood pressure with pooled estimates of 5.4 mmHg for systolic blood pressure and 2.7 mmHg...
33 KB (3,147 words) - 04:22, 29 March 2025
Methionine (redirect from L-methionine)
or hydrogen sulfide. First, aspartic acid is converted via β-aspartyl semialdehyde into homoserine by two reduction steps of the terminal carboxyl group...
30 KB (3,083 words) - 04:36, 29 March 2025
In organic chemistry, a semialdehyde is a compound containing an aldehyde and a carboxylic acid functional groups. Semialdehydes are common in biochemistry...
2 KB (114 words) - 23:00, 13 August 2023
aromatic residues. The main amino acids involved are serine, histidine, and aspartic acid. They all play a role in cleaving the peptide bond. These three amino...
27 KB (2,828 words) - 15:30, 9 January 2025
Amino acid synthesis (section Erythrose 4-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate: phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan)
transsulfuration pathway starts with aspartic acid. Relevant enzymes include aspartokinase, aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, homoserine dehydrogenase...
31 KB (3,932 words) - 13:25, 23 December 2024
Glutamic acid (redirect from L-Glutamic Acid)
nine α-amino-acids and the third ionization processes of glutamic acid, aspartic acid and tyrosine". Thermochimica Acta. 141: 297–303. Bibcode:1989TcAc...
36 KB (3,308 words) - 11:10, 24 May 2025
carboxylase. Oxaloacetate can also arise from trans- or de- amination of aspartic acid. Oxaloacetate is an intermediate of the citric acid cycle, where it...
12 KB (1,159 words) - 03:48, 25 May 2025
Homoserine dehydrogenase (redirect from L-homoserine:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase)
reaction L-homoserine + NAD(P)+ ⇌ {\displaystyle \rightleftharpoons } L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NAD(P)H + H+ The 2 substrates of this enzyme are L-homoserine...
19 KB (2,018 words) - 05:09, 23 September 2024
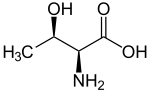
Threonine (redirect from L-Threonine)
plants and microorganisms, threonine is synthesized from aspartic acid via α-aspartyl-semialdehyde and homoserine. Homoserine undergoes O-phosphorylation;...
19 KB (1,733 words) - 11:24, 25 May 2025
transferring the guanidine group of L-arginine by the enzyme L-Arg:Gly-amidinotransferase (AGAT) to the amino acid glycine. From L-arginine, ornithine is thus...
9 KB (844 words) - 12:52, 1 April 2025
participates in lysine biosynthesis. Bacteria, plants and fungi metabolise aspartic acid to produce four amino acids - lysine, threonine, methionine and isoleucine...
7 KB (758 words) - 13:49, 26 August 2023
starting from aspartic β-semialdehyde. The genes involved in the biosynthesis are called ectA, ectB and ectC, and they encode the enzymes L-2,4-diaminobutyric...
9 KB (732 words) - 03:37, 19 May 2025
TβL resembles that of lysine, where the first dedicated step is the DapA-catalyzed condensation of aspartic acid semialdehyde with pyruvate to form L-2...
9 KB (1,045 words) - 17:25, 17 September 2023
List of EC numbers (EC 3) (redirect from EC 3.4)
(thermomycolin), EC 3.4.21.66 (thermitase) and EC 3.4.21.67 (endopeptidase So) EC 3.4.4.17: Now covered by the microbial aspartic proteinases EC 3.4.23.20 (penicillopepsin)...
119 KB (15,563 words) - 19:44, 6 May 2025
tyrosine, tryptophan, histidine, aspartic acid, and anthranilic acid. Nicotinic acid can be synthesized from tryptophan or aspartic acid. Ways of alkaloid biosynthesis...
69 KB (5,418 words) - 07:17, 25 May 2025
Ornithine (redirect from L-ornithine)
release by athletes is not recommended." L-ornithine L-aspartate (LOLA), a stable salt of ornithine and aspartic acid, has been used in the treatment of...
9 KB (854 words) - 19:06, 26 April 2025
MeSH D08.811.682.657.163.796 – l-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase MeSH D08.811.682.657.163.812 – malonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (acetylating)...
158 KB (15,232 words) - 06:41, 8 March 2024