Marginal demand in economics is the change in demand for a product or service in response to a specific change in its price. Normally, as prices for goods...
1 KB (129 words) - 04:31, 21 March 2023
analysis Marginal concepts Marginal cost Marginal demand Marginal product Marginal product of labor Marginal propensity to consume Marginal rate of substitution...
2 KB (231 words) - 13:25, 26 October 2020
an explanation for supply in the theory of marginal utility, so he paired a marginal explanation of demand with a more classical explanation of supply...
48 KB (6,503 words) - 19:00, 1 February 2024
the marginal revenue curve, marginal costs could change without necessarily changing the price or quantity. The two seminal papers on kinked demand were...
8 KB (1,146 words) - 10:29, 14 March 2023
marginal utility describes the change in utility (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal...
44 KB (5,679 words) - 16:58, 1 May 2024
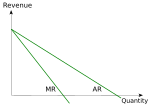
Marginal revenue (or marginal benefit) is a central concept in microeconomics that describes the additional total revenue generated by increasing product...
21 KB (2,858 words) - 06:00, 4 June 2024
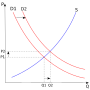
the demand curve, the average revenue curve, and the marginal revenue curve all coincide and are horizontal at the market-given price. The demand curve...
25 KB (3,770 words) - 11:58, 10 June 2024
income should not affect the demand. Marshall's theory exploits that demand curve represents individual's diminishing marginal values of the good. The theory...
9 KB (1,459 words) - 18:35, 27 September 2023
inverse demand function for a linear demand equation and the marginal revenue function. For any linear demand function with an inverse demand equation...
6 KB (918 words) - 19:46, 2 January 2024
Profit maximization (redirect from Profit demand)
the demand curve at the firm's optimal quantity of output. This optimal quantity of output is the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost...
28 KB (4,098 words) - 09:36, 2 June 2024
price. Just as the supply curve parallels the marginal cost curve, the demand curve parallels marginal utility, measured in dollars. Consumers will be...
37 KB (5,087 words) - 03:48, 3 April 2024
downward-sloping demand curves. To sell extra units of output, they would have to lower their output's price. Under such market conditions, marginal revenue product...
5 KB (832 words) - 16:43, 6 April 2024
will impact the quantity demanded) at the quantity it decides to sell. The marginal revenue is solely determined by the demand for the product within the...
19 KB (2,446 words) - 20:40, 4 August 2023
Margin (economics) (section Marginal concepts)
microeconomics and is used to predict the demand and supply of goods and services within an economy. Marginal cost is the change in monetary cost associated...
20 KB (2,895 words) - 14:43, 23 May 2024
The marginal efficiency of capital (MEC) is that rate of discount which would equate the price of a fixed capital asset with its present discounted value...
3 KB (405 words) - 08:55, 18 May 2024
Factor market (section Determinants of resource demand)
since the demand of labour is considered as a derived demand. It is important to note that as the number of workers increases, the marginal product of...
20 KB (3,042 words) - 17:14, 30 December 2023
with both a demand curve and a marginal revenue curve, demand will be elastic at all quantities where marginal revenue is positive. Demand is unit elastic...
45 KB (5,901 words) - 17:00, 15 April 2024
equals marginal costs. A monopoly maximises profits by producing where marginal revenue equals marginal costs. The rules are not equivalent. The demand curve...
95 KB (12,720 words) - 19:28, 11 June 2024
Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand in an economy is more than aggregate supply. It involves inflation rising as real gross domestic product...
4 KB (477 words) - 13:16, 16 May 2024
consumer demand, they are not price takers, but instead either price or quantity setters. Due to the output effect and the price effect, marginal revenue...
23 KB (2,648 words) - 08:24, 1 June 2024
faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). This implies that a factor's price equals the factor's marginal revenue product. It allows for...
45 KB (6,467 words) - 17:21, 23 April 2024
that exceeds marginal costs. The MC company maximises profits where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Since the MC company's demand curve is downwards-sloping...
23 KB (2,662 words) - 12:39, 1 June 2024
markup over marginal cost is inverse to the price elasticity of demand and the Price elasticity of supply: the more elastic the product's demand or supply...
7 KB (1,294 words) - 01:01, 12 April 2024
In economics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is...
21 KB (2,867 words) - 21:36, 22 April 2024
“marginal” in the US corn belt may be one of the better soils available in another context". Changes in product values – such as the ethanol-demand induced...
5 KB (538 words) - 20:21, 5 March 2024
too expensive for them in light of their marginal benefit (price is lowered to artificially increase demand), a tax dissuades consumers from a purchase...
16 KB (2,341 words) - 20:10, 13 May 2024
Complementary good (redirect from Joint demand)
needed] Technically, it displays a negative cross elasticity of demand and that demand for it increases when the price of another good decreases. If A...
10 KB (1,329 words) - 19:31, 11 June 2024
Labour economics (section Neoclassical demand)
by marginal costs. Because optimum resource allocation requires that marginal factor costs equal marginal revenue product, this firm would demand L units...
48 KB (5,977 words) - 17:40, 2 June 2024
determined in the capital market by the respective capital demand and supply. The marginal product of capital determines the real rental price of capital...
7 KB (878 words) - 18:09, 11 October 2023
willingness to pay. The sum of the marginal benefits represent the aggregate willingness to pay or aggregate demand. The marginal cost is, under competitive market...
4 KB (800 words) - 15:35, 12 April 2024