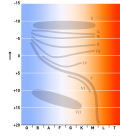
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color versus brightness as a continuous and distinctive...
62 KB (6,924 words) - 18:53, 25 June 2025
A G-type main-sequence star (yellow dwarf or G dwarf) is a main-sequence star of spectral type G. The spectral luminosity class is typically V. Such a...
12 KB (1,164 words) - 19:28, 26 June 2025
Red dwarf (redirect from M-type main sequence)
A red dwarf is the smallest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of fusing star in the Milky Way, at least in...
48 KB (5,552 words) - 00:37, 20 June 2025
Star (section Main sequence)
cores. Such stars are said to be on the main sequence and are called dwarf stars. Starting at zero-age main sequence, the proportion of helium in a star's...
148 KB (16,464 words) - 01:06, 28 June 2025
A K-type main-sequence star (K-type dwarf or orange dwarf) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type K. The luminosity class is typically...
13 KB (1,422 words) - 19:30, 26 June 2025
supergiant Hypergiants absolute magni- tude (MV) A B-type main-sequence star is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B. The spectral...
12 KB (1,356 words) - 19:39, 26 June 2025
Blue main-sequence star may refer to: O-type main-sequence star, main sequence stars ranging above 30,000 K B-type main-sequence star, main sequence stars...
355 bytes (73 words) - 13:52, 14 March 2025
An F-type main-sequence star is a main-sequence, hydrogen-fusing star of spectral type F. Such stars will generally have a luminosity class of V. They...
11 KB (1,229 words) - 18:39, 26 June 2025
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram where it leaves the main sequence after its main fuel is exhausted – the main sequence turnoff. By plotting the turnoff points of...
2 KB (247 words) - 01:12, 14 May 2025
supergiant Hypergiants absolute magni- tude (MV) An O-type main-sequence star is a main-sequence—core hydrogen-burning—star of spectral type O. The spectral...
12 KB (1,342 words) - 19:25, 26 June 2025
White main-sequence star may refer to: A-type main-sequence star, main sequence stars ranging from 7,600 to 10,000 K F-type main-sequence star, main sequence...
362 bytes (75 words) - 14:15, 14 March 2025
An A-type main-sequence star (A dwarf) is a main-sequence (hydrogen burning) star of spectral type A. The spectral luminosity class is typically V. These...
12 KB (1,070 words) - 19:18, 26 June 2025
belonging to K-type stars. Yellow dwarfs comprise the G-type stars of the main sequence, with masses between 0.9 and 1.1 M☉ and surface temperatures between...
36 KB (3,572 words) - 03:46, 19 June 2025
A pre-main-sequence star (also known as a PMS star and PMS object) is a star in the stage when it has not yet reached the main sequence. Earlier in its...
4 KB (481 words) - 02:20, 30 August 2024
Stellar classification (redirect from Blue-white main sequence star)
class III for regular giants, class IV for subgiants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd (or VI) for subdwarfs, and class D (or VII) for white...
107 KB (11,666 words) - 14:52, 17 June 2025
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (redirect from Main line stars)
diagram along the line called the main sequence. During the stage of their lives in which stars are found on the main sequence line, they are fusing hydrogen...
23 KB (2,762 words) - 22:46, 23 April 2025
energy from its outer photosphere. Astronomers classify it as a G-type main-sequence star. The largest objects that orbit the Sun are the eight planets....
224 KB (21,997 words) - 07:08, 29 June 2025
F-type main-sequence stars are thought to be the hottest and more massive stars capable of hosting a planet with extraterrestrial life. Compared to cooler...
10 KB (1,216 words) - 20:10, 26 June 2025
stars in the Milky Way.: §1 After the hydrogen-fusing period of a main-sequence star of low or intermediate mass ends, such a star will expand to a...
154 KB (17,961 words) - 06:00, 27 June 2025
Sun (category G-type main-sequence stars)
elements, including oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. The Sun is a G-type main-sequence star (G2V), informally called a yellow dwarf, though its light is actually...
173 KB (19,378 words) - 03:23, 29 June 2025
amplitude ranges, the main sequence can best be modeled by an inverse power law function. The high peak velocities and the main sequence relationship can also...
29 KB (3,795 words) - 01:57, 24 May 2025
early A-type main-sequence star. KOI-81b is a 13,000 K white dwarf companion of KOI-81 (KIC 8823868), a 10,000 K late B-type main-sequence star. While...
68 KB (8,202 words) - 02:35, 23 March 2025
Helium star (redirect from Helium main sequence)
spectra. Pure helium stars lie on or near a helium main sequence, analogous to the main sequence formed by the more common hydrogen stars. Previously...
4 KB (508 words) - 02:52, 24 June 2025
settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main sequence star. Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its existence. Initially...
50 KB (6,439 words) - 09:11, 24 June 2025
they lie on the Zero Age Helium Main Sequence (He-ZAMS), analogous to and parallel to the hydrogen-burning main sequence but at hotter temperatures. During...
43 KB (5,228 words) - 11:16, 19 June 2025
as the main sequence. Main-sequence stars derive energy from the fusion of hydrogen into helium in their cores. The Sun remains a main-sequence star today...
113 KB (13,512 words) - 22:20, 21 June 2025
infalling gas is depleted, leaving a pre-main-sequence star, which contracts to later become a main-sequence star at the onset of hydrogen fusion producing...
10 KB (1,217 words) - 03:26, 24 May 2025
K-type main-sequence stars, also known as orange dwarfs, may be candidates for supporting extraterrestrial life. These stars are known as "Goldilocks...
10 KB (972 words) - 05:08, 30 November 2024
Convection zone (section Main sequence stars)
solar granulation. Low-mass main-sequence stars, such as red dwarfs below 0.35 solar masses, as well as pre-main sequence stars on the Hayashi track,...
7 KB (837 words) - 11:35, 21 March 2025
type O B A F G K M L T Brown dwarfs White dwarfs Red dwarfs Subdwarfs Main sequence ("dwarfs") Subgiants Giants Red giants Blue giants Bright giants Supergiants...
40 KB (5,378 words) - 22:07, 13 May 2025