In particle physics, particle decay is the spontaneous process of one unstable subatomic particle transforming into multiple other particles. The particles...
10 KB (1,276 words) - 23:41, 8 June 2025
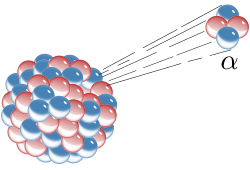
generally produced in the process of alpha decay but may also be produced in different ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek...
33 KB (4,208 words) - 06:51, 21 June 2025
beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of...
14 KB (1,522 words) - 06:37, 4 June 2025
Higgs boson (redirect from Higgs particle)
electric charge, and no colour charge. It is also very unstable, decaying into other particles almost immediately upon generation. The Higgs field is a scalar...
243 KB (26,576 words) - 23:14, 19 June 2025
radioactivity:: 142 alpha-decay -> strong interaction, beta-decay -> weak interaction, gamma-decay -> electromagnetism. In alpha decay, a particle containing two...
96 KB (9,898 words) - 02:56, 20 June 2025
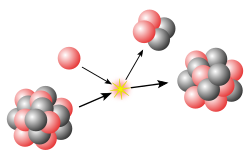
In particle physics, proton decay is a hypothetical form of particle decay in which the proton decays into lighter subatomic particles, such as a neutral...
24 KB (2,555 words) - 14:40, 9 June 2025
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus). The parent nucleus transforms...
19 KB (2,560 words) - 21:31, 19 June 2025
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron)...
64 KB (7,712 words) - 13:14, 19 June 2025
Gamma ray (redirect from Gamma decay)
mostly a result of radioactive decay and secondary radiation from atmospheric interactions with cosmic ray particles. However, there are other rare natural...
60 KB (7,505 words) - 15:39, 16 June 2025
Flavour (particle physics) Generation (particle physics) Koide formula Lepton Since the tauonic lepton number is conserved in weak decays, a tau neutrino...
13 KB (1,418 words) - 23:57, 10 June 2025
Muon (redirect from Muon decay)
of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which...
46 KB (5,576 words) - 22:10, 16 June 2025
particles are truly punctual. Both elementary (such as muons) and composite particles (such as uranium nuclei), are known to undergo particle decay....
18 KB (1,643 words) - 15:49, 14 May 2025
Neutrino (redirect from Ν particle)
this light neutral particle from Chadwick's heavy neutron. In Fermi's theory of beta decay, Chadwick's large neutral particle could decay to a proton, electron...
146 KB (14,425 words) - 11:33, 25 June 2025
W and Z bosons (redirect from W particle)
carrier particle for the electromagnetic force. The W± bosons are best known for their role in nuclear decay. Consider, for example, the beta decay of cobalt-60...
38 KB (3,772 words) - 10:25, 4 June 2025
subatomic particles which have no charge; neutron radiation neutrinos mesons muons Mechanisms that produce particle radiation include: alpha decay Auger effect...
5 KB (616 words) - 10:17, 10 August 2023
Positron emission (redirect from Beta plus decay)
beta particle (β+), the other beta particle being the electron (β−) emitted from the β− decay of a nucleus. An example of positron emission (β+ decay) is...
9 KB (1,145 words) - 22:57, 7 June 2025
Standard Model (redirect from Particle physics standard model)
corresponding particle of generations prior. Thus, there are three generations of quarks and leptons. As first-generation particles do not decay, they comprise...
67 KB (7,518 words) - 12:16, 11 June 2025
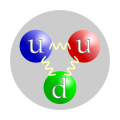
Weak interaction (redirect from Weak decay)
the mechanism of interaction between subatomic particles that is responsible for the radioactive decay of atoms: The weak interaction participates in...
43 KB (4,672 words) - 02:29, 17 June 2025
Pion (redirect from Neutral pion decay)
decay is a prominent quantity in many sub-fields of particle physics, such as chiral perturbation theory. This rate is parametrized by the pion decay...
28 KB (3,019 words) - 18:21, 19 June 2025
Kaon (redirect from K-particle)
Since the mesons decay through weak interactions, parity is not conserved, and the two decays are actually decays of the same particle, now called the...
39 KB (3,250 words) - 17:40, 15 June 2025
physics, a subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a...
36 KB (3,383 words) - 07:57, 24 June 2025
known as a Majorana particle. In 1939, Wendell H. Furry proposed that if neutrinos are Majorana particles, then double beta decay can proceed without...
38 KB (3,818 words) - 01:51, 11 April 2025
Neutron (redirect from N particle)
physics. Neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks. A free neutron spontaneously decays to a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino...
101 KB (11,296 words) - 14:10, 24 June 2025
Lepton (category Elementary particles)
will rapidly change into electrons and neutrinos through a process of particle decay: the transformation from a higher mass state to a lower mass state....
42 KB (4,301 words) - 17:12, 25 May 2025
and the environment. Alpha decay is characterized by the emission of an alpha particle, a 4He nucleus. The mode of this decay causes the parent nucleus...
12 KB (1,404 words) - 21:13, 16 June 2024
J/psi meson (redirect from J particle)
Hadronic decay modes of J/ψ are strongly suppressed because of the OZI rule. This effect strongly increases the lifetime of the particle and thereby...
17 KB (1,827 words) - 12:26, 13 May 2025
Dalitz plot (category Experimental particle physics)
three-body decays are often dominated by resonant processes, in which the particle decays into two decay products, with one of those decay products immediately...
7 KB (777 words) - 20:43, 13 August 2023
Quark (category Elementary particles)
exist. Particles in higher generations generally have greater mass and less stability, causing them to decay into lower-generation particles by means...
77 KB (7,559 words) - 20:07, 9 June 2025
Hadron (redirect from Hadron (subatomic particle))
amounts of time to decay (order of 1034+ years). By way of comparison, free neutrons are the longest-lived unstable particle, and decay with a half-life...
16 KB (1,844 words) - 15:17, 23 June 2025
Lambda baryon (redirect from Lambda particle)
S. Biswas of the University of Melbourne, as a neutral V particle with a proton as a decay product, thus correctly distinguishing it as a baryon, rather...
20 KB (1,432 words) - 04:03, 25 July 2024