sciences, a vector quantity (also known as a vector physical quantity, physical vector, or simply vector) is a vector-valued physical quantity. It is typically...
6 KB (669 words) - 17:07, 20 November 2024
and physics, vector is a term that refers to quantities that cannot be expressed by a single number (a scalar), or to elements of some vector spaces. Historically...
10 KB (2,684 words) - 04:26, 1 June 2025
quantity is a scalar, vector, matrix or tensor), and whether the quantity is conserved. List of photometric quantities List of radiometric quantities...
31 KB (192 words) - 13:44, 29 July 2025
or u → {\displaystyle {\vec {u}}} . Scalar and vector quantities are the simplest tensor quantities, which are tensors that can be used to describe more...
18 KB (1,617 words) - 02:20, 1 July 2025
Dimensional analysis (redirect from Quantity equation)
Vector quantities may be added to each other, yielding a new vector quantity, and a vector quantity may be added to a suitable affine quantity (a vector space...
96 KB (11,981 words) - 14:50, 3 July 2025
direction. Euclidean vectors can be added and scaled to form a vector space. A vector quantity is a vector-valued physical quantity, including units of...
61 KB (9,116 words) - 12:01, 7 May 2025
Flux (redirect from Flux of a vector field)
applied mathematics and vector calculus which has many applications in physics. For transport phenomena, flux is a vector quantity, describing the magnitude...
28 KB (3,869 words) - 23:13, 15 May 2025
Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction Vector may also refer to: Vector, a one-dimensional array data structure Distance-vector routing...
6 KB (741 words) - 06:41, 19 July 2025
Momentum (redirect from Momentum vector)
object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If m is an object's mass and v is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the...
73 KB (9,783 words) - 08:34, 12 July 2025
Velocity (redirect from Velocity vector)
mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning that both magnitude and direction are needed to define it...
25 KB (3,426 words) - 08:31, 29 July 2025
Scalar (physics) (redirect from Scalar quantity)
of physical quantities, such as speed is to velocity. Scalars do not represent a direction. Scalars are unaffected by changes to a vector space basis...
8 KB (1,090 words) - 06:00, 10 March 2025
In classical electromagnetism, magnetic vector potential (often denoted A) is the vector quantity defined so that its curl is equal to the magnetic field...
28 KB (4,378 words) - 22:37, 31 May 2025
Laplace operator (redirect from Vector Laplacian)
scalar field and returns a scalar quantity, the vector Laplacian applies to a vector field, returning a vector quantity. When computed in orthonormal Cartesian...
31 KB (4,697 words) - 22:49, 2 August 2025
Electric potential (redirect from Vector potential difference)
electrostatic field is a vector quantity expressed as the gradient of the electrostatic potential, which is a scalar quantity denoted by V or occasionally...
20 KB (2,250 words) - 04:44, 6 June 2025
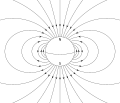
Dipole (section Vector form)
electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points...
27 KB (3,900 words) - 20:03, 28 July 2025
textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar quantity, the magnitude of the gravitational...
31 KB (3,977 words) - 00:23, 20 May 2025
In contrast to the tangent, which is a vector quantity, the curvature at a point is typically a scalar quantity, that is, it is expressed by a single real...
45 KB (6,608 words) - 15:12, 6 July 2025
Pseudovector (redirect from Axial vector)
physics and mathematics, a pseudovector (or axial vector) is a quantity that transforms like a vector under continuous rigid transformations such as rotations...
33 KB (4,332 words) - 14:46, 1 August 2025
generally, elements of any field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that...
87 KB (11,491 words) - 23:41, 28 July 2025
Force (redirect from Force vector)
magnitude and direction of a force are both important, force is a vector quantity (force vector). The SI unit of force is the newton (N), and force is often...
96 KB (11,782 words) - 05:48, 19 July 2025
Gravity of Earth (redirect from Gravity vector)
Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). It is a vector quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude...
32 KB (3,826 words) - 10:21, 3 June 2025
{\displaystyle {\textbf {F}}=m{\textbf {a}}\,} (the bold font indicates a vector quantity, i.e. one with both magnitude and direction). If a = 0 {\displaystyle...
12 KB (1,743 words) - 22:49, 1 April 2025
metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the...
7 KB (836 words) - 00:36, 9 July 2025
=\mathbf {0} } where y is called the conserved (vector) quantity, ∇y is its gradient, 0 is the zero vector, and A(y) is called the Jacobian of the current...
21 KB (2,509 words) - 04:57, 26 July 2025
metre per second is the unit of both speed (a scalar quantity) and velocity (a vector quantity, which has direction and magnitude) in the International...
8 KB (780 words) - 22:07, 27 July 2025
In physics, the Poynting vector (or Umov–Poynting vector) represents the directional energy flux (the energy transfer per unit area, per unit time) or...
34 KB (4,642 words) - 18:24, 30 July 2025
denote the net magnetization vector. Although in physics and mathematics the notation to represent a physical quantity can be arbitrary, it is generally...
2 KB (179 words) - 23:05, 13 January 2024
Vector calculus or vector analysis is a branch of mathematics concerned with the differentiation and integration of vector fields, primarily in three-dimensional...
22 KB (2,138 words) - 01:58, 28 July 2025
Impulse (physics) (category Vector physical quantities)
=\mathbf {p} _{2}-\mathbf {p} _{1}.} Momentum is a vector quantity, so impulse is also a vector quantity: ∑ F × Δ t = Δ p . {\displaystyle \sum \mathbf {F}...
7 KB (868 words) - 15:02, 3 July 2025
In vector calculus and physics, a vector field is an assignment of a vector to each point in a space, most commonly Euclidean space R n {\displaystyle...
29 KB (4,105 words) - 02:10, 28 July 2025