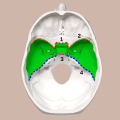
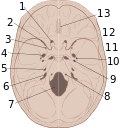
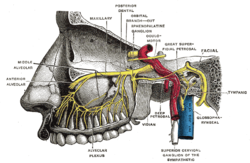
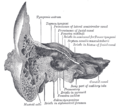
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than...
8 KB (979 words) - 23:56, 15 October 2023
A cranial fossa is formed by the floor of the cranial cavity. There are three distinct cranial fossae: Anterior cranial fossa (fossa cranii anterior),...
3 KB (142 words) - 18:45, 18 May 2024
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid...
6 KB (563 words) - 14:57, 31 January 2024
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the...
6 KB (775 words) - 09:53, 20 May 2025
hypophyseal fossa (the depression in the sphenoid bone). Some examples include: In the skull: Cranial fossa Anterior cranial fossa Middle cranial fossa Interpeduncular...
3 KB (263 words) - 03:25, 9 August 2024
Base of skull (redirect from Cranial base)
Chiasmatic groove Middle clinoid process Groove for sigmoid sinus Trigeminal ganglion Middle cranial fossa Anterior cranial fossa Middle meningeal artery...
3 KB (219 words) - 09:31, 25 February 2025
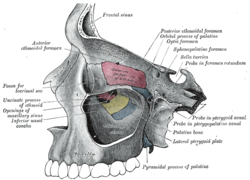
communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina. It has the following boundaries:...
4 KB (356 words) - 22:01, 21 July 2023
into the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through its own canaliculus to reach the infratemporal fossa. Cell bodies...
5 KB (517 words) - 22:09, 18 December 2024
spread into the infratemporal fossa. This can be surgically removed through the middle cranial fossa. The infratemporal fossa can also be used to approach...
8 KB (864 words) - 23:09, 24 May 2025
Skull (redirect from Cranial bone)
same time, the angle of the anterior cranial fossa decreases, and its depth increases towards the middle cranial fossa. In the second trimester, growth continues...
42 KB (4,843 words) - 19:03, 4 June 2025
Several surgicala approaches are described to achieve decompression: Middle cranial fossa approach Translabarynthine approach "Total decompression" can also...
11 KB (1,355 words) - 02:04, 15 April 2025
internal carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into (the middle cranial fossa of) the cranial cavity. Observing the trajectory of the canal from exterior...
8 KB (774 words) - 16:31, 21 March 2025
in the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. It allows for the passage of the maxillary nerve...
4 KB (435 words) - 20:43, 15 May 2024
through the foramen ovale to enter the cranial cavity and supply the dura mater of the floor of the middle cranial fossa and of the trigeminal cave, and to...
3 KB (222 words) - 10:57, 28 February 2025
known as mastoid ecchymosis, is a late indication of fracture of middle cranial fossa of the skull, appearing as bruising over one or both of the mastoid...
2 KB (177 words) - 18:23, 16 June 2025
Sella turcica (redirect from Pituiary fossa)
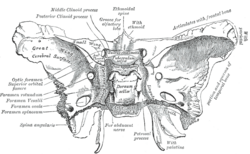
hypophyseal fossa. The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa...
5 KB (563 words) - 21:58, 29 May 2025
supply, in the middle cranial fossa the middle meningeal artery and some accessory arteries are responsible for blood supply, the middle meningeal artery...
15 KB (1,713 words) - 05:34, 23 June 2025
from just anterior to the foramen lacerum in the middle cranial fossa to the pterygopalatine fossa. It transmits the nerve of pterygoid canal (Vidian...
2 KB (159 words) - 15:50, 25 May 2025
Trigeminal ganglion (category Cranial nerves)
minute branches to the tentorium cerebelli, and the dura mater in the middle cranial fossa.[citation needed] Medially to the trigeminal ganglion are the internal...
6 KB (616 words) - 04:48, 29 March 2024
pharyngotympanic tube, superior jugular bulb, posterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa, carotid canal, abducens nerve, sigmoid sinus) to which they...
5 KB (545 words) - 04:07, 25 May 2025
of the head called bobble-head doll syndrome. Cysts in the left middle cranial fossa have been associated with ADHD in a study on affected children. Headaches...
22 KB (2,452 words) - 18:59, 9 June 2025
Greater petrosal nerve (category Cranial nerves)
to reach the pterygopalatine fossa and form the pterygopalatine ganglion).: 498 During surgery of the middle cranial fossa, manipulation of the dura mater...
6 KB (635 words) - 00:48, 20 November 2024
forms the floor of the middle cranial fossa: 508-509 ) at the anterior boundary of the sella turcica (hypophyseal (pituitary) fossa): 509 and posterior...
2 KB (128 words) - 16:16, 15 April 2024
suture) is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bone. It is in the middle cranial fossa. This article incorporates...
1 KB (53 words) - 18:46, 29 February 2024
foramen lacerum. The anterior surface forms the posterior part of the middle cranial fossa of the base of the skull, and is continuous with the inner surface...
13 KB (1,819 words) - 10:48, 20 June 2025
bone forming the lateral part of the posterior wall of: 509 the middle cranial fossa.: 566-567 : 420, 509 The arcuate eminence indicates the position...
2 KB (146 words) - 19:02, 1 December 2024
to the middle cranial fossa. The greater petrosal nerve travels through it to branch from the facial nerve and reach the middle cranial fossa on its way...
960 bytes (60 words) - 20:08, 17 January 2024
Skull fracture (section Cranial burst fracture)
sphenoid wings at the base of the skull. The middle cranial fossa, a depression at the base of the cranial cavity forms the thinnest part of the skull...
22 KB (2,808 words) - 04:49, 18 October 2024
They then enter the middle cranial fossa above foramen lacerum, travel through the cavernous sinus in the middle cranial fossa and then travel with the...
13 KB (1,300 words) - 14:31, 10 April 2025
is a continuation of the tegmen tympani and separates it from the middle cranial fossa. The lateral wall of the antrum is formed by a plate of bone which...
2 KB (215 words) - 22:29, 27 December 2023