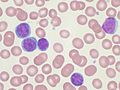
In immunology, a memory B cell (MBC) is a type of B lymphocyte that forms part of the adaptive immune system. These cells develop within germinal centers...
24 KB (3,168 words) - 13:25, 7 June 2025
When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast...
32 KB (3,744 words) - 10:38, 22 June 2025
Memory T cells are a subset of T lymphocytes that might have some of the same functions as memory B cells. Their lineage is unclear. Antigen-specific...
32 KB (3,781 words) - 20:52, 25 May 2025
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large...
24 KB (2,793 words) - 13:14, 18 July 2025
brain. Memory B cell, an antibody producing cell Memory T cell, an infection fighting cell Memory cell (computing), a building block of computer memory and...
411 bytes (88 words) - 23:05, 13 August 2022
adaptive immune memory. After the inflammatory immune response to danger-associated antigen, some of the antigen-specific T cells and B cells persist in the...
30 KB (3,584 words) - 14:08, 1 August 2025
Germinal center (section Memory B cell differentiation)
cells and durable memory B cells. There are several key differences between naive B cells and GC B cells. Naive B cells do not undergo lots of cell division...
22 KB (2,788 words) - 17:43, 5 July 2025
naive B cell either becomes a memory B cell or a plasma cell that secretes antibodies specific to the antigen that was originally bound. Plasma cells do...
3 KB (300 words) - 16:25, 25 May 2025
conversely to memory B cells, which are quiescent and respond quickly to antigens upon recall. Initially, it was believed that memory B cells replenish LLPCs...
12 KB (1,254 words) - 17:30, 16 June 2025
Humoral immunity (section B cell activation)
cells either become plasma cells or memory cells. The memory B cells remain inactive here; later, when these memory B cells encounter the same antigen...
17 KB (1,673 words) - 10:01, 25 May 2025
to B cell receptors that inhibits cell division. Because the infant's immune system is not stimulated and B cell division is inhibited, few memory B cells...
22 KB (2,368 words) - 21:22, 11 July 2025
Epstein–Barr virus (redirect from E-B Virus)
is brought under control, EBV latency persists in the individual's memory B cells for the rest of their life. The virus is about 122–180 nm in diameter...
66 KB (6,850 words) - 08:23, 10 August 2025
ISBN 978-0-443-01657-8. Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002). "Table 22-1, Blood Cells". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). Garland...
13 KB (786 words) - 17:47, 16 July 2025
The B-cell receptor (BCR) is a transmembrane protein on the surface of a B cell. A B-cell receptor is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin molecule...
18 KB (2,180 words) - 06:36, 17 December 2024
plasma cells and memory B cells. Adhesion between FDCs and B cells is mediated by ICAM-1 (CD54)–LFA-1 (CD11a) and VCAM–VLA-4 molecules. Activated B-cells with...
16 KB (1,896 words) - 01:02, 15 July 2025
mainly a defect in the differentiation process of B cells into memory and plasma cells. There are also T cell abnormalities in CVID including counts, percentages...
35 KB (3,371 words) - 05:28, 19 July 2025
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (redirect from Leukemia, B-Cell, chronic)
white blood cell. In patients with CLL, B cell lymphocytes can begin to collect in their blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. These cells do not function...
76 KB (8,155 words) - 18:57, 17 July 2025
Original antigenic sin (section In B cells)
infection, long-lived memory B cells are generated, which remain in the body and protect from subsequent infections. These memory B cells respond to specific...
12 KB (1,251 words) - 06:47, 7 February 2025
center-dependent memory B cells capable of quick immune re-activation in the future if ever the same antigen is re-encountered. TFH cells are also thought...
16 KB (1,936 words) - 01:12, 26 March 2025
Lymphoid cells (lymphocytes) include T cells (subdivided into helper T cells, memory T cells, cytotoxic T cells), B cells (subdivided into plasma cells and...
32 KB (3,212 words) - 07:45, 19 July 2025
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is...
49 KB (5,613 words) - 18:19, 16 July 2025
killer T cells, the CD4+ helper T (TH) cells function by further activating memory B cells and cytotoxic T cells, which leads to a larger immune response...
73 KB (9,255 words) - 07:29, 19 July 2025
The memory cell is the fundamental building block of computer memory. The memory cell is an electronic circuit that stores one bit of binary information...
28 KB (3,028 words) - 20:48, 23 June 2025
Within the immune system, follicular B cells (FO B cells) are a type of B cell that reside in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles (containing germinal...
3 KB (426 words) - 01:32, 26 March 2025
Antibody (redirect from Receptors, antigen, b-cell)
marrow. B cells can also differentiate into memory B cells which can persist for decades, similarly to long-lived plasma cells. These cells can be rapidly...
126 KB (13,978 words) - 08:05, 1 August 2025
Marginal-zone B cells (MZ B cells) are noncirculating mature B cells that in humans segregate anatomically into the marginal zone (MZ) of the spleen and...
12 KB (1,506 words) - 19:36, 4 August 2025
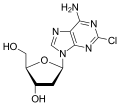
Cladribine (section In hairy cell leukemia)
others, is a medication used to treat hairy cell leukemia (formally named leukemic reticuloendotheliosis) and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cladribine...
36 KB (3,642 words) - 00:02, 11 June 2025
cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that...
57 KB (7,167 words) - 05:00, 19 July 2025
Tissue-resident memory T cells or TRM cells represent a subset of a long-lived memory T cells that occupies epithelial, mucosal and other tissues (skin...
25 KB (3,066 words) - 20:54, 18 July 2025
Epstein–Barr virus–associated lymphoproliferative diseases (section EBV+ B cell lymphoproliferative diseases)
or more types of lymphoid cells (a type of white blood cell), i.e. B cells, T cells, NK cells, and histiocytic-dendritic cells, are infected with the Epstein–Barr...
140 KB (16,974 words) - 21:10, 12 May 2025