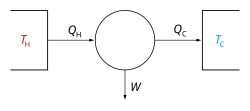
the Carnot engine and the 3-level maser. Quantum refrigerators share the structure of quantum heat engines with the purpose of pumping heat from a cold...
36 KB (5,134 words) - 19:11, 25 May 2025
heat engines include the thermal power station, internal combustion engine, firearms, refrigerators and heat pumps. Power stations are examples of heat engines...
28 KB (3,858 words) - 21:27, 4 March 2025
described by the laws of quantum mechanics. Quantum refrigerators are devices that consume power with the purpose to pump heat from a cold to a hot reservoir...
19 KB (2,456 words) - 21:41, 8 June 2025
cooling and then is absorbed into the second coolant; heat is needed to reset the two coolants to their initial states. Absorption refrigerators are commonly...
16 KB (2,003 words) - 09:15, 10 June 2025
Third law of thermodynamics (section Specific heat)
zero". New Scientist. Levy, A.; Alicki, R.; Kosloff, R. (2012). "Quantum refrigerators and the third law of thermodynamics". Phys. Rev. E. 85 (6): 061126...
28 KB (3,882 words) - 07:19, 1 June 2025
An ideal refrigerator or heat pump can be thought of as an ideal heat engine that is operating in a reverse Carnot cycle. Heat pump cycles and refrigeration...
19 KB (2,394 words) - 11:44, 25 May 2025
Thermal efficiency (category Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning)
such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the ratio...
22 KB (3,338 words) - 09:05, 15 January 2025
Cryocooler (redirect from Stirling refrigerator)
cryogenic refrigerators. Their input powers can be as high as 1 MW. In most cases cryocoolers use a cryogenic fluid as the working substance and employ moving...
15 KB (2,094 words) - 03:07, 25 May 2025
class of problems in quantum thermodynamics is periodically driven systems. Periodic quantum heat engines and power-driven refrigerators fall into this class...
40 KB (5,074 words) - 14:21, 24 May 2025
This timeline of heat engine technology describes how heat engines have been known since antiquity but have been made into increasingly useful devices...
20 KB (2,616 words) - 22:52, 14 April 2025
Second law of thermodynamics (redirect from Heat engine statement)
If we choose engines such that work done by the one cycle engine and the two cycle engine are same, then the efficiency of each heat engine is written as...
107 KB (15,472 words) - 01:32, 4 May 2025
1 newton. Engine An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy. Heat engines convert heat into work via...
279 KB (31,753 words) - 07:09, 28 January 2025
Refrigeration (redirect from Reverse Carnot engine)
alloy stretching and relaxing. Many Stirling cycle heat engines can be run backwards to act as a refrigerator, and therefore these engines have a niche use...
84 KB (10,620 words) - 19:29, 13 June 2025
operates, unlike all existing heat engines, as a fully coherent, closed system. Kurizki and coworkers developed an approach to quantum sensing that eludes the...
19 KB (1,807 words) - 01:25, 2 February 2025
Thermodynamics (redirect from Heat generation)
applied to heat. The initial application of thermodynamics to mechanical heat engines was quickly extended to the study of chemical compounds and chemical...
48 KB (5,843 words) - 01:18, 16 June 2025
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic...
92 KB (12,978 words) - 04:20, 26 May 2025
or Einstein refrigerator is an absorption refrigerator which has no moving parts, operates at constant pressure, and requires only a heat source to operate...
8 KB (760 words) - 02:23, 25 May 2025
and calling these heat engines is an acceptable use of the term." Mechanical efficiency of heat engines, p. 1 (2007) by James R. Senf: "Heat engines are...
66 KB (8,475 words) - 18:14, 23 May 2025
Entropy (redirect from Entropy and Expansion of Universe)
by a reversible heat engine was found to be the product of the Carnot efficiency (i.e., the efficiency of all reversible heat engines with the same pair...
111 KB (14,228 words) - 21:07, 24 May 2025
thermoacoustics. In contrast with other cryocoolers (e.g. Stirling cryocooler and GM-refrigerators), this cryocooler can be made without moving parts in the low temperature...
22 KB (2,830 words) - 17:10, 19 September 2024
Zero-point energy (redirect from Quantum vacuum zero point energy)
L. A.; Palao, J. P.; Alonso, D.; Adesso, G. (2014). "Quantum-enhanced absorption refrigerators". Scientific Reports. 4 (3949): 3949. arXiv:1308.4174...
206 KB (26,528 words) - 19:35, 4 June 2025
Carnot cycle (redirect from Engine cycle)
steady-state heat engines" (PDF). Physical Review E. 102 (4). However, fluctuations [in reservoir temperature] make impractical such engines. Sources Carnot...
25 KB (3,234 words) - 11:10, 19 May 2025
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature...
21 KB (2,500 words) - 00:24, 16 June 2025
to solar power. These refrigerators are increasingly being used to store vaccines in remote areas. Solar-powered refrigerators and other solar appliances...
7 KB (772 words) - 01:51, 5 September 2024
efficiency of heat engines only, whereas what was called the third law dealt with entropy increases. Gradually, this resolved itself and a zeroth law was...
20 KB (2,893 words) - 08:03, 9 May 2025
Thermodynamic cycle (redirect from Heat cycle)
of heat engine they seek to model. The most common cycles used to model internal combustion engines are the Otto cycle, which models gasoline engines, and...
19 KB (2,956 words) - 02:05, 11 April 2025
Maxwell's demon (category Philosophy of thermal and statistical physics)
decreases in A and increases in B, contrary to the second law of thermodynamics. A heat engine operating between the thermal reservoirs A and B could extract...
39 KB (4,675 words) - 02:54, 25 May 2025
leading, inter alia, to fundamental limits on the efficiency of heat engines and refrigerators. The thermodynamic characterisation of systems in equilibrium...
34 KB (3,683 words) - 09:08, 9 June 2025
Algorithmic cooling (category Quantum information science)
Leonard J.; Vazirani, Umesh V. (1999-01-01). "Molecular scale heat engines and scalable quantum computation". Proceedings of the thirty-first annual ACM symposium...
45 KB (7,131 words) - 08:33, 3 April 2025
Sensible heat is heat exchanged by a body or thermodynamic system in which the exchange of heat changes the temperature of the body or system, and some macroscopic...
4 KB (530 words) - 11:23, 15 August 2024