Celestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of objects in outer space. Historically, celestial mechanics applies principles...
20 KB (2,548 words) - 07:51, 28 May 2025
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to rockets, satellites, and other spacecraft. The motion of...
40 KB (5,763 words) - 07:34, 23 May 2025
is a Russian theoretical physicist specializing in relativistic celestial mechanics and astrometry. He worked as a chief-scientist at the Institute of...
8 KB (818 words) - 03:38, 16 April 2025
N-body problem (redirect from N-body mechanics)
problem is the problem of predicting the individual motions of a group of celestial objects interacting with each other gravitationally. Solving this problem...
67 KB (8,738 words) - 19:30, 27 May 2025
history of both physics and mathematics, particularly classical celestial mechanics. Kepler's equation is M = E − e sin E {\displaystyle M=E-e\sin...
24 KB (3,610 words) - 07:52, 14 May 2025
contributions to pure and applied mathematics, mathematical physics, and celestial mechanics. In his research on the three-body problem, Poincaré became the first...
104 KB (11,422 words) - 12:08, 12 May 2025
optical devices. Transformation optics can go beyond cloaking (mimic celestial mechanics) because its control of the trajectory and path of light is highly...
28 KB (3,145 words) - 07:26, 14 April 2025
sections may occur on surfaces of higher order, too (see image). In celestial mechanics, for bound orbits in a spherical potential, the definition above...
11 KB (1,373 words) - 05:16, 22 March 2025
Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy is a scientific journal covering the fields of astronomy and astrophysics. It was established as Celestial...
3 KB (169 words) - 03:29, 2 March 2025
the interrelatedness of celestial mechanics and the Earth sciences and enabled a consistent transition from celestial mechanics to the Earth sciences and...
76 KB (8,844 words) - 18:13, 1 June 2025
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (category Lagrangian mechanics)
to the fields of analysis, number theory, and both classical and celestial mechanics. In 1766, on the recommendation of Leonhard Euler and d'Alembert...
47 KB (6,147 words) - 14:36, 24 May 2025
ordinary classical mechanics to consider systems in an unknown state; often used to derive thermodynamic properties. Celestial mechanics, the motion of bodies...
22 KB (2,553 words) - 16:40, 30 May 2025
Tokyo) was a Japanese astronomer noted for his contributions to celestial mechanics. Hagihara graduated from Tokyo Imperial University with a degree...
7 KB (662 words) - 12:52, 10 May 2025
Lagrange point (category Lagrangian mechanics)
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (/ləˈɡrɑːndʒ/; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects...
51 KB (5,819 words) - 07:28, 1 June 2025
five-volume Mécanique céleste (Celestial Mechanics) (1799–1825). This work translated the geometric study of classical mechanics to one based on calculus,...
107 KB (13,312 words) - 14:54, 1 June 2025
motion of terrestrial and celestial objects were replaced by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Newtonian mechanics, which explain how Kepler's...
44 KB (5,795 words) - 15:07, 22 April 2025
Лексель). Lexell made important discoveries in polygonometry and celestial mechanics; the latter led to a comet named in his honour. La Grande Encyclopédie...
25 KB (3,003 words) - 13:52, 26 May 2025
space—what they are, rather than where they are", which is studied in celestial mechanics. Among the subjects studied are the Sun (solar physics), other stars...
30 KB (3,285 words) - 20:06, 9 May 2025
Orbit (redirect from Orbit (celestial mechanics))
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a...
57 KB (8,123 words) - 06:52, 24 April 2025
Astronomy (section Astrometry and celestial mechanics)
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry...
103 KB (10,550 words) - 18:32, 6 May 2025
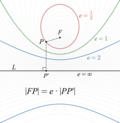
In celestial mechanics, true anomaly is an angular parameter that defines the position of a body moving along a Keplerian orbit. It is the angle between...
11 KB (1,872 words) - 15:40, 27 May 2025
1877) was a French astronomer and mathematician who specialized in celestial mechanics and is best known for predicting the existence and position of Neptune...
20 KB (2,088 words) - 05:06, 30 May 2025
Antiparallelogram (section Celestial mechanics)
bow-tie linkages, and are used in the design of non-circular gears. In celestial mechanics, they occur in certain families of solutions to the 4-body problem...
17 KB (1,853 words) - 07:20, 6 February 2025
Imre Izsák (section Celestial mechanics)
student. Attending lectures by István Földes raised his interest in celestial mechanics. During his college years, he was an assistant at the observatory...
7 KB (1,050 words) - 17:00, 29 June 2021
Group on cartographic coordinates and rotational elements: 2006". Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy. 98 (3): 155–180. Bibcode:2007CeMDA..98....
223 KB (20,254 words) - 21:14, 1 June 2025
Gravity (section Gravity and quantum mechanics)
the unification of Earth-bound observations of acceleration with celestial mechanics.: 4 In his book, Newton described gravitation as a universal force...
82 KB (8,639 words) - 18:06, 1 June 2025
velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for...
24 KB (3,437 words) - 15:52, 6 March 2025
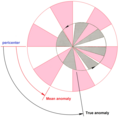
In celestial mechanics, the mean anomaly is the fraction of an elliptical orbit's period that has elapsed since the orbiting body passed periapsis, expressed...
10 KB (1,404 words) - 22:10, 12 February 2025
Great conjunction (section Celestial mechanics)
to the same right ascension, periods must be used with respect to the celestial equinox, giving about 763 years. See Etz. Etz D., (2000), Conjunctions...
35 KB (3,142 words) - 02:15, 2 April 2025
In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for an object to escape from contact with or orbit of a primary body...
28 KB (3,648 words) - 13:53, 3 February 2025