A physical quantity (or simply quantity) is a property of a material or system that can be quantified by measurement. A physical quantity can be expressed...
18 KB (1,616 words) - 20:27, 9 March 2025
number of physical quantities. The first table lists the fundamental quantities used in the International System of Units to define the physical dimension...
30 KB (192 words) - 17:22, 2 April 2025
Dimensional analysis (redirect from Dimension of a physical quantity)
analysis of the relationships between different physical quantities by identifying their base quantities (such as length, mass, time, and electric current)...
96 KB (11,919 words) - 09:55, 11 May 2025
Quantity or amount is a property that can exist as a multitude or magnitude, which illustrate discontinuity and continuity. Quantities can be compared...
14 KB (2,386 words) - 15:18, 18 January 2025
and expanded. The base quantities of a given system of physical quantities is a subset of those quantities, where no base quantity can be expressed in terms...
10 KB (1,105 words) - 20:27, 9 March 2025
sciences, a vector quantity (also known as a vector physical quantity, physical vector, or simply vector) is a vector-valued physical quantity. It is typically...
6 KB (669 words) - 17:07, 20 November 2024
Intensive and extensive properties (redirect from Extensive quantity)
extensive property is a physical quantity whose value is proportional to the size of the system it describes, or to the quantity of matter in the system...
20 KB (2,466 words) - 08:54, 19 February 2025
Unit of measurement (redirect from Physical unit)
a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite...
26 KB (3,382 words) - 06:39, 8 May 2025
divisor quantity, the specific quantity is a massic quantity. If volume is the divisor quantity, the specific quantity is a volumic quantity.[citation...
9 KB (1,163 words) - 16:09, 19 January 2025
quantifiable physical property is called physical quantity. Measurable physical quantities are often referred to as observables. Some physical properties...
7 KB (552 words) - 14:22, 4 February 2025
Scalar (physics) (redirect from Scalar quantity)
Scalar quantities or simply scalars are physical quantities that can be described by a single pure number (a scalar, typically a real number), accompanied...
8 KB (1,090 words) - 06:00, 10 March 2025
A physical constant, sometimes fundamental physical constant or universal constant, is a physical quantity that cannot be explained by a theory and therefore...
22 KB (2,668 words) - 15:09, 14 April 2025
Vector (mathematics and physics) (redirect from Physical vector)
sciences, a vector quantity (also known as a vector physical quantity, physical vector, or simply vector) is a vector-valued physical quantity. It is typically...
10 KB (2,694 words) - 21:32, 3 May 2025
Quantity calculus is the formal method for describing the mathematical relations between abstract physical quantities. Its roots can be traced to Fourier's...
4 KB (541 words) - 00:27, 30 October 2024
constants listed here are known values of physical constants expressed in SI units; that is, physical quantities that are generally believed to be universal...
32 KB (1,713 words) - 16:38, 26 September 2024
Stress (mechanics) (redirect from Physical stress)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes forces present during deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such...
44 KB (5,562 words) - 04:17, 13 December 2024
corresponding to seven base physical quantities. They are the second, with the symbol s, which is the SI unit of the physical quantity of time; the metre, symbol...
72 KB (6,140 words) - 23:58, 13 May 2025
the material derivative describes the time rate of change of some physical quantity (like heat or momentum) of a material element that is subjected to...
14 KB (2,003 words) - 07:38, 8 April 2025
Sievert (section Physical quantities)
To calculate the value of stochastic health risk in sieverts, the physical quantity absorbed dose is converted into equivalent dose and effective dose...
68 KB (6,585 words) - 20:37, 9 May 2025
Moment (physics) (category Physical quantities)
a physical quantity such as a force or electric charge. Moments are usually defined with respect to a fixed reference point and refer to physical quantities...
22 KB (2,893 words) - 14:58, 22 February 2025
Observable (redirect from Observable quantities)
In physics, an observable is a physical property or physical quantity that can be measured. In classical mechanics, an observable is a real-valued "function"...
12 KB (1,404 words) - 19:03, 16 April 2025
Base unit of measurement (redirect from Fundamental quantity)
measurement adopted for a base quantity. A base quantity is one of a conventionally chosen subset of physical quantities, where no quantity in the subset can be...
10 KB (1,208 words) - 20:27, 9 March 2025
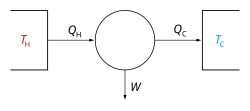
Energy (redirect from Physical energy)
body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation...
59 KB (7,390 words) - 03:32, 3 May 2025
Dimensionless quantities, or quantities of dimension one, are quantities implicitly defined in a manner that prevents their aggregation into units of measurement...
22 KB (2,254 words) - 01:06, 12 April 2025
axis) Spectrogram of dolphin vocalizations In the physical sciences, the spectrum of a physical quantity (such as energy) may be called continuous if it...
22 KB (2,734 words) - 03:36, 24 January 2025
List of common physics notations (redirect from List of physical symbols)
This is a list of common physical constants and variables, and their notations. Note that bold text indicates that the quantity is a vector. List of letters...
20 KB (82 words) - 18:53, 22 February 2025
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. It...
104 KB (13,012 words) - 12:29, 2 May 2025
"intensity" of a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. The fundamental...
28 KB (3,471 words) - 02:36, 17 April 2025
Field (physics) (redirect from Physical field)
In science, a field is a physical quantity, represented by a scalar, vector, or tensor, that has a value for each point in space and time. An example...
36 KB (4,401 words) - 21:49, 15 April 2025
processing, signals are analog and digital representations of analog physical quantities. In information theory, a signal is a codified message, that is,...
30 KB (3,517 words) - 19:45, 14 April 2025