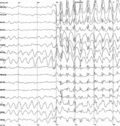
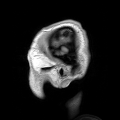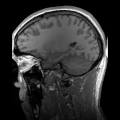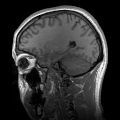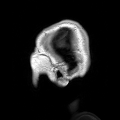
Primary and secondary brain injuries identify the processes involved, while focal and diffuse brain injury describe the severity and localization.[citation...
47 KB (5,145 words) - 17:54, 10 June 2025
Focal and diffuse brain injury are ways to classify brain injury: focal injury occurs in a specific location, while diffuse injury occurs over a more widespread...
7 KB (774 words) - 18:10, 10 June 2025
head injury occurs when an object pierces the skull and breaches the dura mater. Brain injuries may be diffuse, occurring over a wide area, or focal, located...
43 KB (5,232 words) - 03:02, 26 May 2025
Diffuse axonal injury (DAI) is a brain injury in which scattered lesions occur over a widespread area in white matter tracts as well as grey matter. DAI...
29 KB (3,091 words) - 18:21, 10 June 2025
cause of most focal injuries, and movement of the brain within the skull, termed noncontact or inertial loading, usually causes diffuse injuries. The violent...
149 KB (16,263 words) - 17:37, 10 June 2025
state marker for schizophrenia. Focal and diffuse brain injury Thiruppathy, S. P.; Muthukumar, N. (2004). "Mild head injury: Revisited". Acta Neurochirurgica...
8 KB (906 words) - 09:51, 8 December 2024
Coup and contrecoup injuries are considered focal brain injuries – those that occur in a particular spot in the brain – as opposed to diffuse injuries, which...
12 KB (1,343 words) - 10:30, 11 March 2025
Cerebral hypoxia (redirect from Anoxic brain injury)
in order of increasing severity: diffuse cerebral hypoxia (DCH), focal cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and global cerebral ischemia. Prolonged...
31 KB (3,541 words) - 00:04, 19 February 2025
Concussion (redirect from Mild traumatic brain injury)
Concussion involves diffuse (as opposed to focal) brain injury, meaning that the dysfunction occurs over a widespread area of the brain rather than in a...
118 KB (12,235 words) - 18:07, 10 June 2025
Bruising to the brain may occur. Bruising may cause widespread damage to the nerve tracts that can lead to a condition of diffuse axonal injury. A fractured...
170 KB (18,988 words) - 02:37, 3 June 2025
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (redirect from Chronic traumatic brain injury associated with boxing)
hydrocephalus, attenuation of the corpus callosum, diffuse axonal injury, neurofibrillary tangles, and damage to the cerebellum are implicated in the syndrome...
69 KB (7,243 words) - 15:51, 8 June 2025
Dementia with Lewy bodies (redirect from Diffuse Lewy body disease)
clarified the distinction by stating that diffuse Lewy body dementia is more commonly called diffuse Lewy body disease and refers to the underlying disease process...
135 KB (14,436 words) - 12:01, 25 May 2025
focal, multifocal, or diffuse. 4 infants had multifocal hepatic injuries (4 to 20 injuries) and 4 infants had diffuse injuries (more than 20 injuries)...
33 KB (4,376 words) - 15:55, 23 May 2025
causes structural damage to the brain, such as a sharp blow to the head, a diffuse axonal injury, or childhood brain damage (e.g., shaken baby syndrome)...
45 KB (5,317 words) - 04:34, 25 May 2025
Electroencephalography (redirect from Brain activity)
after cardiac arrest, and brain death. EEG used to be a first-line method of diagnosis for tumors, stroke, and other focal brain disorders, but this use...
133 KB (15,926 words) - 19:52, 3 June 2025
areas. The injury is produced by an acute focal disturbance in an area of the brain, from traumatic brain injury or stroke, for example. Regarding dysfunctional...
7 KB (761 words) - 17:26, 1 June 2024
and focal axonal spheroids leading to demyelination. Spheroids in HDLS resemble to some extent those produced by shear stress in a closed head injury...
18 KB (2,136 words) - 12:39, 16 May 2025
Psychoorganic syndrome (category Mental disorders due to brain damage)
stems from a defect in brain tissue, usually atrophy from another neurological disorder. "In pathological findings, focal or diffuse signs of atrophy without...
10 KB (1,198 words) - 22:41, 10 August 2024
A brain tumor (sometimes referred to as brain cancer) occurs when a group of cells within the brain turn cancerous and grow out of control, creating a...
86 KB (9,324 words) - 14:25, 1 June 2025
Congenital hyperinsulinism (redirect from Hyperinsulinism, focal)
permanent brain damage, and even death. For those with focal HI, there is the potential for a cure with surgery. For those with diffuse HI, diazoxide...
78 KB (7,819 words) - 16:42, 28 March 2025
Intracranial hemorrhage (redirect from Brain hemmorage)
aneurysm is located more proximally, it will produce diffuse SAH pattern. CTA or MRA would produce focal outpouching or increase in diameter of the vessel...
34 KB (3,886 words) - 08:15, 25 May 2025
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (section Signs and symptoms)
of one side of the body). SAH is a frequent occurrence in traumatic brain injury and carries a poor prognosis if it is associated with deterioration in...
81 KB (9,274 words) - 17:56, 10 June 2025
primarily of diffuse axonal injury (widespread damage to white matter) without any focal damage (damage to specific areas). Sometimes, injury of the brainstem...
57 KB (7,467 words) - 09:12, 3 March 2024
Vascular dementia (category Mental disorders due to brain damage)
Restricted blood flow due to strokes reduces oxygen and glucose delivery to the brain, causing cell injury and neurological deficits in the affected region....
24 KB (2,465 words) - 08:58, 25 May 2025
Neuroimaging (redirect from Brain scan)
disease and Pick's disease) where the early damage is too diffuse and makes too little difference in brain volume and gross structure to change CT and standard...
42 KB (5,150 words) - 21:39, 29 May 2025
and other substances in and on the artery walls) microembolism, causing transient focal ischaemia, a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain or...
6 KB (541 words) - 20:14, 1 December 2024
Catatonia (section Signs and symptoms)
HIV and herpes simplex virus (HSV). The research is limited, but some evidence suggests that people can develop catatonia after traumatic brain injury without...
72 KB (7,751 words) - 23:50, 11 June 2025
both translational and rotational acceleration produce focal lesions but that only rotational acceleration produced diffuse axonal injury. When damage is...
27 KB (3,149 words) - 08:16, 24 May 2025
50 μm) injection results in distal, diffuse embolism [6]. However, the quality of MCAO – and thus the volume of brain infarcts – is very variable, a fact...
17 KB (1,941 words) - 15:59, 22 April 2024
Right hemisphere brain damage (RHD) is the result of injury to the right cerebral hemisphere. The right hemisphere of the brain coordinates tasks for functional...
38 KB (5,077 words) - 08:15, 7 January 2024