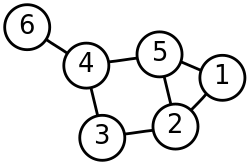
computer science, graph theory is the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context...
50 KB (6,237 words) - 21:13, 9 May 2025
In discrete mathematics, particularly in graph theory, a graph is a structure consisting of a set of objects where some pairs of the objects are in some...
28 KB (3,671 words) - 04:30, 15 May 2025
mathematics and computer science, connectivity is one of the basic concepts of graph theory: it asks for the minimum number of elements (nodes or edges) that need...
17 KB (2,062 words) - 23:37, 25 March 2025
In the mathematical discipline of graph theory, a matching or independent edge set in an undirected graph is a set of edges without common vertices. In...
24 KB (3,032 words) - 23:25, 29 June 2025
In graph theory, a tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path, or equivalently a connected acyclic undirected...
27 KB (3,383 words) - 16:48, 14 March 2025
In graph theory, a clique (/ˈkliːk/ or /ˈklɪk/) is a subset of vertices of an undirected graph such that every two distinct vertices in the clique are...
20 KB (2,483 words) - 12:35, 24 June 2025
In mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a directed graph (or digraph) is a graph that is made up of a set of vertices connected by directed...
16 KB (1,937 words) - 05:02, 12 April 2025
Appendix:Glossary of graph theory in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. This is a glossary of graph theory. Graph theory is the study of graphs, systems of nodes...
109 KB (16,011 words) - 12:09, 30 June 2025
specifically in graph theory, a vertex (plural vertices) or node is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed: an undirected graph consists of a set...
6 KB (806 words) - 05:45, 12 April 2025
In graph theory, a cycle in a graph is a non-empty trail in which only the first and last vertices are equal. A directed cycle in a directed graph is...
15 KB (1,857 words) - 03:10, 25 February 2025
In graph theory, a loop (also called a self-loop or a buckle) is an edge that connects a vertex to itself. A simple graph contains no loops. Depending...
3 KB (390 words) - 05:43, 12 April 2025
In graph theory, a component of an undirected graph is a connected subgraph that is not part of any larger connected subgraph. The components of any graph...
30 KB (3,443 words) - 23:25, 29 June 2025
In graph theory, a path in a graph is a finite or infinite sequence of edges which joins a sequence of vertices which, by most definitions, are all distinct...
10 KB (1,175 words) - 20:53, 19 June 2025
In mathematics, spectral graph theory is the study of the properties of a graph in relationship to the characteristic polynomial, eigenvalues, and eigenvectors...
15 KB (1,844 words) - 20:28, 19 February 2025
In graph theory, the diameter of a connected undirected graph is the farthest distance between any two of its vertices. That is, it is the diameter of...
9 KB (1,087 words) - 01:54, 25 June 2025
mathematical field of graph theory, the distance between two vertices in a graph is the number of edges in a shortest path (also called a graph geodesic) connecting...
7 KB (933 words) - 09:31, 18 April 2025
In graph theory, a lattice graph, mesh graph, or grid graph is a graph whose drawing, embedded in some Euclidean space R n {\displaystyle \mathbb {R}...
4 KB (547 words) - 11:50, 28 June 2025
In graph theory, a cut is a partition of the vertices of a graph into two disjoint subsets. Any cut determines a cut-set, the set of edges that have one...
10 KB (1,132 words) - 00:50, 30 August 2024
In graph theory, an independent set, stable set, coclique or anticlique is a set of vertices in a graph, no two of which are adjacent. That is, it is a...
30 KB (3,564 words) - 07:50, 15 July 2025
topological graph theory is a branch of graph theory. It studies the embedding of graphs in surfaces, spatial embeddings of graphs, and graphs as topological...
5 KB (565 words) - 01:25, 16 August 2024
In graph theory, the degree (or valency) of a vertex of a graph is the number of edges that are incident to the vertex; in a multigraph, a loop contributes...
10 KB (1,276 words) - 13:10, 18 November 2024
In graph theory, a planar graph is a graph that can be embedded in the plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges intersect...
36 KB (4,592 words) - 10:18, 9 July 2025
Algebraic graph theory is a branch of mathematics in which algebraic methods are applied to problems about graphs. This is in contrast to geometric, combinatoric...
7 KB (671 words) - 13:31, 13 February 2025
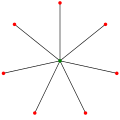
In graph theory, a star Sk is the complete bipartite graph K1,k : a tree with one internal node and k leaves (but no internal nodes and k + 1 leaves when...
7 KB (702 words) - 06:39, 6 March 2025
In graph theory, a k-degenerate graph is an undirected graph in which every subgraph has at least one vertex of degree at most k {\displaystyle k} . That...
31 KB (3,769 words) - 02:53, 17 March 2025
In graph theory, two graphs G {\displaystyle G} and G ′ {\displaystyle G'} are homeomorphic if there is a graph isomorphism from some subdivision of G...
8 KB (932 words) - 20:42, 18 May 2025
essence, extremal graph theory studies how global properties of a graph influence local substructure. Results in extremal graph theory deal with quantitative...
10 KB (1,360 words) - 19:17, 15 July 2025
In graph theory, the girth of an undirected graph is the length of a shortest cycle contained in the graph. If the graph does not contain any cycles (that...
7 KB (903 words) - 07:28, 19 December 2024
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a snark is an undirected graph with exactly three edges per vertex whose edges cannot be colored with only three...
23 KB (2,760 words) - 03:12, 27 January 2025
Bivariegated graph Cage (graph theory) Cayley graph Circle graph Clique graph Cograph Common graph Complement of a graph Complete graph Cubic graph Cycle graph De...
7 KB (663 words) - 02:52, 24 September 2024