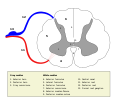
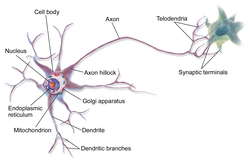
A spinal interneuron, found in the spinal cord, relays signals between (afferent) sensory neurons, and (efferent) motor neurons. Different classes of...
19 KB (2,239 words) - 08:59, 25 May 2025
independently control reflexes. It is also the location of groups of spinal interneurons that make up the neural circuits known as central pattern generators...
44 KB (5,278 words) - 20:52, 24 May 2025
Interneurons (also called internuncial neurons, association neurons, connector neurons, or intermediate neurons) are neurons that are not specifically...
14 KB (1,422 words) - 06:55, 8 February 2025
the spinal cord, made up of groups of spinal interneurons, that is involved in the rhythmic response of ejaculation. This is known as the spinal generator...
38 KB (4,018 words) - 09:54, 7 April 2025
Grey columns (redirect from Spinal cord horn)
of the spinal cord. The anterior grey column is made up of alpha motor neurons, gamma motor neurons, and small neurons thought to be interneurons. It affects...
22 KB (2,764 words) - 14:19, 21 October 2024
Scratch reflex (section Spinal)
Berkowitz A (2008). "Physiology and morphology of shared and specialized spinal interneurons for locomotion and scratching". Journal of Neurophysiology. 99 (6):...
16 KB (2,246 words) - 11:43, 3 January 2025
extension of the lower leg. In invertebrates reflex interneurons do not necessarily reside in the spinal cord, for example as in the lateral giant neuron...
6 KB (596 words) - 07:43, 14 April 2025
output) to the same region of the spinal cord, others projecting into the brain. One target is a set of spinal interneurons that project to motor neurons...
73 KB (9,361 words) - 07:36, 13 April 2025
cardinal classes of spinal interneurons. The ventral neurons are considered to be members of the spinal CPG network. Each of these interneuron class can be further...
72 KB (8,855 words) - 18:29, 23 May 2025
Motor neuron (redirect from Spinal motor nerves)
lower motor neurons. Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons...
26 KB (2,989 words) - 16:08, 13 April 2025
transcription factor gene that is pivotal in interneuron differentiation in the ventral spinal cord. The spinal interneurons V0 and V1 are derived from progenitor...
2 KB (290 words) - 16:09, 30 March 2022
University of California, Los Angeles. She studies how the sensory interneurons in the spinal cord are first established during development and then connect...
16 KB (1,630 words) - 14:48, 28 May 2025
(July 2008). "Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 9 (7): 557–568...
35 KB (1,773 words) - 00:20, 19 May 2025
specific movements involving their muscle field. In contrast, spinal cord premotor interneurons had smaller muscle fields and were active through broader...
22 KB (2,320 words) - 19:02, 21 May 2025
down the spinal cord to synapse onto the interneuron circuitry of the spinal cord and also directly onto the alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord which...
32 KB (4,239 words) - 14:52, 26 September 2024
Rexed laminae (redirect from Spinal lamina V)
motor interneurons Lamina IX: hypaxial (body wall muscles), lateral (in limb regions) and medial (back muscles) motor neurons, also phrenic and spinal accessory...
4 KB (493 words) - 10:51, 14 October 2024
two destinations in the spinal cord: transmission cells that carry the pain signal up to the brain, and inhibitory interneurons that impede transmission...
17 KB (1,895 words) - 05:28, 25 May 2025
mono-synaptic pathway. The medium-latency reflex (MLR) utilizes interneurons within the spinal cord and is typically ~80-90 ms. The long-latency reflex (LLR)...
18 KB (2,293 words) - 09:44, 8 February 2025
signal which travels back to the spinal cord and synapses (without interneurons) at the level of L3 or L4 in the spinal cord, completely independent of...
8 KB (960 words) - 14:07, 23 May 2025
Spinothalamic tract (redirect from Spinal lemniscus)
spinothalamic tract is a nerve tract in the anterolateral system in the spinal cord. This tract is an ascending sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the...
14 KB (1,583 words) - 03:27, 23 October 2024
The central pattern generators are made up of different groups of spinal interneurons. There are four principal types of neural circuits that are responsible...
23 KB (2,711 words) - 04:55, 28 April 2025
Renshaw cells are inhibitory interneurons found in the gray matter of the spinal cord, and are associated in two ways with an alpha motor neuron. They...
13 KB (1,578 words) - 02:03, 8 August 2024
effect by increasing gamma-aminobutyric acid transmission among spinal interneurons. The blocking effect of amitriptyline on sodium channels may also...
93 KB (8,717 words) - 12:18, 23 May 2025
Spinal shock was first explored by Robert Whytt in 1750 as a loss of sensation accompanied by motor paralysis with initial loss but gradual recovery of...
5 KB (605 words) - 02:21, 21 November 2024
Corticospinal tract (category Spinal cord tracts)
the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord, controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. There are...
5 KB (623 words) - 21:01, 3 May 2025
descends the reticulospinal tract where it innervates motor neurons and spinal interneurons. It is the main auditory tract in the brainstem that connects the...
8 KB (895 words) - 07:58, 18 February 2025
contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are...
79 KB (9,164 words) - 16:39, 10 May 2025
Trigeminal nerve (section Spinal trigeminal nucleus)
information is processed and modified at each level in the chain by interneurons and input from other areas of the nervous system. For example, cells...
34 KB (4,131 words) - 12:25, 4 September 2024
spinal cord cells, triggering the sympathetic nervous system and somatic motor responses, while emotions like fear further perpetuate the interneuron...
24 KB (3,014 words) - 17:52, 19 May 2025
oblongata, and travel as part of the spinal cord until they synapse with interneurons in the grey column of the spinal cord. There is some variation in terminology...
16 KB (1,679 words) - 05:45, 8 December 2024