Red Cell, formally designated as OP-06D, was a classified United States Navy (USN) military unit designed to test the security of USN facilities. Created...
16 KB (1,841 words) - 18:35, 5 April 2025
Red cell may refer to: Red blood cell, a type of cell in the blood that transports oxygen Red Cell, a term in US government parlance for teams that test...
415 bytes (91 words) - 09:17, 20 September 2018
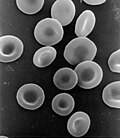
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (from Ancient Greek erythros 'red' and kytos 'hollow vessel', with -cyte translated as 'cell' in modern...
65 KB (7,853 words) - 03:30, 1 June 2025
Complete blood count (redirect from Red blood cell count)
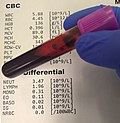
provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration...
106 KB (12,446 words) - 06:39, 6 April 2025
Red blood cell concentrates, also known as red cell concentrates or packed red blood cells, are red blood cells that have been separated for blood transfusion...
44 KB (5,184 words) - 21:47, 29 May 2025
Hematocrit (redirect from Volume of packed red cells)
(vol%) of red blood cells (RBCs) in blood, measured as part of a blood test. The measurement depends on the number and size of red blood cells. It is normally...
27 KB (2,901 words) - 14:41, 24 February 2025
Red cell genotyping, also known as blood group genotyping, is a molecular technique used to identify genetic variants responsible for antigens on the surface...
5 KB (540 words) - 14:49, 5 June 2025
Red blood cell distribution width (RDW), as well as various types thereof (RDW-CV or RCDW and RDW-SD), is a measure of the range of variation of red blood...
7 KB (773 words) - 09:46, 27 October 2024
A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms...
7 KB (642 words) - 22:19, 26 December 2024
Blood type (redirect from Red cell antigens)
of antibodies and inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins...
57 KB (6,302 words) - 23:06, 30 May 2025
In hematology, red cell agglutination or autoagglutination is a phenomenon in which red blood cells clump together, forming aggregates. It is caused by...
4 KB (407 words) - 03:17, 5 November 2023
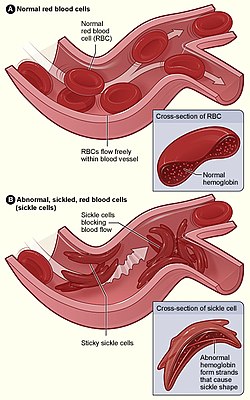
cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to the red blood...
132 KB (14,234 words) - 18:19, 30 May 2025
Urinary cast (redirect from Red blood cell cast)
significance of this occurrence is not felt to be great. The presence of red blood cells within the cast is always pathological and is strongly indicative of...
10 KB (1,162 words) - 09:16, 30 May 2025
Blood transfusion (redirect from Red blood cell transfusion)
components of the blood, such as red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and other clotting factors. White blood cells are transfused only in very rare circumstances...
130 KB (14,220 words) - 22:31, 1 June 2025
Red blood cells (erythrocytes) from donors contain normal hemoglobin (HbA), and transfusion of normal red blood cells into people with sickle cell disease...
15 KB (1,698 words) - 17:57, 31 January 2025
Macrocytic anemia (redirect from Large-Cell anemia)
by the presence of predominantly larger-than-normal erythrocytes (red blood cells, or RBCs) accompanied by low numbers of RBC, which often carry an insufficient...
11 KB (1,269 words) - 13:54, 1 March 2025
Blood compatibility testing (redirect from Red blood cell phenotyping)
the ability of antibodies to cause red blood cells to clump together when they bind to antigens on the cell surface, a phenomenon called agglutination...
51 KB (6,442 words) - 03:48, 5 May 2025
Hemolysis (redirect from Red blood cell breakdown)
(/hiːˈmɒlɪsɪs/), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding...
29 KB (2,618 words) - 06:35, 2 June 2025
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (redirect from Mean cell hemoglobin)
corpuscular hemoglobin, or "mean cell hemoglobin" (MCH), is the average mass of hemoglobin (Hb) per red blood cell (RBC) in a sample of blood. It is...
3 KB (328 words) - 05:25, 26 March 2025
Codocyte (redirect from Target cell)
known as target cells, are red blood cells that have the appearance of a shooting target with a bullseye. In optical microscopy these cells appear to have...
5 KB (703 words) - 18:31, 28 November 2024
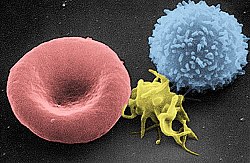
mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes)...
10 KB (1,299 words) - 18:44, 28 March 2025
Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) or erythroblastopenia refers to a type of aplastic anemia affecting the precursors to red blood cells but usually not to...
6 KB (570 words) - 21:25, 6 September 2024
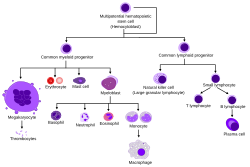
Erythropoiesis (from Greek erythro, meaning red and poiesis, meaning to make) is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development...
14 KB (1,771 words) - 19:13, 4 June 2025
Richard Marcinko (section Red Cell)
unit was the Naval Security Coordination Team OP-06D, unofficially named Red Cell. Marcinko was indicted for conspiracy, conflict of interest and lying to...
31 KB (3,221 words) - 02:51, 30 April 2025
characterized by smaller than normal red blood cells (called microcytes). The normal mean corpuscular volume of a red blood cell is approximately 80–100 fL. When...
16 KB (1,710 words) - 12:47, 24 May 2025
Washed red blood cells are red blood cells that have had most of the plasma, platelets and white blood cells removed and replaced with saline or another...
5 KB (588 words) - 15:35, 18 July 2024
Aplasia (section Pure red cell aplasia)
the failure of the body to produce blood cells. It may occur at any time, and has multiple causes. Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) is caused by the selective...
11 KB (1,184 words) - 20:04, 23 May 2025
Blood (redirect from Peripheral blood cell)
cells are mainly red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and (in mammals) platelets (thrombocytes). The most abundant cells are...
59 KB (6,824 words) - 02:48, 27 May 2025
own red blood cells (RBCs). These antibodies attach to red cells, causing them to break down (lyse), and reducing the number of oxygen-carrying red blood...
32 KB (3,724 words) - 05:58, 23 May 2025
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (redirect from Red blood cell sedimentation rate)
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a...
25 KB (2,810 words) - 23:35, 23 May 2025