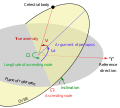
rotational axis. Prograde or direct motion is more normal motion in the same direction as the primary rotates. However, "retrograde" and "prograde" can also...
41 KB (4,723 words) - 15:41, 20 May 2025
vantage point. Direct motion or prograde motion is motion in the same direction as other bodies. While the terms direct and prograde are equivalent in this...
12 KB (1,566 words) - 02:50, 21 February 2025
Prograde can refer to: Retrograde and prograde motion, in astronomy, a type of motion of astronomical bodies Metamorphism#Prograde and retrograde, in...
374 bytes (78 words) - 01:34, 10 February 2022
A distant retrograde orbit (DRO), as most commonly conceived, is a spacecraft orbit around a moon that is highly stable because of its interactions with...
12 KB (1,174 words) - 16:53, 20 February 2025
east to west along its ground track, in what is called "apparent retrograde" motion. This effect occurs because the satellite orbits more slowly than...
14 KB (1,948 words) - 19:20, 17 March 2025
center of mass. While nominally a mean, and theoretically so in the case of two-body motion, in practice the mean motion is not typically an average over time...
13 KB (1,900 words) - 01:47, 27 February 2023
Orbit (redirect from Orbital motion)
first order). A prograde or retrograde impulse (i.e. an impulse applied along the orbital motion) changes both the eccentricity and the orbital period...
57 KB (8,123 words) - 06:52, 24 April 2025
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler in 1609 (except the third law, which was fully published in 1619), describe...
60 KB (8,838 words) - 04:04, 5 May 2025
plane of reference. The orbital inclination is 0° for prograde orbits, and π (180°) for retrograde ones.[citation needed] If the plane of reference is a...
5 KB (689 words) - 18:00, 15 March 2025
than a point gravitational source, resulting in a non-closed orbit. A prograde relativistic shift happens because of relativistic effects from a massive...
3 KB (321 words) - 03:26, 27 September 2024
Apsis (redirect from Perihelion and aphelion)
are apogee and perigee. For the Sun, the suffix is -helion, so the names are aphelion and perihelion. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic...
42 KB (3,925 words) - 03:57, 22 May 2025
the normal orbit is prograde, an orbit in the same direction as the planet rotates. Inclinations greater than 90° describe retrograde orbits (backward)...
11 KB (1,470 words) - 02:33, 8 May 2025
is equatorial (in the same plane as the equator of Mars), circular, and prograde (rotating about Mars's axis in the same direction as the planet's surface)...
3 KB (374 words) - 15:25, 26 October 2024
than the sidereal day of the planet. An Earth satellite that is in (a prograde) subsynchronous orbit will appear to drift eastward as seen from the Earth's...
2 KB (153 words) - 10:44, 31 July 2023
Moons of Jupiter (section Origin and evolution)
outer irregular satellites whose prograde and retrograde orbits are much farther from Jupiter and have high inclinations and eccentricities. The largest of...
122 KB (6,843 words) - 12:22, 17 May 2025
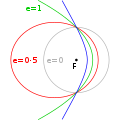
Parabolic trajectory (section Equation of motion)
orbit with the eccentricity equal to 1 and is an unbound orbit that is exactly on the border between elliptical and hyperbolic. When moving away from the...
7 KB (1,091 words) - 22:08, 14 October 2024
Hohmann transfer requires 15 hours and 34 minutes. Δv applied prograde Δv applied retrograde Evidently, the bi-elliptic orbit spends more of its delta-v...
15 KB (2,056 words) - 20:50, 7 July 2024
Jyotish Kepler's laws of planetary motion Occultation Parallax Retrograde and prograde motion Sidereal time Solstice Robin M. Green, Spherical Astronomy,...
6 KB (662 words) - 17:07, 22 October 2023
Earth). By convention, the inclination of a Prograde orbit is specified as an angle less than 90°. Retrograde orbit: An orbit counter to the direction of...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
Sidereal time (redirect from Sidereal motion)
day for retrograde rotation, as the rotation of the planet would be against the direction of orbital motion. If a planet rotates prograde, and the sidereal...
19 KB (2,589 words) - 17:05, 30 April 2025
Elliptic orbit (redirect from Elliptical motion)
the Sun are ellipses with the Sun at one focus, and described this in his first law of planetary motion. Later, Isaac Newton explained this as a corollary...
19 KB (2,744 words) - 16:48, 20 March 2025
Hill sphere (section Example and derivation)
explain the preponderance of retrograde moons around Jupiter; however, Saturn has a more even mix of retrograde/prograde moons so the reasons are more...
27 KB (2,976 words) - 05:15, 11 May 2025
gravitational constant. In a parabolic or hyperbolic trajectory, the motion is not periodic, and the duration of the full trajectory is infinite. For celestial...
17 KB (2,080 words) - 13:46, 24 March 2025
400 km (250 mi), and is of increasing commercial importance in a variety of scenarios and for multiple applications, in both private and government satellite...
19 KB (2,232 words) - 09:45, 28 March 2025
life to reduce the probability of colliding with operational spacecraft and generating space debris. A graveyard orbit is used when the change in velocity...
9 KB (1,036 words) - 14:10, 10 May 2025
discovery was made with the help of radial velocity measurements that showed retrograde apsidal precession of the brown dwarf pair, which could not be explained...
11 KB (1,231 words) - 04:17, 22 May 2025
low Earth orbit, compared to the retrograde burn applied near the Moon in the traditional trans-lunar injection, and allow for a doubling of payload....
8 KB (825 words) - 16:35, 8 March 2025
In astronomy, perturbation is the complex motion of a massive body subjected to forces other than the gravitational attraction of a single other massive...
21 KB (2,425 words) - 08:15, 1 April 2025
over Australia. Geosynchronous satellites are launched to the east into a prograde orbit that matches the rotation rate of the equator. The smallest inclination...
33 KB (3,231 words) - 03:30, 12 January 2025
orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between 2,000 and 35,786 km (1,243 and 22,236 mi) above sea level. The boundary between MEO and LEO is an...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024