In computer science, in the field of databases, read–write conflict, also known as unrepeatable reads, is a computational anomaly associated with interleaved...
3 KB (325 words) - 08:37, 28 May 2025
computer science, in the field of databases, write–read conflict (also known as reading uncommitted data and dirty read), is a computational anomaly associated...
2 KB (249 words) - 18:06, 28 May 2025
2PL does not overcome all the time. Concurrency control Read–write conflict Write–read conflict Stearns, Richard E.; Rosenkrantz, Daniel J. (1981). Distributed...
2 KB (247 words) - 15:22, 10 June 2025
Parallel RAM (redirect from Exclusive Read Exclusive Write)
estimated using two parameters O(time) and O(time × processor_number). Read/write conflicts, commonly termed interlocking in accessing the same shared memory...
11 KB (1,275 words) - 23:27, 23 May 2025
Hazard (computer architecture) (redirect from Read after write (Hazard))
used to resolve data hazards: insert a pipeline bubble whenever a read after write (RAW) dependency is encountered, guaranteed to increase latency, or...
10 KB (1,237 words) - 10:14, 13 February 2025
Parallel external memory (section Read/write conflicts)
concurrently read/write conflicts occur. Like in the PRAM model, three different variations of this problem are considered: Concurrent Read Concurrent Write (CRCW):...
16 KB (1,961 words) - 08:49, 16 October 2023
Each transaction involves a read (A or B), and a write (C). The only conflict between these transactions is the write on C. The following is one possible...
3 KB (519 words) - 22:58, 20 March 2023
Cache (computing) (redirect from Write-through)
write): Data at the missed-write location is loaded to cache, followed by a write-hit operation. In this approach, write misses are similar to read misses...
30 KB (4,140 words) - 19:28, 12 June 2025
Two-phase locking (section Read and write locks)
are read-locks (shared locks) and write-locks (exclusive locks). Below are the rules for read-locks and write-locks: A transaction is allowed to read an...
7 KB (777 words) - 11:30, 17 December 2024
variable from Read/Write Conflicting to Read/Write Non-conflicting. The actual local (private) instances of the Read/Write Conflicting variables are created...
16 KB (2,407 words) - 16:46, 8 June 2024
Eventual consistency (section Conflict resolution)
might not be consistent (the write might not persist after conflicts are reconciled, and the read might not get the latest write) Soft-state: without consistency...
10 KB (1,087 words) - 05:44, 7 June 2025
Database transaction schedule (redirect from Conflict serializability)
considered conflicting if and only if they are a read-write, write-read, or write-write conflict. The following set of actions is conflicting: R1(X), W2(X)...
20 KB (2,514 words) - 12:34, 28 May 2025
In parallel programming, the code is divided into threads. The read-write conflicting variables are split between threads and each thread has a copy of...
12 KB (1,607 words) - 13:58, 5 June 2025
must first transfer this information to the memory so the other device can read it. The TURBOchannel protocol specifies that each option has its own physical...
10 KB (1,232 words) - 08:40, 14 May 2025
Isolation (database systems) (redirect from Phantom read)
conflict and transaction 1 is rolled back with a serialization failure. Under lock-based concurrency control, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads may...
19 KB (2,121 words) - 23:57, 3 May 2025
throughput) than SS2PL whenever read-write conflicts are present (identical blocking behavior for write-read and write-write conflicts; comparable locking overhead)...
93 KB (12,831 words) - 15:42, 21 August 2024
registers will be read and written by this instruction and where conflicts write after read (WAR) and read after write (RAW) and write after write (WAW) are detected...
9 KB (1,155 words) - 05:08, 6 February 2025
Remix culture (redirect from Read/write culture)
Remix culture, also known as read-write culture, is a term describing a culture that allows and encourages the creation of derivative works by combining...
71 KB (8,281 words) - 16:57, 31 May 2025
data in both 8-Kbyte on-chip caches lessens the fetch and operand read/write conflicts compared to the 486. To reduce access time and implementation cost...
40 KB (3,895 words) - 17:55, 21 June 2025
Accepted(N,<WriteB,ReadA> . <ReadB>) | | |<--------X--X-------->|->| Accepted(N,<ReadB> . <WriteB,ReadA>) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | !! Conflict detected...
63 KB (6,819 words) - 05:59, 22 April 2025
Literacy (category Learning to read)
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy"...
178 KB (20,175 words) - 09:31, 20 June 2025
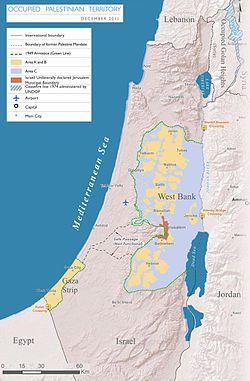
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is an ongoing military and political conflict about land and self-determination within the territory of the former Mandatory...
306 KB (33,157 words) - 22:07, 19 June 2025
Dual-ported video RAM (redirect from Read-while-write)
memory devices. This conflicted with the need for the central processing unit (CPU) to write data to memory for the video system to read, as both could not...
8 KB (1,254 words) - 13:38, 2 June 2025
Snapshot isolation (redirect from Write skew)
taken. Such a write–write conflict will cause the transaction to abort. In a write skew anomaly, two transactions (T1 and T2) concurrently read an overlapping...
14 KB (1,724 words) - 01:56, 27 December 2024
allows to reduce the amount of memory that needs to be tracked for read-write conflicts and therefore increase the probability of successful commit of the...
27 KB (2,487 words) - 10:57, 19 March 2025
CTIA and GTIA (section HPOSP0 $D000 Write)
dual purposes performing different functions as a Read vs a Write register. Therefore, no code should read Hardware registers expecting to retrieve the previously...
81 KB (8,990 words) - 16:16, 16 June 2025
definition: Two accesses to (reads of or writes to) the same variable are said to be conflicting if at least one of the accesses is a write ... When a program contains...
36 KB (4,513 words) - 15:53, 3 June 2025
ordering of operation pairs, write-after-write, read-after-write, or read/write-after-read, can be relaxed. In the relaxed write atomicity model, a process...
57 KB (7,554 words) - 14:11, 31 October 2024
actions is a write operation, and the actions access the same object (read or write). Cycles of committed transactions can be prevented by aborting an undecided...
5 KB (757 words) - 19:00, 27 December 2023
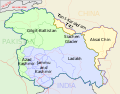
The Kashmir conflict is a territorial conflict over the Kashmir region, primarily between India and Pakistan, and also between China and India in the northeastern...
356 KB (40,365 words) - 17:30, 9 June 2025