contributed an understanding of protein folding and structure mediated by hydrophobic interactions. The first protein to have its amino acid chain sequenced...
105 KB (10,974 words) - 18:23, 16 July 2025
Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical...
74 KB (8,383 words) - 11:23, 12 July 2025
Parkin is a 465-amino acid residue E3 ubiquitin ligase, a protein that in humans and mice is encoded by the PARK2 gene. Parkin plays a critical role in...
48 KB (5,285 words) - 07:39, 20 July 2025
G-protein activation. However, the possibility for interaction does allow for G-protein-independent signaling to occur. There are three main G-protein-mediated...
82 KB (9,410 words) - 15:41, 22 July 2025
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation...
41 KB (4,511 words) - 07:50, 9 July 2025
native structure of a protein. Tertiary structure of a protein involves a single polypeptide chain; however, additional interactions of folded polypeptide...
76 KB (8,712 words) - 18:23, 16 July 2025
non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at...
38 KB (4,246 words) - 18:23, 16 July 2025
affects a large portion of proteins. Even if a protein is not phosphorylated itself, its interactions with other proteins may be regulated by phosphorylation...
68 KB (8,044 words) - 07:04, 26 July 2025
Protein–protein interactions can be designed using protein design algorithms because the principles that rule protein stability also rule protein–protein binding...
64 KB (7,724 words) - 15:52, 16 July 2025
website. Biology portal Protein design Protein function prediction Protein–protein interaction prediction Gene prediction Protein structure prediction software...
74 KB (9,218 words) - 14:10, 20 July 2025
activator like effectors. Structural proteins that bind DNA are well-understood examples of non-specific DNA-protein interactions. Within chromosomes, DNA is held...
22 KB (2,637 words) - 06:01, 3 April 2025
Protein–protein interaction prediction is a field combining bioinformatics and structural biology in an attempt to identify and catalog physical interactions...
25 KB (2,915 words) - 05:18, 2 June 2025
biology research in order to track protein interactions in real time. The first fluorescent tag, green fluorescent protein (GFP), was isolated from Aequorea...
19 KB (2,305 words) - 05:22, 15 May 2024
chromosome stability, its interaction with the cellular transcriptome, its interaction with other cytoskeletal or synaptic proteins, its involvement in myelination...
58 KB (6,568 words) - 07:28, 19 July 2025
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved...
24 KB (2,763 words) - 14:09, 19 July 2025
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest...
71 KB (8,443 words) - 16:27, 25 May 2025
P53 (redirect from Protein P53)
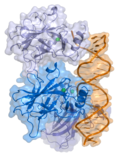
p53, also known as tumor protein p53, TP53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory transcription...
127 KB (13,874 words) - 23:30, 21 July 2025
Protein–protein interaction screening refers to the identification of Protein–protein interaction with high-throughput screening methods such as computer-...
6 KB (726 words) - 13:48, 18 November 2021
Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside...
52 KB (6,403 words) - 14:07, 18 July 2025
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently...
7 KB (697 words) - 00:43, 24 June 2025
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label GFP...
66 KB (7,627 words) - 10:56, 14 July 2025
between a protein and a functional, proteinaceous unit was difficult to elucidate. More recently, people refer to protein–protein interaction when discussing...
21 KB (2,342 words) - 06:32, 6 July 2025
Denaturation (biochemistry) (redirect from Denatured protein)
Der Waals Interactions) and protein-solvent interactions. As a result, this process is heavily reliant on environmental state that the protein resides in...
32 KB (3,193 words) - 02:31, 28 June 2025
molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding of large proteins or macromolecular protein complexes. There are a...
29 KB (3,502 words) - 12:50, 3 March 2025
heat shock proteins function as intra-cellular chaperones for other proteins. They play an important role in protein–protein interactions such as folding...
49 KB (5,534 words) - 03:33, 12 July 2025
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic...
19 KB (2,273 words) - 23:40, 21 July 2025
microfilaments or microtubules. Actin-based motor proteins (myosin) move along microfilaments through interaction with actin, and microtubule motors (dynein...
14 KB (1,568 words) - 17:00, 22 June 2025
Antifreeze proteins (AFPs) or ice structuring proteins refer to a class of polypeptides produced by certain animals, plants, fungi and bacteria that permit...
53 KB (6,367 words) - 16:12, 17 July 2025
Cross-link (redirect from Protein crosslinking)
field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies...
18 KB (1,797 words) - 10:15, 25 May 2025
assembly of multi-protein complexes by increasing the probability of any appropriate protein–protein interactions. Peripheral membrane proteins may interact...
55 KB (4,432 words) - 17:51, 17 July 2025