Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle...
62 KB (7,395 words) - 18:51, 7 June 2025
fiber. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus and stomach. Smooth muscle has no myofibrils...
37 KB (4,497 words) - 01:20, 7 June 2025
disease called tetanus) is a sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a very high...
8 KB (725 words) - 20:01, 8 June 2023
Sliding filament theory (redirect from Sliding filament theory of muscle contraction)
The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement. According...
20 KB (2,662 words) - 03:05, 10 July 2025
the basic functional, contractile units of the muscle fiber necessary for muscle contraction. Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats...
119 KB (13,832 words) - 14:57, 27 June 2025
to or interference with the different stages of muscle contraction. There are two main causes of muscle fatigue: the limitations of a nerve’s ability to...
21 KB (2,521 words) - 09:48, 18 June 2025
Uterine contractions are muscle contractions of the uterine smooth muscle that can occur at various intensities in both the non-pregnant and pregnant...
15 KB (1,720 words) - 19:57, 10 June 2025
Fasciculation (redirect from Muscle twitch)
A fasciculation, or muscle twitch, is a spontaneous, involuntary muscle contraction and relaxation, involving fine muscle fibers. They are common, with...
10 KB (908 words) - 03:42, 24 April 2025
that cause involuntary muscle contractions, mimicking the effects of voluntary exercise. In addition to directly stimulating muscle fibers, recent research...
27 KB (3,027 words) - 20:42, 29 May 2025
Spasm (redirect from Muscle spasm)
sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder. A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by...
5 KB (410 words) - 18:39, 16 July 2025
muscles, but nonetheless arise through activation of the central nervous system, albeit not engaging cortical structures until after the contraction has...
23 KB (2,576 words) - 17:31, 17 July 2025
Tremor (redirect from Muscle quivering)
A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic muscle contraction and relaxation involving oscillations or twitching movements of one or more body parts...
37 KB (4,302 words) - 20:23, 1 July 2025
multiunit smooth muscle. Smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle in terms of structure, function, regulation of contraction, and excitation-contraction...
37 KB (4,737 words) - 17:18, 22 January 2025
twelfth rib. Contraction of one of the pair of muscles causes lateral flexion of the lumbar spine, elevation of the pelvis, or both. Contraction of both causes...
8 KB (1,045 words) - 13:34, 10 September 2024
isotonic contraction, tension remains the same, whilst the muscle's length changes. Isotonic contractions differ from isokinetic contractions in that in...
5 KB (560 words) - 21:11, 9 February 2023
Myofilament (redirect from Muscle filament)
and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act together in muscle contraction, and in order of size are a thick one of mostly myosin, a thin one...
13 KB (1,711 words) - 04:44, 25 March 2025
Muscular system (redirect from Muscle system)
of small muscle fibers. Each fiber comprises many tiny strands called fibrils, impulses from nerve cells control the contraction of each muscle fiber. Skeletal...
15 KB (1,735 words) - 13:06, 29 May 2025
Myofibril (redirect from Muscle fibril)
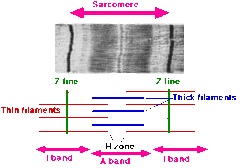
along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments...
10 KB (1,235 words) - 02:00, 14 March 2025
do work. Nerves control the contraction of muscles by determining the number, sequence, and force of muscular contraction. When a nerve experiences synaptic...
21 KB (2,577 words) - 11:26, 24 May 2025
slide past each other in a process called excitation-contraction coupling. Diseases of the heart muscle known as cardiomyopathies are of major importance...
42 KB (5,073 words) - 03:27, 16 June 2025
Tension headache (redirect from Muscle contraction headaches)
radiates from the lower back of the head, the neck, the eyes, or other muscle groups in the body typically affecting both sides of the head. Tension-type...
33 KB (3,325 words) - 15:02, 9 March 2025
which was based on careful experiments involving tetanized muscle contraction where various muscle loads and associated velocities were measured. They were...
10 KB (1,761 words) - 00:55, 20 June 2025
Eccentric training (section Muscle injury)
eccentric contraction is the motion of an active muscle while it is lengthening under load. Eccentric training is repetitively doing eccentric muscle contractions...
34 KB (4,342 words) - 15:10, 15 July 2025
arrector pili muscles, also known as hair erector muscles, are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the...
7 KB (671 words) - 08:09, 24 May 2025
Sarcomere (section Contraction)
access to the actin cross-bridge binding sites, permitting muscle contraction. Muscle contraction ends when calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic...
13 KB (1,565 words) - 13:56, 2 July 2025
Hypotonia (redirect from Poor muscle tone)
the muscle relaxes and returns to its normal resting state." "...The child with low tone has muscles that are slow to initiate a muscle contraction, contract...
22 KB (2,500 words) - 13:10, 25 May 2025
the production of an electrical impulse (action potential) to the contraction of muscles in the heart. This process is of vital importance as it allows for...
13 KB (1,426 words) - 06:43, 2 June 2025
during rhythmic contraction actually increases blood flow through the muscle, and may be responsible for a portion of the increase in muscle blood flow immediately...
6 KB (644 words) - 22:02, 23 May 2025
muscle fibres. In 1952, he was joined by a German physiologist Rolf Niedergerke. Together they discovered in 1954 the mechanism of muscle contraction...
25 KB (2,742 words) - 13:29, 4 June 2025
onset of exercise phosphocreatine is broken down to provide ATP for muscle contraction. ATP hydrolysis results in products of ADP and inorganic phosphate...
6 KB (723 words) - 21:38, 6 October 2023