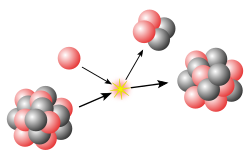
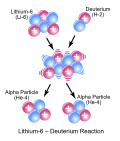Nuclear binding energy in experimental physics is the minimum energy that is required to disassemble the nucleus of an atom into its constituent protons...
52 KB (7,079 words) - 10:18, 30 May 2025
In physics and chemistry, binding energy is the smallest amount of energy required to remove a particle from a system of particles or to disassemble a...
14 KB (1,342 words) - 13:09, 1 April 2025
number), as illustrated in the nuclear binding energy curve. Additionally, the alternation in the nuclear binding energy between even and odd atomic numbers...
42 KB (4,383 words) - 11:16, 1 June 2025
electricity Nuclear binding energy, the energy needed to fuse or split a nucleus of an atom Nuclear potential energy, the potential energy of the particles...
498 bytes (104 words) - 16:51, 15 October 2024
against the nuclear force. Conversely, energy is released when a nucleus is created from free nucleons or other nuclei: the nuclear binding energy. Because...
29 KB (3,514 words) - 16:17, 26 May 2025
the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises as a result of the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before...
113 KB (12,225 words) - 02:37, 28 May 2025
energy of the fragments (heating the bulk material where fission takes place). Like nuclear fusion, for fission to produce energy, the total binding energy...
77 KB (9,897 words) - 05:16, 23 May 2025
Atomic mass (redirect from Nuclear mass)
in the nucleus, with minor contributions from the electrons and nuclear binding energy. The atomic mass of atoms, ions, or atomic nuclei is slightly less...
22 KB (2,778 words) - 19:04, 20 May 2025
nucleon. With 8.8 MeV binding energy per nucleon, iron-56 is one of the most tightly bound nuclei. The high nuclear binding energy for 56Fe represents the...
3 KB (377 words) - 20:49, 12 May 2025
Strong interaction (redirect from Strong nuclear force)
differences in the binding energies of the nuclear force with regard to nuclear fusion versus nuclear fission. Nuclear fusion accounts for most energy production...
18 KB (2,015 words) - 22:56, 31 May 2025
Nuclear astrophysics studies the origin of the chemical elements and isotopes, and the role of nuclear energy generation, in cosmic sources such as stars...
20 KB (2,254 words) - 13:04, 15 November 2024
make use of the nuclear binding energy released when atomic nucleons are either separated (fission) or brought together (fusion). The energy available is...
47 KB (1,644 words) - 15:04, 20 May 2025
Mass excess (redirect from Excess energy)
Thus, the mass excess is an expression of the nuclear binding energy, relative to the binding energy per nucleon of carbon-12 (which defines the dalton)...
4 KB (605 words) - 11:08, 7 September 2023
Even and odd atomic nuclei (category Nuclear physics)
A. Most importantly, oddness of both Z and N tends to lower the nuclear binding energy, making odd nuclei generally less stable. This effect is not only...
21 KB (2,587 words) - 01:18, 15 May 2025
reaction; its source is the nuclear binding energy. Using Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula E = mc2, the amount of energy released can be determined...
20 KB (2,406 words) - 18:12, 7 February 2025
This is observed in the nuclear binding energy of atomic nuclei, where a mass defect is measured. It is believed that mass-energy equivalence becomes important...
47 KB (6,268 words) - 15:15, 27 May 2025
Iron peak (section Binding energy)
abundant than would be expected from this trend. A graph of the nuclear binding energy per nucleon for all the elements shows a sharp increase to a peak...
3 KB (347 words) - 09:17, 4 November 2024
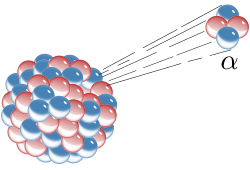
Alpha decay (category Nuclear physics)
is the most common form because of the combined extremely high nuclear binding energy and relatively small mass of the alpha particle. Like other cluster...
19 KB (2,542 words) - 19:16, 24 February 2025
energy includes: Nuclear binding energy, the energy required to split a nucleus of an atom. Nuclear potential energy, the potential energy of the particles...
1 KB (179 words) - 19:03, 18 February 2025
occur. Energy in excess of the threshold value becomes kinetic energy of the ejected particle. By contrast, nuclear binding energy is the energy needed...
2 KB (248 words) - 11:41, 12 February 2022
much stronger type of binding energy, the nuclear binding energy, is involved in nuclear processes. Due to this, most nuclear excited states decay by...
33 KB (3,808 words) - 15:19, 30 March 2025
Mass number (redirect from Nuclear number)
protons and neutrons. Nuclear binding energy varies between nuclei. A nucleus with greater binding energy has a lower total energy, and therefore a lower...
8 KB (1,101 words) - 03:37, 29 April 2025
2.2 × 10 − 5 {\displaystyle 2.2\times 10^{-5}} . The nuclear binding energy is the minimum energy that is required to disassemble the nucleus of an atom...
90 KB (11,630 words) - 13:07, 24 May 2025
Nuclide (category Nuclear physics)
known as nuclear species) are a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, Z, their number of neutrons, N, and their nuclear energy state....
18 KB (1,693 words) - 03:22, 25 November 2024
Beta decay (redirect from Superallowed Nuclear Beta Decay)
decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability...
64 KB (7,657 words) - 18:21, 18 May 2025
Droplet Model (FRDM), due to the possible good reproduction of nuclear binding energy on the whole chart, with the necessary accuracy for predictions...
33 KB (4,580 words) - 14:02, 26 May 2025
potential energies Mechanical wave – (≥0), a form of mechanical energy propagated by a material's oscillations Nuclear binding energy – energy that binds...
20 KB (2,299 words) - 12:45, 3 March 2025
Valley of stability (redirect from Nuclear valley)
In nuclear physics, the valley of stability (also called the belt of stability, nuclear valley, energy valley, or beta stability valley) is a characterization...
31 KB (4,212 words) - 15:19, 26 May 2025
Therefore, nuclei with a full outer proton shell will have a higher nuclear binding energy than other nuclei with a similar total number of protons. The same...
30 KB (4,126 words) - 04:28, 2 March 2025
Retrieved 2011-10-17. Duckworth, Henry E.; Wilkinson, D. H. (2008). "Nuclear binding energy". AccessScience. McGraw-Hill Companies. Archived from the original...
23 KB (2,175 words) - 11:21, 30 May 2025