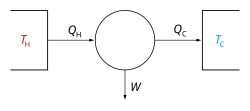
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change...
20 KB (2,906 words) - 18:44, 29 April 2025
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol c) of a substance is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance...
55 KB (8,516 words) - 03:45, 2 June 2025
The molar heat capacity of a chemical substance is the amount of energy that must be added, in the form of heat, to one mole of the substance in order...
50 KB (5,707 words) - 19:29, 21 March 2025
the heat capacity ratio, also known as the adiabatic index, the ratio of specific heats, or Laplace's coefficient, is the ratio of the heat capacity at...
18 KB (2,324 words) - 16:04, 11 August 2024
The table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as well as the specific heat capacity of some substances and engineering materials...
16 KB (830 words) - 16:23, 19 May 2025
The volumetric heat capacity of a material is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the volume of the sample. It is the amount of energy...
15 KB (2,157 words) - 23:22, 3 April 2025
The heat capacity rate is heat transfer terminology used in thermodynamics and different forms of engineering denoting the quantity of heat a flowing...
5 KB (693 words) - 04:38, 14 January 2025
Debye model (redirect from Debye theory of specific heat capacities)
phonon contribution to the specific heat (heat capacity) in a solid. It treats the vibrations of the atomic lattice (heat) as phonons in a box in contrast...
47 KB (9,147 words) - 14:07, 29 March 2025
Einstein solid (redirect from Einstein's theory of specific heat capacity)
specific heat problem in classical mechanics. The original theory proposed by Einstein in 1907 has great historical relevance. The heat capacity of solids...
11 KB (1,958 words) - 17:08, 17 April 2025
capacity is the heat capacity per unit amount (SI unit: mole) of a pure substance, and the specific heat capacity, often called simply specific heat,...
92 KB (12,978 words) - 04:20, 26 May 2025
Properties of water (redirect from Heat capacity of water)
relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity. Water is amphoteric, meaning that it can exhibit properties of an acid...
90 KB (9,586 words) - 02:08, 27 May 2025
refractive index specific conductance (or electrical conductivity) specific heat capacity, cp specific internal energy, u specific rotation, [α] specific volume...
20 KB (2,466 words) - 08:54, 19 February 2025
2003; Section 4, Properties of the Elements and Inorganic Compounds; Heat Capacity of the Elements at 25 °C As quoted at http://www.webelements.com/ from...
17 KB (209 words) - 17:51, 18 September 2024
Coolant (redirect from Heat transfer medium)
the heat is transferred by convective or forced flow. Water is the most common coolant. Its high heat capacity and low cost make it a suitable heat-transfer...
16 KB (2,053 words) - 01:54, 27 May 2025
In thermodynamics, the heat capacity at constant volume, C V {\displaystyle C_{V}} , and the heat capacity at constant pressure, C P {\displaystyle C_{P}}...
10 KB (2,080 words) - 17:41, 28 April 2025
Cooling capacity is the measure of a cooling system's ability to remove heat. It is equivalent to the heat supplied to the evaporator/boiler part of the...
2 KB (246 words) - 21:06, 17 October 2024
that temperature is low enough that heat capacities are not influenced by molecular vibration (see heat capacity). However, vibrational modes simply cause...
53 KB (7,495 words) - 06:28, 25 May 2025
heating system heats the radiator in a room. Water is the most common heat transfer fluid because of its economy, high heat capacity and favorable transport...
11 KB (1,435 words) - 18:04, 23 May 2025
Temperature (section Heat capacity)
Q}{\Delta T}}.} If heat capacity is measured for a well-defined amount of substance, the specific heat is the measure of the heat required to increase...
104 KB (12,997 words) - 13:37, 26 May 2025
Isobaric process (section Specific heat capacity)
m}\end{aligned}}} where cP is molar heat capacity at a constant pressure. To find the molar specific heat capacity of the gas involved, the following equations...
12 KB (1,891 words) - 13:11, 17 November 2024
History of thermodynamics (redirect from Theory of heat)
the term heat capacity, named and first investigated by Scottish chemist Joseph Black in the 1750s. In the mid- to late 19th century, heat became understood...
34 KB (3,780 words) - 15:53, 31 March 2025
Thermal reservoir (redirect from Heat bath)
system with a heat capacity so large that the temperature of the reservoir changes relatively little when a significant amount of heat is added or extracted...
2 KB (276 words) - 09:47, 28 May 2025
Enthalpy of fusion (redirect from Latent heat of fusion)
processes independently and using the specific heat capacity of water to be 4.18 J/(g⋅K); thus, to heat 1 kg of ice from 273.15 K to water at 293.15 K...
12 KB (1,696 words) - 23:19, 4 May 2025
physics the electronic specific heat, sometimes called the electron heat capacity, is the specific heat of an electron gas. Heat is transported by phonons and...
17 KB (3,067 words) - 21:49, 20 December 2024
The Heat Capacity Mapping Mission (HCMM) spacecraft was the first of a series of Applications Explorer Mission (AEM) of the Explorer program. The objective...
7 KB (681 words) - 07:48, 26 July 2024
energies for a system at a given temperature, from which the system's heat capacity can be computed. However, equipartition also gives the average values...
91 KB (11,997 words) - 12:08, 7 May 2025
Thermal mass (category Heat transfer)
matter "thermal mass" describes. Most writers use it as a synonym for heat capacity, the ability of a body to store thermal energy. It is typically referred...
7 KB (872 words) - 08:40, 24 April 2025
glycol lowers the specific heat capacity of water mixtures relative to pure water. A 1:1 mix by mass has a specific heat capacity of about 3140 J/(kg·°C)...
31 KB (3,192 words) - 05:00, 15 May 2025
Calorimeter (section Heat flow calorimeter)
calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal...
26 KB (3,848 words) - 11:37, 29 December 2024
1, below). This is why the noble gases all have the same specific heat capacity per atom and why that value is lowest of all the gases. Molecules (two...
103 KB (13,522 words) - 10:24, 31 May 2025