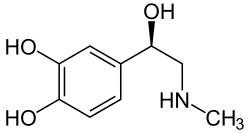
Catecholamines A catecholamine (/ˌkætəˈkoʊləmiːn/; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic...
20 KB (2,115 words) - 20:42, 25 May 2025
enzyme inhibitor and is therefore a drug involved in inhibiting the catecholamine biosynthetic pathway. AMPT inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase whose enzymatic...
25 KB (2,271 words) - 22:37, 29 May 2025
The catecholamines are a group of neurotransmitters composed of the endogenous substances dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), and adrenaline (epinephrine)...
69 KB (8,690 words) - 22:15, 27 May 2025
Norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (redirect from Catecholamine releasing agent)
A norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (NDRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of norepinephrine (and epinephrine) and dopamine in the body...
7 KB (556 words) - 21:37, 14 January 2025
Monoamine precursor (redirect from Catecholamine precursors)
Monoamine precursors are precursors of monoamines and monoamine neurotransmitters in the body. The amino acids L-tryptophan and L-5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP;...
5 KB (359 words) - 02:24, 27 February 2025
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (redirect from Catecholamine O-methyltransferase)
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT; EC 2.1.1.6) is one of several enzymes that degrade catecholamines (neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine)...
29 KB (3,236 words) - 00:14, 10 July 2024
A norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) is a type of drug that inhibits the reuptake of the monoamine neurotransmitters norepinephrine and...
5 KB (463 words) - 05:51, 28 January 2025
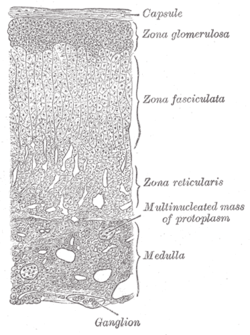
Adrenal gland (section Catecholamines)
processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress...
50 KB (5,636 words) - 00:12, 10 April 2025
These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they release catecholamines into the bloodstream which cause the most common symptoms, including...
165 KB (17,973 words) - 21:53, 29 May 2025
an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is...
140 KB (14,335 words) - 21:36, 31 May 2025
pathophysiology is not well understood, but a sudden massive surge of catecholamines such as adrenaline and noradrenaline from extreme stress or a tumor...
60 KB (6,601 words) - 17:25, 23 May 2025
part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecholamines, including epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline)...
9 KB (929 words) - 20:57, 23 May 2025
Catecholaminergic means "related to catecholamines". The catecholamine neurotransmitters include dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine...
835 bytes (53 words) - 17:56, 13 September 2021
are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced...
33 KB (2,983 words) - 09:03, 18 May 2025
Substituted phenethylamine (redirect from Catecholamine analogue)
citation needed] Numerous endogenous compounds – including hormones, catecholamines such as dopamine and noradrenaline, and many trace amines (e.g. adrenaline...
31 KB (888 words) - 20:07, 31 May 2025
Monoamine-depleting agent (redirect from Catecholamine-depleting agent)
Monoamine-depleting agents are a group of drugs which reversibly deplete one or more of the monoamine neurotransmitters – serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine...
4 KB (341 words) - 13:12, 22 May 2025
trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier...
34 KB (3,078 words) - 12:50, 13 April 2025
Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (redirect from Serotonin-catecholamine reuptake inhibitor)
antidepressant. Tetrabenazine, a similar agent to reserpine, which also depletes catecholamine stores, and to a lesser degree 5-HT, was shown to induce depression...
141 KB (16,545 words) - 22:09, 29 May 2025
Adrenaline (category Catecholamines)
treatment. The adrenal medulla is a major contributor to total circulating catecholamines (L-DOPA is at a higher concentration in the plasma), though it contributes...
57 KB (6,581 words) - 02:40, 20 May 2025
and anatomical features. These genes have been shown to affect the catecholamine synthesis pathway, with the majority of the genes affecting the fight-or-flight...
187 KB (17,650 words) - 01:45, 31 May 2025
artificial vanilla flavorings and is an end-stage metabolite of the catecholamines (epinephrine, and norepinephrine). It is produced via intermediary metabolites...
5 KB (338 words) - 19:11, 13 January 2025
adrenal medulla. This causes the release of catecholamines. The chromaffin cells release catecholamines: ~80% of adrenaline (epinephrine) and ~20% of...
13 KB (1,403 words) - 12:24, 14 December 2024
however, with catecholamine-induced calcium uptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which increases lusitropy. Increased catecholamine levels promote...
3 KB (349 words) - 08:58, 26 January 2025
Julius Axelrod (section Catecholamine research)
Nobel Committee honored him for his work on the release and reuptake of catecholamine neurotransmitters, a class of chemicals in the brain that include epinephrine...
17 KB (1,597 words) - 02:47, 10 March 2025
Chemical structures of the catecholamines Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic...
9 KB (911 words) - 05:07, 28 May 2025
catecholamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine. Concomitantly, adrenocortical cells secrete corticosteroids. These hormones (i.e., catecholamines...
22 KB (2,588 words) - 01:07, 24 May 2025
sympathetic nervous system is driven by precisely timed releases of a catecholamine, which is a process that determines the concentration of calcium ions...
8 KB (985 words) - 23:27, 24 May 2025
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (redirect from Double tachycardia induced by catecholamines)
to emotional stress—situations in which chemical messengers known as catecholamines, such as adrenaline, are released within the body. Blackouts may be...
42 KB (4,772 words) - 18:48, 28 May 2025
targets. It is a hydrophilic psychedelic compound structurally related to catecholamines but acting on the serotonergic system, first synthesized in 1919, with...
97 KB (8,622 words) - 19:29, 27 May 2025
secretory cells which may be filled with neurotransmitters, such as catecholamines or neuropeptides. LDVCs release their content through SNARE-mediated...
2 KB (156 words) - 17:33, 25 May 2025