In geometry, a straight line, usually abbreviated line, is an infinitely long object with no width, depth, or curvature, an idealization of such physical...
29 KB (4,225 words) - 18:36, 24 April 2025
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a straight line that is bounded by two distinct endpoints (its extreme points), and contains every point on the...
11 KB (1,526 words) - 10:06, 18 May 2025
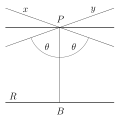
postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with: For any given line R and point P not on R, in the plane containing both line R and point P there are...
56 KB (6,970 words) - 13:36, 7 May 2025
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry, Elements...
59 KB (7,198 words) - 13:24, 17 May 2025
affine geometries and Euclidean geometry is a special instance of this type of geometry. In some other geometries, such as hyperbolic geometry, lines...
23 KB (2,771 words) - 20:35, 16 February 2025
elliptic geometry. In elliptic geometry, two lines perpendicular to a given line must intersect. In fact, all perpendiculars to a given line intersect...
18 KB (2,656 words) - 19:30, 16 May 2025
In geometry, line coordinates are used to specify the position of a line just as point coordinates (or simply coordinates) are used to specify the position...
10 KB (1,622 words) - 17:24, 29 January 2025
Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle...
102 KB (10,101 words) - 16:23, 8 May 2025
In geometry, central lines are certain special straight lines that lie in the plane of a triangle. The special property that distinguishes a straight line...
13 KB (1,781 words) - 00:54, 15 May 2024
non-Euclidean geometry consists of two geometries based on axioms closely related to those that specify Euclidean geometry. As Euclidean geometry lies at the...
45 KB (6,066 words) - 03:48, 14 May 2025
finite geometry is any geometric system that has only a finite number of points. The familiar Euclidean geometry is not finite, because a Euclidean line contains...
22 KB (2,841 words) - 13:36, 12 April 2024
projective geometry may be thought of as an extension of Euclidean geometry in which the "direction" of each line is subsumed within the line as an extra...
38 KB (5,099 words) - 13:20, 23 January 2025
Tangent (redirect from Tangent (geometry))
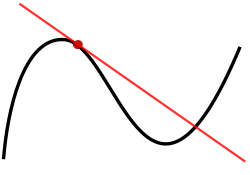
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at...
26 KB (4,113 words) - 07:46, 3 May 2025
Spherical geometry or spherics (from Ancient Greek σφαιρικά) is the geometry of the two-dimensional surface of a sphere or the n-dimensional surface of...
15 KB (1,955 words) - 21:52, 19 April 2025
In mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts...
40 KB (5,612 words) - 22:13, 23 December 2024
of geometry a line without endpoints continues indefinitely in the positive and negative directions. A line with one endpoint as a ray, and a line with...
20 KB (2,549 words) - 17:44, 4 April 2025
In geometry, a point is an abstract idealization of an exact position, without size, in physical space, or its generalization to other kinds of mathematical...
15 KB (1,649 words) - 10:02, 16 May 2025
Galois geometry (named after the 19th-century French mathematician Évariste Galois) is the branch of finite geometry that is concerned with algebraic...
10 KB (1,454 words) - 11:02, 9 October 2024
independent of any metric, affine geometry is often considered as the study of parallel lines. Therefore, Playfair's axiom (Given a line L and a point P not on L...
20 KB (2,632 words) - 10:01, 21 October 2024
Look up Line, line, or líne in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Line most often refers to: Line (geometry), object that has zero thickness and curvature...
9 KB (1,063 words) - 23:12, 7 April 2025
In geometry, a half-space is either of the two parts into which a plane divides the three-dimensional Euclidean space. If the space is two-dimensional...
3 KB (391 words) - 03:51, 4 December 2024
Taxicab geometry or Manhattan geometry is geometry where the familiar Euclidean distance is ignored, and the distance between two points is instead defined...
19 KB (2,507 words) - 20:38, 16 April 2025
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms that can be stated in terms of geometry. Some purely geometrical...
15 KB (2,106 words) - 15:15, 19 May 2025
In geometry, inversive geometry is the study of inversion, a transformation of the Euclidean plane that maps circles or lines to other circles or lines...
30 KB (4,386 words) - 20:16, 14 April 2025
Concurrent lines (redirect from Concurrent (geometry))
In geometry, lines in a plane or higher-dimensional space are concurrent if they intersect at a single point. The set of all lines through a point is called...
11 KB (1,453 words) - 01:10, 24 March 2025
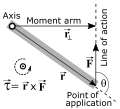
on the body, which tends to rotate it.[citation needed] For the simple geometry associated with the figure, there are three equivalent equations for the...
3 KB (339 words) - 02:51, 21 February 2025
The line of sight, also known as visual axis or sightline (also sight line), is an imaginary line between a viewer/observer/spectator's eye(s) and a subject...
3 KB (399 words) - 22:36, 16 January 2025
In geometry, a pencil is a family of geometric objects with a common property, for example the set of lines that pass through a given point in a plane...
19 KB (2,937 words) - 03:41, 11 January 2025
Pole and polar (redirect from Polar (geometry))
In geometry, a pole and polar are respectively a point and a line that have a unique reciprocal relationship with respect to a given conic section. Polar...
13 KB (1,358 words) - 15:10, 28 March 2025
Absolute geometry is a geometry based on an axiom system for Euclidean geometry without the parallel postulate or any of its alternatives. Traditionally...
8 KB (1,057 words) - 07:07, 15 February 2025