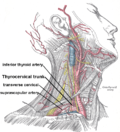
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles...
26 KB (2,953 words) - 17:39, 24 July 2025
The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve and additionally receives...
7 KB (875 words) - 01:36, 25 May 2025
Pharyngeal nerve Superior laryngeal nerve Aortic nerve Superior cervical cardiac branches of vagus nerve Inferior cervical cardiac branch Recurrent laryngeal nerve...
31 KB (3,601 words) - 09:11, 16 June 2025
Larynx (redirect from Laryngeal diseases)
to the recurrent laryngeal nerve would cause this condition. It is also worth noting that all muscles are innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch...
36 KB (4,197 words) - 18:01, 23 July 2025
Spasmodic dysphonia (redirect from Laryngeal dystonia)
and laryngeal nerve crush. Recurrent laryngeal nerve resection involves removing a section of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Recurrent laryngeal nerve avulsion...
47 KB (5,013 words) - 01:58, 1 August 2025
plexus, the recurrent laryngeal nerve, the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve, or a combination of these (the recurrent laryngeal nerve being the...
10 KB (1,064 words) - 04:18, 15 July 2025
paresis, also known as recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis or vocal fold paralysis, is an injury to one or both recurrent laryngeal nerves (RLNs), which...
37 KB (4,230 words) - 16:30, 15 July 2025
Ortner's syndrome is a rare cardiovocal syndrome and involves recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy from cardiovascular disease. It was first described by Norbert...
12 KB (1,252 words) - 22:08, 24 June 2025
Inferior thyroid artery (redirect from Inferior laryngeal artery)
laryngeal artery The inferior laryngeal artery - accompanied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve - passes superior-ward upon the trachea deep to the inferior pharyngeal...
6 KB (707 words) - 14:24, 17 July 2025
Parasympathetic nervous system (redirect from Parasympathetic nerve)
branches. The largest branch is the recurrent laryngeal nerve. From the left vagus nerve the recurrent laryngeal nerve hooks around the aorta to travel back...
31 KB (3,871 words) - 01:13, 16 December 2024
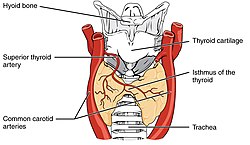
Thyroid (section Blood, lymph and nerve supply)
receives parasympathetic nerve supply from the superior laryngeal nerve and the recurrent laryngeal nerve. There are many variants in the size and shape of...
74 KB (8,009 words) - 20:44, 18 July 2025
nerve, then branches off into the recurrent laryngeal nerve which passes back up the neck to the larynx. Thus, these nerve cells have a length of nearly 5 m...
124 KB (12,140 words) - 21:46, 28 July 2025
jugular vein and vagus nerve. At the lower part of the neck, on the right side of the body, the right recurrent laryngeal nerve crosses obliquely behind...
16 KB (1,958 words) - 04:13, 7 April 2025
Cranial nerves (redirect from Cerebral nerve)
of its branches, the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Damage to this nerve may result in difficulties swallowing. The accessory nerve (XI) supplies the sternocleidomastoid...
42 KB (4,693 words) - 18:54, 1 December 2024
arytenoid cartilage of the same side. It is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Each acts to open the vocal folds by pulling the vocal fold of...
8 KB (872 words) - 13:38, 18 July 2025
in more than 20% of patients. Laryngeal nerve injury in about 1% of patients, in particular the recurrent laryngeal nerve: Unilateral damage results in...
9 KB (1,036 words) - 20:18, 16 June 2025
identifying the nerve or utilizing intraoperative neuroimaging during surgery, when trying to prevent injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid...
65 KB (7,358 words) - 17:35, 16 July 2025
colli muscle and the first thoracic vertebra (T1). The right recurrent laryngeal nerve winds around the lower and back part of the vessel. The first...
21 KB (2,354 words) - 13:51, 23 May 2025
and potential removal of carcinoma. Its risks are injury of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, hypoparathyroidism (due to removal of the parathyroid glands)...
64 KB (6,540 words) - 16:30, 19 July 2025
Pharynx (redirect from Laryngeal part of the pharynx)
epithelium. It is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus and by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The vascular supply to the laryngopharynx includes the superior...
19 KB (2,075 words) - 10:44, 27 July 2025
neck situated lateral to the trachea and esophagus alongside the recurrent laryngeal nerve. They drain to the deep cervical lymph nodes. "paratracheal lymph...
1 KB (88 words) - 12:05, 18 July 2025
the brachiocephalic vein, subclavian artery, phrenic nerve, recurrent laryngeal nerve, vagus nerve, or, characteristically, compression of a sympathetic...
16 KB (1,729 words) - 06:50, 19 July 2025
identifying the nerve or utilizing intraoperative neuroimaging during surgery, when trying to prevent injury to recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid...
43 KB (4,953 words) - 18:48, 16 July 2025
recurrent laryngeal nerve. Continuous electromyography of the arytenoid muscle can provide confidence to surgeons that the recurrent laryngeal nerve is...
4 KB (293 words) - 21:24, 16 July 2025
innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X) via its external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve and its recurrent laryngeal nerve, and not through the pharyngeal...
5 KB (455 words) - 12:52, 18 July 2025
cartilage of the same side posteriorly. It is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. It acts to close the rima glottidis, thus closing the airway...
3 KB (334 words) - 03:18, 18 July 2025
lie the recurrent laryngeal nerve as well as the internal laryngeal nerve, a branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. The internal laryngeal nerve supplies...
4 KB (449 words) - 14:25, 18 July 2025
into the left and right main bronchi. The left recurrent laryngeal nerve branching off the left vagus nerve and hooking under the ligamentum arteriosum between...
17 KB (1,415 words) - 21:25, 23 May 2025
Esophageal plexus Ethmoidal nerves External laryngeal nerve External nasal nerve Facial nerve Femoral nerve Frontal nerve Gastric plexuses Geniculate ganglion...
8 KB (845 words) - 00:22, 2 May 2024
Cough reflex (redirect from Arnold's nerve reflex)
equalise the pressure. The glottis closes (muscles innervated by recurrent laryngeal nerve) and the vocal cords contract to shut the larynx. The abdominal...
6 KB (796 words) - 19:43, 17 July 2025