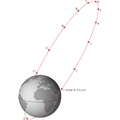
The areosynchronous orbits (ASO) are the synchronous orbits for artificial satellites around the planet Mars. They are the martian equivalent of the geosynchronous...
3 KB (374 words) - 15:25, 26 October 2024
An areostationary orbit, areosynchronous equatorial orbit (AEO), or Mars geostationary orbit is a circular areosynchronous orbit (ASO) approximately...
8 KB (802 words) - 22:37, 12 April 2025
keeps the perigee shift small. Areosynchronous orbit (ASO): A synchronous orbit around the planet Mars with an orbital period equal in length to Mars'...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
orbit at the 22,300-mile altitude. An areostationary orbit or areosynchronous equatorial orbit (abbreviated AEO) is a circular areosynchronous orbit...
3 KB (417 words) - 02:17, 5 May 2025
for synchronous orbits around Mars are areostationary and areosynchronous orbits. [citation needed] For a stationary synchronous orbit: R s y n = G ( m...
5 KB (574 words) - 08:55, 8 May 2025
Earth's orbit List of orbits Orbital mechanics Celestial sphere Heliocentric orbit Areosynchronous orbit Areostationary orbit Escape velocity Satellite...
17 KB (1,997 words) - 15:59, 21 April 2025
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35,786 km (22,236 mi) in altitude...
49 KB (4,893 words) - 06:24, 20 May 2025
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi), or 8.317 light-minutes, in a counterclockwise direction as viewed...
17 KB (1,860 words) - 12:44, 24 March 2025
trajectory In orbital mechanics, a Lissajous orbit (pronounced [li.sa.ʒu]), named after Jules Antoine Lissajous, is a quasi-periodic orbital trajectory that...
8 KB (766 words) - 02:34, 13 November 2024
Halo orbit A halo orbit is a periodic, non-planar orbit associated with one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics...
11 KB (1,104 words) - 03:04, 27 February 2025
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours...
33 KB (3,231 words) - 03:30, 12 January 2025
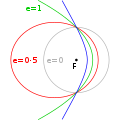
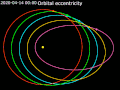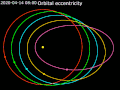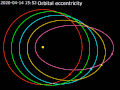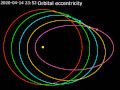
value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is...
27 KB (2,870 words) - 10:05, 8 May 2025
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy...
17 KB (2,080 words) - 13:46, 24 March 2025
The Moon orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the fixed stars in about 27.3 days (a tropical...
38 KB (4,679 words) - 20:03, 21 May 2025
A near-equatorial orbit is an orbit that lies close to the equatorial plane of the primary body orbited. Such an orbit has an inclination near 0°. On Earth...
5 KB (689 words) - 18:00, 15 March 2025
A Molniya orbit (Russian: Молния, IPA: [ˈmolnʲɪjə] , "Lightning") is a type of satellite orbit designed to provide communications and remote sensing coverage...
28 KB (3,117 words) - 21:22, 22 December 2024
A parking orbit is a temporary orbit used during the launch of a spacecraft. A launch vehicle follows a trajectory to the parking orbit, then coasts for...
8 KB (888 words) - 03:13, 4 February 2025
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given...
14 KB (1,657 words) - 19:06, 16 March 2025
subsynchronous orbit is an orbit of a satellite that is nearer the planet than it would be if it were in synchronous orbit, i.e. the orbital period is less...
2 KB (153 words) - 10:44, 31 July 2023
In astrodynamics, an orbit equation defines the path of orbiting body m 2 {\displaystyle m_{2}\,\!} around central body m 1 {\displaystyle m_{1}\,\!}...
8 KB (1,317 words) - 19:17, 9 December 2024
Parabolic trajectory (redirect from Escape orbit)
mechanics a parabolic trajectory is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity equal to 1 and is an unbound orbit that is exactly on the border between elliptical...
7 KB (1,091 words) - 22:08, 14 October 2024
occupy an inclined orbit around Earth if the orbit exhibits an angle other than 0° to the equatorial plane. This angle is called the orbit's inclination. A...
3 KB (338 words) - 20:20, 12 June 2024
In stellar dynamics, a box orbit refers to a particular type of orbit that can be seen in triaxial systems, i.e. systems that do not possess a symmetry...
2 KB (179 words) - 08:42, 12 March 2023
the orbital speed of an astronomical body or object (e.g. planet, moon, artificial satellite, spacecraft, or star) is the speed at which it orbits around...
11 KB (1,411 words) - 23:02, 25 April 2025
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between 2,000...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024
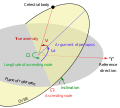
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star...
57 KB (8,123 words) - 06:52, 24 April 2025
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to rockets, satellites, and other spacecraft. The motion of...
40 KB (5,763 words) - 07:34, 23 May 2025
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital...
11 KB (1,470 words) - 02:33, 8 May 2025
elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity...
19 KB (2,744 words) - 16:48, 20 March 2025
astronautics, the Hohmann transfer orbit (/ˈhoʊmən/) is an orbital maneuver used to transfer a spacecraft between two orbits of different altitudes around...
27 KB (3,642 words) - 22:55, 25 April 2025