Computer Power and Human Reason: From Judgment to Calculation is a 1976 nonfiction book by German-American computer scientist Joseph Weizenbaum in which...
4 KB (343 words) - 07:47, 9 May 2025
2016-02-22. Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976). Computer Power and Human Reason: From Judgment to Calculation. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. pp. 2, 3, 6, 182, 189...
3 KB (307 words) - 16:26, 7 August 2024
ELIZA effect (category Human–computer interaction)
Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976). Computer power and human reason : from judgment to calculation. San Francisco, Cal.: W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 0-7167-0464-1...
16 KB (1,832 words) - 10:23, 9 June 2025
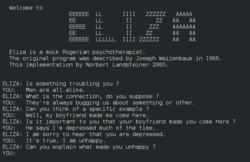
ELIZA (section Design and implementation)
Weizenbaum and motivated him to write his book Computer Power and Human Reason: From Judgment to Calculation, in which he explains the limits of computers, as...
33 KB (3,816 words) - 19:04, 30 June 2025
Computer Power and Human Reason displays his ambivalence towards computer technology and lays out his case: the possibility of programming computers to...
16 KB (1,570 words) - 13:25, 21 June 2025
Penguin. Retrieved 18 November 2019. Weizenbaum J (1976), Computer Power and Human Reason, W.H. Freeman & Company, ISBN 978-0-14-022535-8, OCLC 10952283...
174 KB (20,268 words) - 07:13, 14 July 2025
significant addition to the field of computer ethics. He published a book titled Computer Power and Human Reason, which talked about how artificial intelligence...
27 KB (3,030 words) - 08:36, 17 June 2025
Computer Science Logo Style: Beyond programming by Brian Harvey 1997 ISBN 0-262-58150-7 page 278 Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976). Computer power and human reason:...
17 KB (2,042 words) - 15:40, 20 December 2024
possessed by humans. Reason is sometimes referred to as rationality. Reasoning involves using more-or-less rational processes of thinking and cognition to...
96 KB (11,585 words) - 14:10, 22 June 2025
Computers] (in German) (1st ed.). Berlin: Projekt Verlag. pp. 53–70. ISBN 9783897334670. Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976). Computer Power and Human Reason:...
28 KB (1,297 words) - 20:39, 2 July 2025
Algorithmic bias (redirect from Biased computer systems)
successfully and consistently reproduced that human logic. In his 1976 book Computer Power and Human Reason, artificial intelligence pioneer Joseph Weizenbaum...
141 KB (15,686 words) - 00:09, 25 June 2025
Alan Turing (category Computer chess people)
1959 by W. Heffer & Sons, Ltd) Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976). Computer Power and Human Reason. London: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-0463-3. Whitemore, Hugh;...
148 KB (15,067 words) - 15:18, 7 July 2025
Criticism of technology (category Science and technology studies)
The title essay is available online here Joseph Weizenbaum, Computer Power and Human Reason: From Judgement to Calculation, W.H.Freeman & Co Ltd, New Edition...
9 KB (1,016 words) - 05:32, 4 June 2025
from the original on 2 July 2008 Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976), Computer Power and Human Reason, W.H. Freeman & Company "The history of artificial intelligence:...
123 KB (4,787 words) - 00:50, 12 July 2025
Ethics of artificial intelligence (category Ethics of science and technology)
BBC News. Retrieved 12 February 2021. Weizenbaum J (1976). Computer Power and Human Reason. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman & Company. ISBN 978-0-7167-0464-5...
148 KB (15,269 words) - 00:25, 6 July 2025
Artificial general intelligence (redirect from Human-level AI)
available sometime between 2015 and 2025, if the exponential growth in computer power at the time of writing continued. The Human Brain Project, an EU-funded...
129 KB (14,235 words) - 22:59, 11 July 2025
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems. Research in HCI covers the design and the...
50 KB (5,817 words) - 04:22, 12 July 2025
Virtual assistant (section Devices and objects)
Computers in Human Behavior. 17 (3): 295–314. doi:10.1016/S0747-5632(01)00004-8. ISSN 0747-5632. Weizenbaum, Joseph (1976). Computer power and human reason :...
49 KB (5,274 words) - 21:12, 10 July 2025
revolutionary tactical and control computer designed by Dr. Richard Daystrom (William Marshall). The M-5 is to handle all ship functions without human assistance...
8 KB (940 words) - 01:54, 5 January 2025
human brain activity". Nature. 452 (7185): 352–5. Bibcode:2008Natur.452..352K. doi:10.1038/nature06713. PMC 3556484. PMID 18322462. Sandberg, Anders;...
66 KB (7,314 words) - 11:09, 14 July 2025
Power cycling is the act of turning a piece of equipment, usually a computer, off and then on again. Reasons for power cycling include having an electronic...
5 KB (571 words) - 16:31, 6 October 2024
and database theory concerns the management of repositories of data. Human–computer interaction investigates the interfaces through which humans and computers...
73 KB (6,717 words) - 14:38, 7 July 2025
This article documents the progress of significant human–computer chess matches. Chess computers were first able to beat strong chess players in the late...
33 KB (3,934 words) - 16:00, 4 May 2025
batteries, and human power. System designers building parallel computers, such as Google's hardware, pick CPUs based on their speed per watt of power, because...
22 KB (2,841 words) - 23:36, 9 March 2025
Turing test (category Human–computer interaction)
me, and still received rational answers" the king became satisfied that Gulliver was not a machine. Tests where a human judges whether a computer or an...
102 KB (12,548 words) - 09:05, 14 July 2025
Technological singularity (category Harv and Sfn no-target errors)
the human brain, which has not, according to Paul R. Ehrlich, changed significantly for millennia. But with the increasing power of computers and other...
113 KB (12,117 words) - 13:39, 14 July 2025
Information technology (redirect from Electronics and computer industry)
is an application of computer science and computer engineering. The term is commonly used as a synonym for computers and computer networks, but it also...
40 KB (4,403 words) - 04:46, 12 July 2025
Humans (Homo sapiens) or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus Homo. They are...
263 KB (25,563 words) - 04:22, 12 July 2025
Programming language (redirect from Computer programming language)
used to produce a computer program. A language allows a programmer to develop human readable content that can be consumed by a computer but only after translation...
63 KB (7,319 words) - 15:22, 10 July 2025
Neuralink (redirect from Neuralink human testing)
implantable brain–computer interfaces (BCIs), also known as brain implants. It was founded by Elon Musk and a team of eight scientists and engineers. Neuralink...
67 KB (6,188 words) - 00:37, 1 July 2025