In probability theory and computer science, a log probability is simply a logarithm of a probability. The use of log probabilities means representing...
7 KB (938 words) - 06:13, 19 November 2024
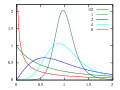
In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normally...
90 KB (12,551 words) - 04:27, 2 May 2025
terms of log probability, two events are independent if and only if the log probability of the joint event is the sum of the log probability of the individual...
28 KB (4,642 words) - 08:40, 3 January 2025
Likelihood function (redirect from Log-likelihood)
and the log-likelihood is the "weight of evidence". Interpreting negative log-probability as information content or surprisal, the support (log-likelihood)...
64 KB (8,546 words) - 13:13, 3 March 2025
A prior probability distribution of an uncertain quantity, simply called the prior, is its assumed probability distribution before some evidence is taken...
43 KB (6,753 words) - 20:06, 15 April 2025
Entropy (information theory) (redirect from Entropy of a probability distribution)
} is the logarithm, which gives 0 surprise when the probability of the event is 1. In fact, log is the only function that satisfies а specific set of...
72 KB (10,210 words) - 18:29, 22 April 2025
takes value 1 with probability p and value 0 with probability q = 1 − p. The Rademacher distribution, which takes value 1 with probability 1/2 and value −1...
22 KB (2,620 words) - 07:59, 2 May 2025
In probability and statistics, the log-logistic distribution (known as the Fisk distribution in economics) is a continuous probability distribution for...
19 KB (2,053 words) - 09:15, 4 October 2024
Exponential distribution (redirect from Exponential probability distribution)
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution or negative exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the distance...
43 KB (6,647 words) - 17:34, 15 April 2025
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible outcomes...
48 KB (6,687 words) - 05:52, 4 May 2025
logarithmic scale, as in log probability. Similar to multiplication operations in linear-scale becoming simple additions in log-scale, an addition operation...
7 KB (1,152 words) - 17:21, 23 June 2024
Cross-entropy (redirect from Log loss)
Q} be probability density functions of p {\displaystyle p} and q {\displaystyle q} with respect to r {\displaystyle r} . Then − ∫ X P ( x ) log Q (...
19 KB (3,264 words) - 23:00, 21 April 2025
x)=1-p(x)} is the probability of x {\displaystyle x} not occurring. Then we have the following definition of the log-odds: log-odds ( x ) = log ( p ( x )...
27 KB (4,443 words) - 19:23, 5 May 2025
Geometric distribution (category Infinitely divisible probability distributions)
In probability theory and statistics, the geometric distribution is either one of two discrete probability distributions: The probability distribution...
35 KB (5,094 words) - 10:50, 5 May 2025
such as decibels (see Decibel § Addition), log probability, or log-likelihoods. The operations on the log semiring can be defined extrinsically by mapping...
6 KB (1,025 words) - 22:15, 28 March 2023
Exponential family (redirect from Log-partition function)
)+B(x)\right].} In terms of log probability, log ( f X ( x | θ ) ) = η ( θ ) ⋅ T ( x ) − A ( θ ) + B ( x ) . {\displaystyle \log(f_{X}{\left(x\ {\big |}\...
86 KB (11,203 words) - 22:36, 20 March 2025
probability distribution Q is different from a true probability distribution P. Mathematically, it is defined as D KL ( P ∥ Q ) = ∑ x ∈ X P ( x ) log...
77 KB (13,054 words) - 15:51, 28 April 2025
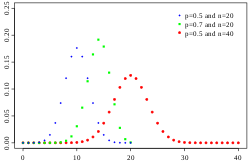
Binomial distribution (redirect from Binomial probability)
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes...
53 KB (7,554 words) - 05:20, 9 January 2025
In probability theory, a log-t distribution or log-Student t distribution is a probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is distributed...
8 KB (825 words) - 03:01, 3 December 2023
Logistic regression (section As a "log-linear" model)
function that converts log-odds to probability is the logistic function, hence the name. The unit of measurement for the log-odds scale is called a logit...
127 KB (20,645 words) - 05:20, 16 April 2025
In probability theory and statistics, the log-Laplace distribution is the probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm has a Laplace distribution...
2 KB (230 words) - 20:34, 15 April 2024
Odds ratio (redirect from Log odds ratio)
ratio (OR) and sample log odds ratio (LOR): The following joint probability distributions contain the population cell probabilities, along with the corresponding...
49 KB (7,058 words) - 20:11, 12 March 2025
Poisson distribution (redirect from Poisson probability)
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution (/ˈpwɑːsɒn/) is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a...
81 KB (11,215 words) - 20:38, 26 April 2025
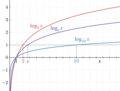
Logarithm (redirect from Log (mathematics))
formula: log b x = log 10 x log 10 b = log e x log e b . {\displaystyle \log _{b}x={\frac {\log _{10}x}{\log _{10}b}}={\frac {\log _{e}x}{\log _{e}b}}...
98 KB (11,674 words) - 16:13, 4 May 2025
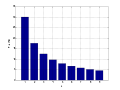
Benford's law (category Theory of probability distributions)
with probability P ( d ) = log 10 ( d + 1 ) − log 10 ( d ) = log 10 ( d + 1 d ) = log 10 ( 1 + 1 d ) . {\displaystyle P(d)=\log _{10}(d+1)-\log _{10}(d)=\log...
65 KB (7,418 words) - 01:12, 5 May 2025
determined by the events of highest probability. H 0 ( X ) {\displaystyle \mathrm {H} _{0}(X)} is log n {\displaystyle \log n} where n {\displaystyle n} is...
22 KB (3,526 words) - 01:18, 25 April 2025
distribution in log space (e.g. log-probability or log-density) instead. That is, work with h ( x ) = log g ( x ) {\displaystyle h\left(x\right)=\log g\left(x\right)}...
26 KB (4,455 words) - 08:48, 9 April 2025
Reciprocal distribution (redirect from Log-uniform distribution)
In probability and statistics, the reciprocal distribution, also known as the log-uniform distribution, is a continuous probability distribution. It is...
3 KB (358 words) - 03:51, 9 April 2025
Boltzmann machine (section Unit state probability)
distribution that the energy of a state is proportional to the negative log probability of that state) yields: Δ E i = − k B T ln ( p i=off ) − ( − k B T...
29 KB (3,676 words) - 20:14, 28 January 2025