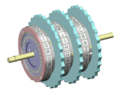
The (Hagelin) C-52 and CX-52 were cipher machines manufactured by Crypto AG starting 1951/1952. These pin-and-lug type cipher machines were advanced successors...
6 KB (673 words) - 02:26, 9 March 2025
The Enigma machine is a cipher device developed and used in the early- to mid-20th century to protect commercial, diplomatic, and military communication...
93 KB (11,280 words) - 20:30, 23 April 2025
Angōki Taipu-A (暗号機 タイプA, "Type A Cipher Machine"), codenamed Red by the United States, was a diplomatic cryptographic machine used by the Japanese Foreign...
9 KB (1,108 words) - 19:27, 6 March 2025
The C-35 and C-36 were cipher machines designed by Swedish cryptographer Boris Hagelin in the 1930s. These were the first of Hagelin's cipher machines to...
4 KB (436 words) - 18:20, 21 December 2024
The Combined Cipher Machine (CCM) (or Combined Cypher Machine) was a common cipher machine system for securing Allied communications during World War...
5 KB (568 words) - 04:37, 18 December 2023
cryptography, a rotor machine is an electro-mechanical stream cipher device used for encrypting and decrypting messages. Rotor machines were the cryptographic...
17 KB (2,462 words) - 12:35, 29 November 2024
kyūnana-shiki ōbun injiki) or "Type B Cipher Machine", codenamed Purple by the United States, was an encryption machine used by the Japanese Foreign Office...
31 KB (3,931 words) - 14:58, 29 January 2025
RC4 (redirect from RC4 Cipher)
In cryptography, RC4 (Rivest Cipher 4, also known as ARC4 or ARCFOUR, meaning Alleged RC4, see below) is a stream cipher. While it is remarkable for its...
44 KB (5,081 words) - 14:07, 26 April 2025
cipher machine. The Imperial Japanese Navy used the machine for communications from late 1942 until 1944. JADE was similar to another cipher machine,...
3 KB (279 words) - 17:50, 18 September 2024
Index of cryptography articles (section C)
Burrows–Abadi–Needham logic • Burt Kaliski C2Net • C-36 (cipher machine) • C-52 (cipher machine) • Caesar cipher • Camellia (cipher) • CAPICOM • Capstone (cryptography)...
67 KB (2,933 words) - 10:14, 4 January 2025
cryptography, a block cipher is a deterministic algorithm that operates on fixed-length groups of bits, called blocks. Block ciphers are the elementary building...
51 KB (6,569 words) - 08:42, 11 April 2025
Boris Hagelin (category Cipher-machine cryptographers)
patent 3,083,263 U.S. patent 3,485,948 C-36 (cipher machine) M-209 C-52 (cipher machine) Bengt Beckman. Codebreakers: Arne Beurling and the Swedish crypto...
5 KB (457 words) - 22:01, 5 October 2024
M-209 (redirect from C-38 (cipher machine))
designated CSP-1500 by the United States Navy (C-38 by the manufacturer) is a portable, mechanical cipher machine used by the US military primarily in World...
19 KB (2,670 words) - 19:22, 2 July 2024
Siemens and Halske T52 (redirect from Siemens Cipher Machine)
teleprinter"), or Schlüsselfernschreibmaschine (SFM), was a World War II German cipher machine and teleprinter produced by the electrical engineering firm Siemens...
7 KB (917 words) - 13:45, 13 September 2024
The (Hagelin) CD-57 was a portable, mechanical cipher machine manufactured by Crypto AG, first produced in 1957. It was derived from the earlier CD-55...
3 KB (250 words) - 07:17, 15 October 2024
SZ42b were German rotor stream cipher machines used by the German Army during World War II. They were developed by C. Lorenz AG in Berlin. The model...
34 KB (3,790 words) - 01:12, 17 April 2025
de:Heinrich Emil Weber Geoff Sullivan and Frode Weierud: The Swiss NEMA Cipher Machine. Cryptologia, 23(4), October 1999, pp310–328. Walter Schmid: Die Chiffriermaschine...
5 KB (488 words) - 19:40, 12 March 2025
Cryptanalysis of the Enigma (redirect from M4 (cipher))
transmissions, was given the codename Ultra. The Enigma machines were a family of portable cipher machines with rotor scramblers. Good operating procedures,...
139 KB (17,799 words) - 16:48, 3 May 2025
Schlüsselgerät 41 (category Broken stream ciphers)
The Schlüsselgerät 41 ("Cipher Machine 41"), also known as the SG-41 or Hitler mill, was a rotor cipher machine, first produced in 1941 in Nazi Germany...
9 KB (832 words) - 18:55, 24 February 2025
Jefferson disk (redirect from Wheel cipher)
Jefferson disk, also called the Bazeries cylinder or wheel cypher, is a cipher system commonly attributed to Thomas Jefferson that uses a set of wheels...
13 KB (1,601 words) - 04:33, 27 April 2025
Mercury was a British cipher machine used by the Air Ministry from 1950 until at least the early 1960s. Mercury was an online rotor machine descended from Typex...
4 KB (509 words) - 18:29, 27 August 2022
Lorenz cipher. This achieved the decryption of messages in the German teleprinter cipher produced by the Lorenz SZ40/42 in-line cipher machine. Both the...
17 KB (1,855 words) - 18:15, 23 October 2024
Fialka (category Rotor machines)
cryptography, Fialka (M-125) is the name of a Cold War-era Soviet cipher machine. A rotor machine, the device uses 10 rotors, each with 30 contacts along with...
12 KB (1,494 words) - 11:00, 6 May 2024
Grille (cryptography) (redirect from Trellis cipher)
In the history of cryptography, a grille cipher was a technique for encrypting a plaintext by writing it onto a sheet of paper through a pierced sheet...
17 KB (2,249 words) - 08:05, 27 April 2025
XXTEA (category Block ciphers)
cryptography, Corrected Block TEA (often referred to as XXTEA) is a block cipher designed to correct weaknesses in the original Block TEA. XXTEA is vulnerable...
9 KB (1,115 words) - 08:11, 28 June 2024
of a set of pinwheels and a rotating cage. Other cipher machines which used pinwheels include the C-52, the CD-57 and the Siemens and Halske T52. Pinwheels...
3 KB (378 words) - 22:31, 9 January 2024
Bombe (section The Enigma machine)
kryptologiczna), which had been designed in Poland at the Biuro Szyfrów (Cipher Bureau) by cryptologist Marian Rejewski, who had been breaking German Enigma...
67 KB (7,962 words) - 16:41, 3 May 2025
writer) stream cipher machines at both ends of a telegraph link using the 5-bit International Telegraphy Alphabet No. 2 (ITA2). These machines were subsequently...
81 KB (8,661 words) - 20:10, 10 March 2025