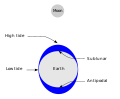
Tidal locking between a pair of co-orbiting astronomical bodies occurs when one of the objects reaches a state where there is no longer any net change...
47 KB (5,091 words) - 09:10, 17 May 2025
forces, but are not caused by the rotation. Further tidal phenomena include solid-earth tides, tidal locking, breaking apart of celestial bodies and formation...
24 KB (2,884 words) - 19:46, 21 May 2025
Proxima Centauri b (section Tidal locking)
number of considerations: Both the activity of Proxima Centauri and tidal locking would hinder the establishment of these conditions on the planet. Unlike...
74 KB (8,339 words) - 12:29, 24 May 2025
Moon (section Tidal effects)
The Moon rotates always facing Earth with the same near side. This tidal locking results from Earth's gravitational pull having synchronized the Moon's...
270 KB (26,421 words) - 12:10, 27 May 2025
Natural satellite (section Tidal locking)
small orbital inclination and eccentricity) in the Solar System are tidally locked to their respective primaries, meaning that the same side of the natural...
43 KB (3,564 words) - 16:01, 3 May 2025
rotation. See supersynchronous orbit. The process eventually leads to tidal locking, usually of the smaller body first, and later the larger body (e.g....
37 KB (4,801 words) - 15:43, 24 May 2025
dwarfs are likely to be tidally locked to their primary: that is, their days are as long as their orbits. While tidal locking may adversely affect planets...
38 KB (3,779 words) - 14:38, 17 April 2025
bodies are tidally locked to each other. The dwarf planet systems Pluto–Charon and Eris–Dysnomia are the only known examples of mutual tidal locking in the...
56 KB (5,641 words) - 07:42, 28 May 2025
dwarf systems are unlikely to be habitable, due to high probability of tidal locking, likely lack of atmospheres, and the high stellar variation many such...
47 KB (5,676 words) - 01:13, 25 May 2025
TOI-2257 b (section Tidal locking)
conditions that combat tidal locking. On the other hand, the planet's eccentricity could be a factor working against tidal locking in and of itself; the...
11 KB (1,243 words) - 09:32, 13 December 2024
K2-332 b (section Tidal locking)
com. Retrieved November 21, 2023. Barnes, Rory (December 1, 2017). "Tidal locking of habitable exoplanets". Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy...
7 KB (817 words) - 18:06, 12 March 2024
orbit (tidal circularization) and the rotational periods of the two bodies adjust towards matching the orbital period (tidal locking). Sustained tidal heating...
10 KB (1,240 words) - 14:46, 12 March 2025
Gliese 581c (section Tidal lock)
resulting from this tidal locking may play a major role in the planet's geology. Models proposed by scientists predict that tidal heating could yield...
38 KB (3,772 words) - 19:50, 24 May 2025
Kepler-296e (section Tidal locking)
gravitysimulator.org. Retrieved 27 November 2023. Barnes, Rory (1 December 2017). "Tidal locking of habitable exoplanets". Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy...
9 KB (854 words) - 22:42, 10 February 2024
stabilize Earth's axis, causes tides and gradually slows Earth's rotation. Tidal locking causes the Moon to always face Earth with the same side. Earth, like...
219 KB (19,417 words) - 23:18, 26 May 2025
results in tidal interactions stronger than those on Earth. All the planets have reached an equilibrium with slow planetary rotations and tidal locking, which...
188 KB (20,696 words) - 08:19, 22 May 2025
Arnold tongue (redirect from Phase locking)
instruments, orbital resonance and tidal locking of orbiting moons, mode-locking in fiber optics and phase-locked loops and other electronic oscillators...
21 KB (3,182 words) - 17:11, 25 May 2025
Eyeball planet (category Tidal forces)
An eyeball planet is a hypothetical type of tidally locked planet, for which tidal locking induces spatial features (for example in the geography or composition...
8 KB (806 words) - 04:30, 12 May 2025
Orbit (section Tidal locking)
is the orbital period. See also Kepler’s third law. Some bodies are tidally locked with other bodies, meaning that one side of the celestial body is permanently...
57 KB (8,123 words) - 06:52, 24 April 2025
with these maria that make up the man is always facing Earth due to a tidal locking, or synchronous orbit. Thought to have occurred because of the gravitational...
15 KB (1,815 words) - 11:44, 19 May 2025
Gliese 581g (section Tidal locking)
been dubbed "Eyeball Earth" by the author. Modeling of the effect of tidal locking on Gliese 581g's possible atmosphere, using a general circulation model...
58 KB (5,454 words) - 14:23, 26 May 2025
Tide (redirect from Tidal flow)
global atmospheric flow Tidal barrage – Dam-like structure Tidal island – Island accessible by foot at low tide Tidal locking – Situation in which an...
109 KB (13,077 words) - 15:20, 26 May 2025
retrograde rotation about its axis, a result of competing forces of solar tidal locking and differential heating of Venus's massive atmosphere. A Venusian day...
223 KB (20,254 words) - 00:30, 28 May 2025
Charon, Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra. Charon, the largest, is mutually tidally locked with Pluto, and is massive enough that Pluto and Charon are sometimes...
39 KB (3,708 words) - 01:44, 4 May 2025
Physics Publishing. ISBN 0-7503-0874-5. Gunn, Alastair (n.d.). "What is tidal locking?". Science Focus. BBC. Retrieved 27 April 2024. Guzewich, Scott D.;...
87 KB (9,961 words) - 05:03, 21 May 2025
extremely close distances to the stars cause tidal locking, an important factor in habitability. For a tidally locked planet, the sidereal day is as long as...
139 KB (13,879 words) - 19:12, 24 April 2025
stationary in Mercury's sky. The 3:2 resonant tidal locking is stabilized by the variance of the tidal force along Mercury's eccentric orbit, acting on...
156 KB (16,132 words) - 19:06, 22 May 2025
surface of planets orbiting them at a distance that does not induce tidal locking. K-type stars may be able to support life far longer than the Sun. Whether...
111 KB (13,137 words) - 13:57, 26 May 2025
Europa (moon) (section Tidal friction)
meridian is a line passing through this point. Research suggests that tidal locking may not be full, as a non-synchronous rotation has been proposed: Europa...
138 KB (13,596 words) - 21:29, 24 May 2025
equilibrium between tidal forces slowing it down and atmospheric tides created by solar heating speeding it up. All the large moons are tidally locked to their parent...
199 KB (20,934 words) - 17:02, 8 May 2025