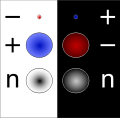
Dirac hole theory is a theory in quantum mechanics, named after English theoretical physicist Paul Dirac, who introduced it in 1929. The theory poses...
3 KB (338 words) - 04:22, 10 April 2024
was originally conceived of as a hole in the Dirac sea, before its experimental discovery in 1932. In hole theory, the solutions with negative time evolution...
14 KB (2,014 words) - 21:53, 23 August 2024
Antiparticle (category Quantum field theory)
proton. Dirac tried to argue that this was due to the electromagnetic interactions with the sea, until Hermann Weyl proved that hole theory was completely...
24 KB (2,655 words) - 00:53, 16 May 2025
component wave functions in Pauli's phenomenological theory of spin. The wave functions in the Dirac theory are vectors of four complex numbers (known as bispinors)...
79 KB (13,114 words) - 00:17, 2 June 2025
Magnetic monopole (redirect from Dirac monopole)
seen so far. The quantum theory of magnetic charge started with a paper by the physicist Paul Dirac in 1931. In this paper, Dirac showed that if any magnetic...
73 KB (8,385 words) - 17:02, 29 April 2025
thought of as "holes" in an infinite electron sea, rather than a new kind of particle, and this theory was referred to as the Dirac hole theory.: 72 : 23 ...
107 KB (14,903 words) - 01:36, 27 May 2025
Virtue theory Physics: Acoustic theory — Antenna theory — Atomic theory — BCS theory — Conformal field theory — Dirac hole theory — Dynamo theory — Landau...
38 KB (4,341 words) - 16:56, 25 May 2025
The simplest and most natural theory of gravity with torsion is the Einstein–Cartan theory. Torsion modifies the Dirac equation in the presence of the...
25 KB (3,034 words) - 19:51, 16 May 2025
the founders of quantum mechanics. Dirac laid the foundations for both quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory. He was the Lucasian Professor of...
92 KB (9,987 words) - 20:37, 2 June 2025
particles, holes are rather quasiparticles; they are different from the positron, which is the antiparticle of the electron. (See also Dirac sea.) In crystals...
18 KB (2,315 words) - 16:37, 18 May 2025
that the positron is not a hole in the sea of electrons-with-negative-energy as in usual Dirac hole theory, but instead is a hole in the sea of...
25 KB (2,770 words) - 04:15, 7 February 2025
Einstein–Cartan theory is purely classical, it also does not fully address the issue of quantum gravity. In the Einstein–Cartan theory, the Dirac equation becomes...
27 KB (3,506 words) - 05:20, 2 June 2025
sufficiently compact area forms into a Schwarzschild black hole. In the Einstein–Cartan–Sciama–Kibble theory of gravity, however, it forms a regular Einstein–Rosen...
7 KB (794 words) - 20:48, 11 May 2025
General relativity (redirect from General theory of relativity)
delay and singularities/black holes. So far, all tests of general relativity have been shown to be in agreement with the theory. The time-dependent solutions...
194 KB (22,692 words) - 07:19, 2 June 2025
entanglement spinor, spinor group, spinor bundle Dirac sea Spin foam Poincaré group gamma matrices Dirac adjoint Wigner's classification anyon Copenhagen...
4 KB (359 words) - 17:50, 16 April 2025
physics, a Dirac string is a one-dimensional curve in space, conceived of by the physicist Paul Dirac, stretching between two hypothetical Dirac monopoles...
3 KB (405 words) - 16:55, 11 April 2025
most comprehensive theory of particles, treats the electron as a point particle. There is no evidence that the electron is a black hole (or naked singularity)...
9 KB (1,167 words) - 03:25, 1 June 2025
fermion Dirac field Dirac gauge Dirac hole theory Dirac Lagrangian Dirac matrices Dirac matter Dirac membrane Dirac picture Dirac sea Dirac spectrum Dirac spinor...
2 KB (218 words) - 05:42, 22 June 2024
mass forms a singular black hole. In the Einstein–Cartan theory, however, the minimal coupling between torsion and Dirac spinors generates a repulsive...
29 KB (3,441 words) - 23:47, 13 May 2025
Black star (semiclassical gravity) (category Black holes)
to the black hole concept from general relativity. The theoretical construct was created through the use of semiclassical gravity theory. A similar structure...
4 KB (470 words) - 21:06, 10 May 2025
surface for the holes. The two conical surfaces touch each other and form a zero-band gap semimetal. The name of Dirac cone comes from the Dirac equation that...
23 KB (1,889 words) - 09:38, 22 May 2025
black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general...
165 KB (18,730 words) - 03:12, 1 June 2025
Steven B. (1995). "The black hole information paradox". arXiv:hep-th/9508151. Dirac, P. A. M. (1975). General theory of relativity. New York : Wiley...
11 KB (616 words) - 18:02, 28 October 2024
Abraham–Lorentz force (redirect from Abraham–Lorentz–Dirac force)
the relativistic version is called the Lorentz–Dirac force or collectively known as Abraham–Lorentz–Dirac force. The equations are in the domain of classical...
39 KB (5,497 words) - 18:43, 23 May 2025
String theory has contributed a number of advances to mathematical physics, which have been applied to a variety of problems in black hole physics,...
122 KB (15,295 words) - 05:10, 31 May 2025
8: INTRODUCTORY THEORY OF CONDUCTIVITY AND HALL EFFECT Chapter 9: DISTRIBUTIONS OF QUANTUM STATES IN ENERGY Chapter 10: FERMI-DIRAC STATISTICS FOR SEMICONDUCTORS...
3 KB (365 words) - 02:12, 11 June 2024
Negative energy (section Dirac sea)
According to the theory of the Dirac sea, developed by Paul Dirac in 1930, the vacuum of space is full of negative energy. This theory was developed to...
10 KB (1,313 words) - 09:01, 5 April 2025
of a micro black hole. Hawking achieved commercial success with several works of popular science in which he discussed his theories and cosmology in general...
189 KB (18,374 words) - 17:21, 26 May 2025
field theory φ4 theory Sine-Gordon Toda field theory Theories whose matter content consists only of spinor fields Dirac theory: free spinor field theory Thirring...
3 KB (276 words) - 18:02, 16 April 2025