In computing and parallel processing, memory semantics refers to the process logic used to control access to shared memory locations, or at a higher level...
1 KB (115 words) - 09:44, 9 July 2023
Programming language (redirect from Static semantics)
cloud computing applications and systems. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Internet of things, Data and Cloud Computing (pp. 1-5)...
63 KB (7,319 words) - 15:22, 10 July 2025
operational semantics) or as a mathematical function (denotational semantics). A language may also be defined by an interpreter in which the semantics of the...
37 KB (4,585 words) - 23:18, 7 June 2025
parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has...
74 KB (8,380 words) - 19:27, 4 June 2025
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed concurrently—during overlapping time periods—instead of sequentially—with...
29 KB (3,004 words) - 17:17, 16 April 2025
Turing machine (redirect from Universal computing machine)
Turing tarpit, any computing system or language that, despite being Turing complete, is generally considered useless for practical computing Unorganised machine...
73 KB (9,422 words) - 16:46, 24 June 2025
Semantics is the study of linguistic meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends...
134 KB (14,269 words) - 15:01, 11 July 2025
common goal for their work. The terms "concurrent computing", "parallel computing", and "distributed computing" have much overlap, and no clear distinction...
57 KB (6,617 words) - 18:52, 16 April 2025
In computing, a cache (/kæʃ/ KASH) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the...
30 KB (4,140 words) - 00:56, 13 July 2025
single-threaded execution of code, the memory model provides the semantics of the Java programming language. The original Java memory model developed in 1995 was...
9 KB (1,186 words) - 03:45, 10 July 2025
categorically-organized fashion." Memory semantics Sparse distributed memory Semantic similarity McRae, Ken; Jones, Michael (2013). "Semantic Memory". In Reisberg, Daniel...
60 KB (7,837 words) - 16:57, 18 July 2025
and introduction of computing hardware, such as I/O devices, from the design and introduction of other components of a computing system, thereby allowing...
14 KB (1,401 words) - 17:47, 16 June 2025
associated with blocking. Concurrent computing Data dependency Non-blocking algorithm Race condition Scheduling (computing) Stallings, William (2004). Operating...
3 KB (315 words) - 21:26, 20 August 2024
of specialization in memory order semantics are the programmers who author software frameworks in support of concurrent computing models. Note that local...
30 KB (3,426 words) - 09:08, 26 January 2025
In computing, a library is a collection of resources that can be used during software development to implement a computer program. Commonly, a library...
23 KB (2,543 words) - 16:28, 18 July 2025
Safe semantics is a computer hardware consistency model. It describes one type of guarantee that a data register provides when it is shared by several...
7 KB (961 words) - 14:13, 12 October 2024
In computing, a memory model describes the interactions of threads through memory and their shared use of the data. A memory model allows a compiler to...
7 KB (801 words) - 15:51, 25 August 2024
Outline of computer science (redirect from Outline of scientific computing)
system for computer science is the ACM Computing Classification System devised by the Association for Computing Machinery. Computer science can be described...
11 KB (1,036 words) - 19:01, 2 June 2025
Cache control instruction (section Scratchpad memory)
committing their contents to main memory. Care is needed since incorrect results are possible. Unlike other cache hints, the semantics of the program are significantly...
7 KB (839 words) - 08:06, 25 February 2025
Referent (category Semantics)
in a relation, the other being called the relatum. In fields such as semantics, semiotics, and the theory of reference, a distinction is made between...
7 KB (948 words) - 09:45, 13 July 2025
In computing, a memory barrier, also known as a membar, memory fence or fence instruction, is a type of barrier instruction that causes a central processing...
12 KB (1,390 words) - 16:10, 19 February 2025
Fork (system call) (category Process (computing))
the memory segments of the parent process. In modern UNIX variants that follow the virtual memory model from SunOS-4.0, copy-on-write semantics are implemented...
17 KB (2,188 words) - 10:29, 12 July 2025
CUDA (redirect from Compute Unified Device Architecture)
In computing, CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a proprietary parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that...
84 KB (4,133 words) - 19:02, 30 June 2025
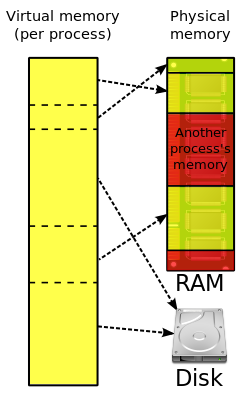
In computing, virtual memory, or virtual storage, is a memory management technique that provides an "idealized abstraction of the storage resources that...
43 KB (5,351 words) - 14:51, 13 July 2025
This is a list of computing and IT acronyms, initialisms and abbreviations. 0–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also References...
108 KB (7,687 words) - 19:54, 18 July 2025
operationalization of generative grammar), morphology (e.g., two-level morphology), semantics (e.g., Lesk algorithm), reference (e.g., within Centering Theory) and...
54 KB (6,609 words) - 05:51, 12 July 2025
capability computing. That is, a single application could be run across the entire system. This is in contrast to cluster-style capacity computing, in which...
7 KB (687 words) - 02:51, 15 July 2024
Computer science (redirect from Computing science)
and databases. In the early days of computing, a number of terms for the practitioners of the field of computing were suggested (albeit facetiously) in...
72 KB (6,671 words) - 02:53, 17 July 2025
Comparison of instruction set architectures (category Computing comparisons)
types, what state there is (such as the main memory and registers) and their semantics (such as the memory consistency and addressing modes), the instruction...
34 KB (1,849 words) - 19:41, 3 July 2025