Bhāskara II ([bʰɑːskərə]; c.1114–1185), also known as Bhāskarāchārya (lit. 'Bhāskara the teacher'), was an Indian polymath, mathematician, and astronomer...
33 KB (3,676 words) - 10:57, 27 July 2025
Book of Bhāskara") and the Laghubhāskarīya ("Small Book of Bhāskara"). On 7 June 1979, the Indian Space Research Organisation launched the Bhāskara I satellite...
11 KB (1,337 words) - 20:17, 26 July 2025
after the ancient Indian mathematicians Bhāskara I and Bhāskara II. R. M. Vasagam was the project director. Bhaskara-I, weighing 444 kg at launch, was launched...
5 KB (299 words) - 01:54, 28 June 2025
History of algebra (section Bhāskara II)
and Indian syncopation may be derived from a common Babylonian source. Bhāskara II (1114 – c. 1185) was the leading mathematician of the 12th century. In...
121 KB (17,047 words) - 04:08, 9 July 2025
manuscript) Brahmagupta's mathematical advances were carried on further by Bhāskara II, a lineal descendant in Ujjain, who described Brahmagupta as the...
44 KB (5,840 words) - 11:12, 27 July 2025
Līlāvatī is a treatise by Indian mathematician Bhāskara II on mathematics, written in 1150 AD. It is the first volume of his main work, the Siddhānta...
7 KB (833 words) - 22:27, 28 March 2025
Bhāskara's wheel was a hypothetical perpetual-motion machine design created around 1150 CE by the Indian mathematician Bhāskara II. The wheel consisted...
2 KB (233 words) - 13:33, 14 September 2024
Brahmagupta, and Bhāskara I. In turn, he influenced later generations of astronomers, including Āryabhaṭa II, Śrīpati, Vaṭeśvara, and Bhāskara II (who later...
5 KB (574 words) - 01:33, 4 December 2024
mathematician and astronomer, and the author of the Maha-Siddhanta. The numeral II is given to him to distinguish him from the earlier and more influential Āryabhaṭa I...
4 KB (421 words) - 03:51, 30 March 2025
a native of Kusumapura or Pataliputra (near present day Patna, Bihar). Bhāskara I describes Aryabhata as āśmakīya, "one belonging to the Aśmaka country...
43 KB (4,899 words) - 14:08, 27 July 2025
"Crown of treatises") is the major treatise of Indian mathematician Bhāskara II. He wrote the Siddhānta Śiromaṇi in 1150 when he was 36 years old. The...
4 KB (294 words) - 14:55, 12 July 2025
who were born or lived in Ujjain include: Sage Sandipani Varāhamihira Bhāskara II Brahmagupta Chashtana Kālidāsa Devi (wife of Ashoka) Shivmangal Singh...
54 KB (4,574 words) - 06:30, 6 August 2025
History of gravitational theory (section Bhāskara II)
direction you may throw them away, and never rise upwards from the earth. Bhāskara II (c. 1114 – c. 1185), another Indian mathematician and astronomer, describes...
90 KB (11,009 words) - 04:55, 20 June 2025
Pāṭīgaṇita-sāra, he was probably a Shaivite Hindu. He was mentioned by Bhāskara II (12th century), and made apparent reference to Brahmagupta (7th century)...
7 KB (701 words) - 18:05, 10 November 2024
ISBN 0-387-25529-X) George E. Andrews and Bruce C. Berndt, Ramanujan's Lost Notebook: Part II, (Springer, 2008, ISBN 978-0-387-77765-8) George E. Andrews and Bruce C. Berndt...
106 KB (11,718 words) - 09:39, 31 July 2025
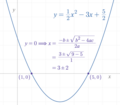
on algebra quoted by Bhāskara II. The modern quadratic formula is sometimes called Sridharacharya's formula in India and Bhaskara's formula in Brazil. The...
35 KB (5,804 words) - 12:53, 8 August 2025
beside some anonymous commentaries: Sanskrit language: Prabhakara (c. 525) Bhaskara I (c. 629) Someshvara (c. 1040) Surya-deva (born 1191), Bhata-prakasha...
17 KB (1,829 words) - 18:00, 31 July 2025
also extended some results found in earlier works, including those of Bhāskara II. However, they did not combine many differing ideas under the two unifying...
33 KB (3,695 words) - 04:27, 21 July 2025
general method for solving the Pell's equation (for all N) was given by Bhāskara II in 1150, extending the methods of Brahmagupta. Called the chakravala...
51 KB (6,703 words) - 16:37, 20 July 2025
Jantar Mantars in India. All were built at the command of the Rajah Jai Singh II, who had a keen interest in mathematics, architecture and astronomy. The largest...
6 KB (527 words) - 08:45, 22 November 2024
1100) authored a mathematical treatise titled Gome-mat Saar. Bhaskara II Bhāskara II (1114–1185) was a mathematician-astronomer who wrote a number of...
107 KB (13,951 words) - 18:35, 8 August 2025
Manava Pāṇini Pingala Yajnavalkya Classical Āryabhaṭa I Āryabhaṭa II Bhāskara I Bhāskara II Melpathur Narayana Bhattathiri Brahmadeva Brahmagupta Govindasvāmi...
24 KB (2,965 words) - 19:09, 1 June 2025
astronomy instruments. The site is one of five built by Maharaja Jai Singh II of Jaipur, from 1723 onwards, revising the calendar and astronomical tables...
11 KB (1,186 words) - 07:37, 30 March 2025
Varahamihira, ninth century Lalla, eleventh century Sripati and Bhaskara. The texts of Bhaskara have dedicated chapters on instruments and he calls them Yantra-adhyaya...
21 KB (2,180 words) - 17:07, 19 June 2025
(IAST: Bījagaṇita) was treatise on algebra by the Indian mathematician Bhāskara II. It is the second volume of his main work Siddhānta Shiromani ("Crown...
4 KB (352 words) - 14:56, 12 July 2025
In mathematics, Bhāskara I's sine approximation formula is a rational expression in one variable for the computation of the approximate values of the trigonometric...
13 KB (2,001 words) - 14:40, 3 May 2025
Manava Pāṇini Pingala Yajnavalkya Classical Āryabhaṭa I Āryabhaṭa II Bhāskara I Bhāskara II Melpathur Narayana Bhattathiri Brahmadeva Brahmagupta Govindasvāmi...
28 KB (3,354 words) - 13:06, 6 July 2025
Calculus (redirect from Calculus II)
and fourth powers allowed him to calculate the volume of a paraboloid. Bhāskara II (c. 1114–1185) was acquainted with some ideas of differential calculus...
76 KB (8,766 words) - 00:56, 6 July 2025
systems. Bhāskara I (629 CE): Authored the astronomical works Mahābhāskariya (Great Book of Bhāskara), Laghubhaskariya (Small Book of Bhaskara), and the...
64 KB (7,407 words) - 21:04, 25 June 2025
Manava Pāṇini Pingala Yajnavalkya Classical Āryabhaṭa I Āryabhaṭa II Bhāskara I Bhāskara II Melpathur Narayana Bhattathiri Brahmadeva Brahmagupta Govindasvāmi...
9 KB (824 words) - 14:19, 19 May 2025