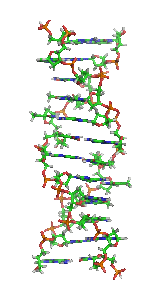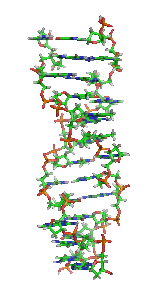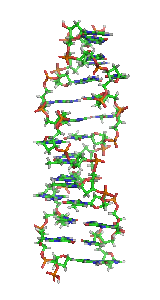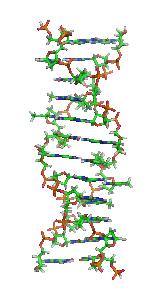
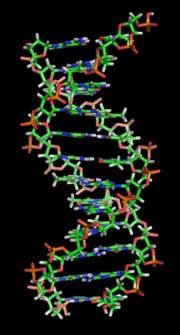
Non-B DNA is DNA in any conformation other than the canonical (B-DNA) conformation, the most common form of DNA found in nature at neutral pH and physiological...
6 KB (796 words) - 09:51, 18 July 2025
Non-coding DNA (ncDNA) sequences are components of an organism's DNA that do not encode protein sequences. Some non-coding DNA is transcribed into functional...
41 KB (4,746 words) - 22:12, 24 July 2025
common B-DNA form. Z-DNA is thought to be one of three biologically active double-helical structures along with A-DNA and B-DNA. Left-handed DNA was first...
34 KB (4,322 words) - 17:50, 16 July 2025
Nucleic acid double helix (redirect from B-DNA)
the Structure of DNA. The DNA double helix biopolymer of nucleic acid is held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common...
46 KB (5,293 words) - 00:42, 24 May 2025
into DNA strands during processes such as transcription and DNA replication. DNA exists in many possible conformations that include A-DNA, B-DNA, and...
168 KB (18,024 words) - 18:52, 29 July 2025
Non-B DB is a database integrating annotations and analysis of non-B DNA-forming sequence motifs. The database provides alternative DNA structure predictions...
2 KB (134 words) - 22:42, 16 July 2023
DnaB helicase is an enzyme in bacteria which opens the replication fork during DNA replication. Although the mechanism by which DnaB both couples ATP hydrolysis...
6 KB (766 words) - 17:05, 27 August 2024
Junk DNA (non-functional DNA) is a DNA sequence that has no known biological function. Most organisms have some junk DNA in their genomes—mostly pseudogenes...
36 KB (3,906 words) - 21:11, 29 July 2025
each other and form a triple helix. In triple-stranded DNA, the third strand binds to a B-form DNA (via Watson–Crick base-pairing) double helix by forming...
48 KB (6,098 words) - 09:02, 24 June 2025
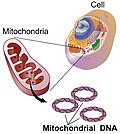
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into...
98 KB (10,787 words) - 11:58, 17 July 2025
Cruciform DNA is a form of non-B DNA, or an alternative DNA structure. The formation of cruciform DNA requires the presence of palindromes called inverted...
28 KB (3,447 words) - 16:00, 30 March 2024
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity...
132 KB (16,142 words) - 16:06, 11 June 2025
Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that identify a base pair. DNA-binding...
22 KB (2,637 words) - 06:01, 3 April 2025
The DNA damage theory of aging proposes that aging is a consequence of unrepaired accumulation of naturally occurring DNA damage. Damage in this context...
97 KB (11,166 words) - 18:24, 9 June 2025
Hepatitis C (redirect from Hepatitis non-A non-B)
Bradley DW, Houghton M (April 1989). "Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome" (PDF). Science. 244 (4902):...
111 KB (12,038 words) - 03:38, 12 July 2025
building block of many RNA secondary structures. Cruciform DNA Cruciform DNA is a form of non-B DNA that requires at least a 6 nucleotide sequence of inverted...
11 KB (1,202 words) - 06:34, 26 April 2024
microscopy (of both DNA alone, and bound to DNA-binding proteins). Although localised or transient non-duplex helical structures exist, non-helical models...
17 KB (1,898 words) - 21:42, 19 July 2025
of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex...
59 KB (7,110 words) - 14:40, 28 July 2025
Transposable element (redirect from DNA transposable element)
by several transposase enzymes. Some transposases non-specifically bind to any target site in DNA, whereas others bind to specific target sequences....
40 KB (5,074 words) - 18:13, 22 July 2025
Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by specific mutations in the non-recombining portions of DNA on the male-specific Y chromosome (Y-DNA). Individuals...
60 KB (5,342 words) - 02:48, 7 July 2025
Rosalind Franklin (redirect from King's College DNA controversy)
Her work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal, and graphite...
174 KB (19,277 words) - 16:54, 27 July 2025
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process by which a cell makes exact copies of its DNA. This process occurs in all living organisms...
61 KB (7,458 words) - 14:41, 28 July 2025
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient sources (typically specimens, but also environmental DNA). Due to degradation processes (including cross-linking...
61 KB (6,377 words) - 10:28, 13 July 2025
Haplogroup B (M60) is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup common to paternal lineages in Africa. It is a primary branch of the haplogroup BT. B (M60) is...
35 KB (3,349 words) - 00:44, 12 June 2025
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus Orthohepadnavirus and a member of the Hepadnaviridae family of...
56 KB (6,831 words) - 06:01, 19 July 2025
widespread in similar configuration in all domains of life. The ribosomal DNA encodes the non-coding ribosomal RNA, integral structural elements in the assembly...
23 KB (2,576 words) - 01:03, 15 July 2025
Inverted repeat (category Repetitive DNA sequences)
(FNLCR). It covers the A-DNA and Z-DNA conformations otherwise known as "non-B DNAs" because they are not the more common B-DNA form of a right-handed Watson-Crick...
31 KB (3,452 words) - 17:50, 22 July 2025
DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without...
118 KB (13,385 words) - 20:31, 17 July 2025
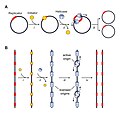
by the helicase DnaB. DnaA consists mainly in two different forms, the active ATP-form and the inactive ADP. The level of active DnaA within a cell is...
34 KB (4,283 words) - 13:04, 23 May 2025
Origin of replication (redirect from DNA replication origin)
helicase DnaB, which is deposited onto each of the single DNA strands by its loader protein DnaC. Although the different DNA binding activities of DnaA have...
113 KB (12,563 words) - 21:58, 15 June 2025