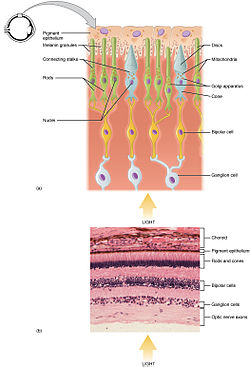
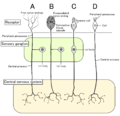
Horizontal cells are the laterally interconnecting neurons having cell bodies in the inner nuclear layer of the retina of vertebrate eyes. They help integrate...
12 KB (1,323 words) - 05:36, 27 June 2024
As a part of the retina, bipolar cells exist between photoreceptors (rod cells and cone cells) and ganglion cells. They act, directly or indirectly, to...
7 KB (752 words) - 03:51, 12 May 2025
In the anatomy of the eye, amacrine cells are interneurons in the retina. They are named from Greek a– 'non' makr– 'long' and in– 'fiber', because of their...
12 KB (1,433 words) - 20:01, 5 February 2025
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological...
26 KB (2,939 words) - 18:31, 17 May 2025
The list of human cell types provides an enumeration and description of the various specialized cells found within the human body, highlighting their...
35 KB (1,773 words) - 00:20, 19 May 2025
outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rods and cones...
84 KB (9,305 words) - 15:55, 23 May 2025
Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells...
14 KB (1,753 words) - 09:32, 12 March 2025
They are found in the brain and retina, in the latter location it is found as the amacrine cell and retina horizontal cells. They are also found in invertebrates...
8 KB (919 words) - 04:04, 28 May 2025
of one retina. In the fovea, which has high acuity, these ganglion cells connect to as few as 5 photoreceptor cells; in other areas of the retina, they...
15 KB (1,891 words) - 02:30, 23 May 2025
precursor cells are biological cells that differentiate into the various cell types of the retina during development. In the vertebrate, these retinal cells differentiate...
5 KB (597 words) - 07:19, 18 July 2023
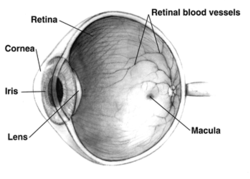
light-sensitive layer of cells known as the retina. The cone cells (for colour) and the rod cells (for low-light contrasts) in the retina detect and convert...
59 KB (7,524 words) - 04:38, 26 May 2025
Visual system (section Retina)
from photoreceptor to bipolar cell. In addition, other neurons in the retina, particularly horizontal and amacrine cells, transmit information laterally...
59 KB (6,928 words) - 21:06, 22 May 2025
influence the sharpness of an image on its retina. Neural factors include the health and functioning of the retina, of the neural pathways to the brain, and...
62 KB (7,723 words) - 20:58, 6 April 2025
AII (A2) amacrine cells are a subtype of amacrine cells. Amacrine cells are neurons that exist in the retina of mammals to assist in interpreting photoreceptive...
12 KB (1,398 words) - 20:29, 9 May 2025
neuronal synapses in the retina of the eye. It consists of a dense network of synapses between dendrites of horizontal cells from the inner nuclear layer...
2 KB (142 words) - 21:13, 21 November 2021
Has an elliptical shape horizontally. Histologically the only region of the retina where GCL has >1 layer of ganglion cells Yellowish appearance = luteal...
26 KB (3,013 words) - 18:55, 25 May 2025
Vision in fish (section The retina)
moving the lens closer to or further from the retina. Fish retinas generally have both rod cells and cone cells (for scotopic and photopic vision), and most...
66 KB (7,937 words) - 20:34, 19 May 2025
vertical meridian than the horizontal meridian. Hopefully, after this, the eye will focus all light on the same location at the retina, and the patient's vision...
38 KB (4,160 words) - 17:02, 23 May 2025
light-detecting photoreceptor cells on the optic disc of the retina where the optic nerve passes through the optic disc. Because there are no cells to detect light...
6 KB (489 words) - 17:47, 29 May 2025
ganglion cells which are regularly arrayed and larger than those found in the rest of the retina, and morphologically appear similar to the cells of the...
68 KB (8,335 words) - 02:50, 25 May 2025
Inner nuclear layer (section Horizontal cells)
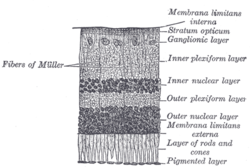
the retina, is made up of a number of closely packed cells, of which there are three varieties: bipolar cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells. The...
3 KB (344 words) - 14:09, 1 November 2023
required shape, nourish and maintain it, and protect it. Three types of cells in the retina convert light energy into electrical energy used by the nervous system:...
80 KB (9,535 words) - 18:14, 23 May 2025
point for the major arteries that supply the retina with blood, and the exit point for the veins from the retina. The optic disc is located 3 to 4 mm to the...
12 KB (1,364 words) - 19:04, 24 May 2025
Sensory neuron (redirect from Receptor cell)
neurons in the retina. The five basic classes of neurons within the retina are photoreceptor cells, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine...
29 KB (3,290 words) - 14:11, 29 March 2025
retinal regeneration. Muller glia are a type of glial cell present in both the teleost and mammalian retina. Retinal regeneration in zebrafish is mediated by...
11 KB (1,201 words) - 22:04, 29 May 2025
Optokinetic response (section Retina)
in the retina with a specialized class of retinal ganglion cell known as ON direction selective retinal ganglion cells (oDSGCs). These cells respond...
17 KB (2,013 words) - 04:14, 26 May 2025
location with no photoreceptor cells, where the retinal ganglion cell axons that compose the optic nerve exit the retina. This location is called the optic...
11 KB (1,402 words) - 17:18, 18 January 2025
Ursodoxicoltaurine (section Photoreceptor cells)
positive effects on the health of the mouse retina, including a reduced accumulation of superoxide radicals, rod cell death, and disruption of cone inner and...
16 KB (1,569 words) - 20:20, 11 October 2024
JA (July 1968). "The response to electric stimulation of horizontal cells in the carp retina". Vision Research. 8 (7): 817–22. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(68)90132-6...
30 KB (3,506 words) - 03:11, 18 April 2025
Receptive field (section Retinal ganglion cells)
single cell further up, they collectively form the receptive field of that cell. For example, the receptive field of a ganglion cell in the retina of the...
23 KB (3,057 words) - 15:43, 9 February 2025