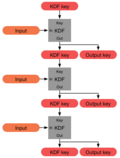
memory-hard function (MHF) is a function that costs a significant amount of memory to efficiently evaluate. It differs from a memory-bound function,...
7 KB (825 words) - 20:22, 12 May 2025
Argon2 (category Cryptographic hash functions)
Balloon Hashing: A Memory-Hard Function Providing Provable Protection Against Sequential Attacks RFC 9106 Argon2 Memory-Hard Function for Password Hashing...
14 KB (1,491 words) - 04:51, 31 March 2025
results or using lookup tables. Memory-bound functions and memory functions are related in that both involve extensive memory access, but a distinction exists...
9 KB (1,189 words) - 18:54, 5 August 2024
Besides his work in delta compression and the introduction of memory-hard functions, he is also known for developing the Tarsnap online backup service...
11 KB (1,154 words) - 04:54, 8 May 2025
Balloon hashing (category Key derivation functions)
Balloon hashing is a key derivation function presenting proven memory-hard password-hashing and modern design. It was created by Dan Boneh, Henry Corrigan-Gibbs...
3 KB (271 words) - 07:14, 28 May 2025
Daniel Dinu; Dmitry Khovratovich (26 December 2015). "Argon2: the memory-hard function for password hashing and other applications" (PDF). Alex Biryukov’s...
3 KB (209 words) - 01:43, 2 June 2025
2009). "Stronger Key Derivation via Sequential Memory-Hard Functions" (PDF). BSDCan'09 Presentation. Retrieved 19 May 2009. Key Derivation Functions...
13 KB (1,640 words) - 18:48, 30 April 2025
different from memory-hard functions in that the bottleneck is not in the number of memory access events, but in the amount of memory required. After...
14 KB (1,564 words) - 17:30, 8 March 2025
PBKDF2 (category Key derivation functions)
scrypt. As presented in "Stronger Key Derivation via Sequential Memory-Hard Functions". presented at BSDCan'09, May 2009. "New 25 GPU Monster Devours...
13 KB (1,337 words) - 12:18, 2 June 2025
Scrypt (category Cryptographic hash functions)
2017. Percival, Colin. "Stronger Key Derivation Via Sequential Memory-Hard Functions" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 April 2019. Retrieved...
17 KB (1,659 words) - 00:33, 20 May 2025
computing, USENIX 2016, with Alex Biryukov Argon2: new generation of memory-hard functions for password hashing and other applications, Euro S&P 2016, with...
13 KB (1,347 words) - 16:58, 23 October 2024
working memory processor. The working memory also retrieves information from previously stored material. Finally, the function of long-term memory is to...
138 KB (16,946 words) - 20:51, 17 June 2025
physical memory into which memory pages are mapped by the operating system. A transfer of pages between main memory and an auxiliary store, such as a hard disk...
21 KB (2,108 words) - 17:14, 20 May 2025
Machine. As presented in "Stronger Key Derivation via Sequential Memory-Hard Functions" Archived 14 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine. presented at BSDCan'09...
11 KB (1,243 words) - 14:53, 14 May 2025
One application of pebbling games is in the security analysis of memory-hard functions in cryptography. The game of pebbling was first suggested by Lagarias...
9 KB (1,146 words) - 20:38, 16 January 2025
runtime. Hard-coded data typically can be modified only by editing the source code and recompiling the executable, although it can be changed in memory or on...
13 KB (1,868 words) - 16:44, 29 May 2025
which use NAND flash memory, slightly exceeded those for HDDs in 2018. Flash storage products had more than twice the revenue of hard disk drives as of 2017[update]...
139 KB (14,137 words) - 13:33, 15 June 2025
Unix System 6, released in 1975, the number of hard links allowed was 127. On Unix-like systems the in-memory counter is 4,294,967,295 (on 32-bit machines)...
14 KB (1,653 words) - 02:28, 1 May 2025
physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks and magnetic tape), where the...
58 KB (5,812 words) - 21:59, 11 June 2025
memory allocation refers to performing manual memory management for dynamic memory allocation in the C programming language via a group of functions in...
36 KB (4,141 words) - 17:14, 15 June 2025
additional data into memory during execution, these will cease to function correctly. This usually occurs because all available memory, including disk swap...
8 KB (965 words) - 19:43, 17 May 2025
plug-in cartridges containing ROM. Strictly speaking, read-only memory refers to hard-wired memory, such as diode matrix or a mask ROM integrated circuit (IC)...
50 KB (5,727 words) - 18:18, 25 May 2025
expensive than non-volatile memory. This type is used for the main memory in most computers, since data is stored on the hard disk while the computer is...
36 KB (3,551 words) - 15:24, 11 February 2025
Computer data storage (redirect from Internal memory)
less power than hard disks. Also, memory may use more power than hard disks. Large caches, which are used to avoid hitting the memory wall, may also consume...
57 KB (6,541 words) - 01:42, 18 June 2025
head, which waits for the requested memory location to pass under the head while the disk spins. As a result, a hard drive's performance is limited by the...
13 KB (1,835 words) - 17:18, 16 May 2024
Ctrl+Alt+Delete. The function of the key combination differs depending on the context but it generally interrupts or facilitates interrupting a function. For instance...
45 KB (3,030 words) - 19:57, 6 January 2025
C (programming language) (redirect from Memory management in C)
computer memory is possible by converting machine addresses to pointers. Procedures (subroutines not returning values) are a special case of function, with...
101 KB (11,258 words) - 07:24, 14 June 2025
storage memory controllers. Tauschek's original drum memory (1932) had a capacity of about 500,000 bits (62.5 kilobytes). One of the earliest functioning computers...
10 KB (1,234 words) - 22:29, 24 September 2024
automatic memory management. The garbage collector attempts to reclaim memory that was allocated by the program, but is no longer referenced; such memory is...
40 KB (4,054 words) - 01:32, 26 May 2025
the more similar the stored vectors. Time can be traced in the memory as a function of where the data are stored, if the data are organized as sequences...
56 KB (7,736 words) - 09:08, 27 May 2025