A DNA sequencer is a scientific instrument used to automate the DNA sequencing process. Given a sample of DNA, a DNA sequencer is used to determine the...
37 KB (3,850 words) - 23:38, 23 March 2024
methods with a DNA sequencer, DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster. DNA sequencing may be used to determine the sequence of individual...
136 KB (15,496 words) - 08:19, 29 May 2025
genomic DNA is repetitive, with over two-thirds of the sequence consisting of repetitive elements in humans. Some of these repeated sequences are necessary...
32 KB (3,832 words) - 20:58, 13 April 2025
Deoxyribonucleic acid (/diːˈɒksɪˌraɪboʊnjuːˌkliːɪk, -ˌkleɪ-/ ; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to...
167 KB (17,915 words) - 22:22, 29 May 2025
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases within the nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. This succession...
22 KB (2,409 words) - 19:05, 21 May 2025
synthesis of DNA and incorporated into recombinant DNA molecules. Using recombinant DNA technology and synthetic DNA, any DNA sequence can be created...
34 KB (3,852 words) - 06:09, 15 December 2024
Non-coding DNA (ncDNA) sequences are components of an organism's DNA that do not encode protein sequences. Some non-coding DNA is transcribed into functional...
42 KB (4,774 words) - 17:56, 3 November 2024
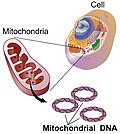
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into...
98 KB (10,782 words) - 17:22, 21 May 2025
Human genome (redirect from Human DNA)
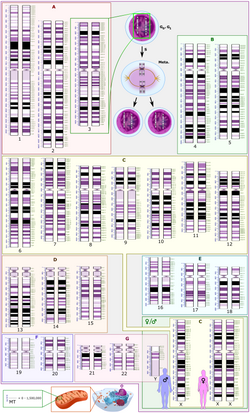
of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found...
99 KB (10,102 words) - 13:33, 2 May 2025
Genome (redirect from DNA genome)
the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding...
44 KB (4,931 words) - 05:45, 26 May 2025
DNA microarray (also commonly known as DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays...
54 KB (5,404 words) - 20:37, 29 May 2025
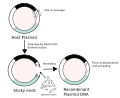
Molecular cloning (redirect from Recombinant DNA technology)
identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned...
32 KB (4,017 words) - 04:13, 12 April 2025
single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional...
22 KB (2,637 words) - 06:01, 3 April 2025
Junk DNA (non-functional DNA) is a DNA sequence that has no known biological function. Most organisms have some junk DNA in their genomes—mostly pseudogenes...
36 KB (3,906 words) - 09:51, 25 May 2025
Coding region (redirect from Coding DNA sequence)
coding region of a gene, also known as the coding DNA sequence (CDS), is the portion of a gene's DNA or RNA that codes for a protein. Studying the length...
22 KB (2,514 words) - 21:25, 25 May 2025
Epigenetics (section DNA methylation)
study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix epi- (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in epigenetics...
159 KB (18,196 words) - 11:58, 20 May 2025
Mutation (redirect from DNA mutations)
alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result...
119 KB (14,264 words) - 20:05, 22 May 2025
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient sources (typically specimens, but also environmental DNA). Due to degradation processes (including cross-linking...
61 KB (6,390 words) - 15:40, 28 May 2025
develops and sells nanopore sequencing products (including the portable DNA sequencer, MinION) for the direct, electronic analysis of single molecules. It...
12 KB (985 words) - 23:48, 28 May 2025
analyzing single molecules of DNA and RNA. The protein sequencer, DNA synthesizer, peptide synthesizer, and DNA sequencer were commercialized through Applied...
76 KB (7,587 words) - 14:19, 24 May 2025
Genetic testing (redirect from DNA testing)
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring...
56 KB (6,629 words) - 20:57, 29 May 2025
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune...
77 KB (8,378 words) - 06:14, 23 May 2025
Transcription (biology) (redirect from DNA transcription)
DNA transcription unit encoding for a protein may contain both a coding sequence, which will be translated into the protein, and regulatory sequences...
58 KB (6,898 words) - 13:44, 24 May 2025
Look up sequencer in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Sequencer may refer to: Drum sequencer (controller), an electromechanical system for controlling...
895 bytes (133 words) - 07:33, 13 July 2019
Gene (redirect from Gene sequence)
Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two...
100 KB (11,208 words) - 22:21, 21 April 2025
In genomics, DNA–DNA hybridization is a molecular biology technique that measures the degree of genetic similarity between DNA sequences. It is used to...
14 KB (1,560 words) - 06:47, 17 May 2025
CRISPR (category Repetitive DNA sequences)
repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. Each sequence within an individual prokaryotic...
115 KB (11,900 words) - 23:21, 29 May 2025
Activator (genetics) (redirect from Activator DNA sequences)
"activation domain". Most activators function by binding sequence-specifically to a regulatory DNA site located near a promoter and making protein–protein...
17 KB (1,959 words) - 01:17, 24 May 2025
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence...
56 KB (6,913 words) - 09:31, 31 May 2025
(mRNA) that directs protein synthesis. The mRNA sequence is determined by the sequence of genomic DNA. In this context, the standard genetic code is referred...
42 KB (1,606 words) - 09:57, 13 March 2025