In mathematical logic, a theory is complete if it is consistent and for every closed formula in the theory's language, either that formula or its negation...
3 KB (396 words) - 18:19, 10 January 2025
In model theory, a first-order theory is called model complete if every embedding of its models is an elementary embedding. Equivalently, every first-order...
4 KB (557 words) - 00:47, 21 September 2023
In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules (such as a model of computation, a computer's instruction set, a programming language, or...
32 KB (3,448 words) - 22:13, 10 March 2025
satisfiable, such as ω-inconsistent theories. A complete consistent theory (or just a complete theory) is a consistent theory T {\displaystyle {\mathcal {T}}}...
13 KB (1,695 words) - 13:05, 5 May 2025
set T {\displaystyle T} . A complete theory is a theory that contains every sentence or its negation. The complete theory of all sentences satisfied by...
63 KB (9,065 words) - 10:26, 2 April 2025
modal logics, a logic is structurally complete if every admissible rule is derivable. A theory is model complete if and only if every embedding of its...
7 KB (771 words) - 18:19, 10 January 2025
In the mathematical area of order theory, completeness properties assert the existence of certain infima or suprema of a given partially ordered set (poset)...
13 KB (1,914 words) - 11:21, 27 January 2025
general theories in science and pre-scientific natural philosophy and natural history that have since been superseded by other scientific theories. Many...
26 KB (3,004 words) - 01:13, 8 May 2025
provability in first-order logic. The completeness theorem applies to any first-order theory: If T is such a theory, and φ is a sentence (in the same language)...
17 KB (2,330 words) - 17:38, 29 January 2025
Complete active space perturbation theory (CASPTn) is a multireference electron correlation method for computational investigation of molecular systems...
5 KB (664 words) - 02:39, 13 April 2025
In set theory, Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, named after mathematicians Ernst Zermelo and Abraham Fraenkel, is an axiomatic system that was proposed in...
46 KB (6,252 words) - 14:45, 16 April 2025
Uninterpreted function (redirect from Free theory)
constants and variables, to form terms. The theory of uninterpreted functions is also sometimes called the free theory, because it is freely generated, and thus...
4 KB (410 words) - 15:10, 21 September 2024
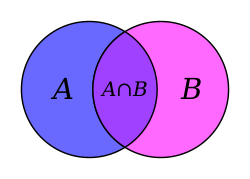
In set theory, the intersection of two sets A {\displaystyle A} and B , {\displaystyle B,} denoted by A ∩ B , {\displaystyle A\cap B,} is the set containing...
12 KB (1,732 words) - 23:16, 26 December 2023
In computational complexity theory, a problem is NP-complete when: It is a decision problem, meaning that for any input to the problem, the output is either...
30 KB (3,617 words) - 20:05, 16 January 2025
Proof theory is a major branch of mathematical logic and theoretical computer science within which proofs are treated as formal mathematical objects, facilitating...
20 KB (2,666 words) - 15:22, 15 March 2025
equivalent as the theory is categorical in κ. Therefore, the theory is complete as all models are equivalent. The assumption that the theory have no finite...
10 KB (1,157 words) - 04:00, 24 March 2025
Consistency (redirect from Consistent theory)
not complete. A consistency proof is a mathematical proof that a particular theory is consistent. The early development of mathematical proof theory was...
20 KB (2,931 words) - 16:30, 13 April 2025
Computability theory, also known as recursion theory, is a branch of mathematical logic, computer science, and the theory of computation that originated...
54 KB (6,425 words) - 20:53, 17 February 2025
Principle of locality (redirect from Local theory)
experiment, raised the possibility that quantum mechanics might not be a complete theory. They described two systems physically separated after interacting;...
23 KB (2,821 words) - 00:44, 3 May 2025
Axiom (section Deductive systems and completeness)
The propositions of field theory do not concern any one particular application; the mathematician now works in complete abstraction. There are many...
34 KB (4,918 words) - 17:20, 17 May 2025
Axiomatic system (redirect from Axiomatic theory)
is called complete with respect to a property if every formula with the property can be derived using the axioms. The more general term theory is at times...
13 KB (1,763 words) - 04:19, 17 May 2025
In set theory, the complement of a set A, often denoted by A c {\displaystyle A^{c}} (or A′), is the set of elements not in A. When all elements in the...
12 KB (1,515 words) - 07:59, 27 January 2025
the sentences of the theory are all true (by the completeness theorem, satisfiability is equivalent to consistency); be complete: for any statement, either...
36 KB (5,269 words) - 20:51, 27 December 2024
about limits. The notion of a completed infinity doesn't belong in mathematics." Development of mathematical set theory was motivated by several mathematicians...
54 KB (6,575 words) - 12:01, 1 May 2025
In set theory, the union (denoted by ∪) of a collection of sets is the set of all elements in the collection. It is one of the fundamental operations through...
14 KB (1,989 words) - 08:46, 6 May 2025
are many "minimal complete set of set-theory operators" that can generate any other set relations. The more popular "Minimal complete operator sets" are...
16 KB (1,957 words) - 15:12, 13 January 2025
In physics, a hidden-variable theory is a deterministic model which seeks to explain the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics by introducing additional...
32 KB (4,032 words) - 11:56, 3 May 2025
Mathematical logic (section Set theory and paradoxes)
Major subareas include model theory, proof theory, set theory, and recursion theory (also known as computability theory). Research in mathematical logic...
69 KB (8,370 words) - 19:50, 19 April 2025
classes of models in various cardinalities. More precisely, for any complete theory T in a language we write I(T, κ) for the number of models of T (up...
7 KB (1,132 words) - 20:43, 19 March 2024
Formal language (redirect from Formal language theory)
are associated with meanings or semantics. In computational complexity theory, decision problems are typically defined as formal languages, and complexity...
27 KB (3,163 words) - 19:01, 18 May 2025