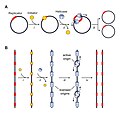
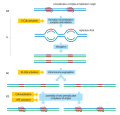
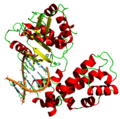
Eukaryotic DNA replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts DNA replication to once per cell cycle. Eukaryotic DNA replication of chromosomal DNA...
121 KB (14,916 words) - 04:06, 3 January 2025
The origin of replication (also called the replication origin) is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the...
113 KB (12,563 words) - 03:12, 16 December 2024
Okazaki fragments (redirect from Semi-discontinuous replication)
Prokaryotes have a short replication process that occurs continuously; eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, only undertake DNA replication during the S-phase...
34 KB (4,470 words) - 07:49, 11 November 2024
of the DNA replication system ensures that the genome is replicated only once per cycle; over-replication induces DNA damage. Deregulation of DNA replication...
14 KB (1,820 words) - 18:46, 3 May 2025
A pre-replication complex (pre-RC) is a protein complex that forms at the origin of replication during the initiation step of DNA replication. Formation...
15 KB (1,928 words) - 17:24, 8 January 2024
near perfect fidelity for DNA replication. In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations (origins of replication) in the genome which contains...
60 KB (7,447 words) - 05:04, 1 June 2025
DNA re-replication (or simply rereplication) is an undesirable and possibly fatal occurrence in eukaryotic cells in which the genome is replicated more...
22 KB (2,860 words) - 19:01, 24 March 2024
Replication protein A (RPA) is the major protein that binds to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) in eukaryotic cells. In vitro, RPA shows a much higher affinity...
7 KB (785 words) - 23:06, 16 February 2025
licensing and DNA replication factor 1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDT1 gene. It is a licensing factor that functions to limit DNA from replicating...
12 KB (1,439 words) - 01:55, 12 October 2024
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority...
16 KB (1,699 words) - 23:12, 22 April 2025
Single-stranded binding protein (redirect from Singlestranded DNA binding protein)
ICP8, is a nuclear protein that, along other replication proteins is required for viral DNA replication during lytic infection. Six herpes virus-group-common...
10 KB (1,016 words) - 04:21, 25 August 2024
of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex...
59 KB (7,106 words) - 00:05, 4 June 2025
Some eukaryotic viruses also replicate their DNA or RNA via the rolling circle mechanism. As a simplified version of natural rolling circle replication, an...
24 KB (2,920 words) - 00:14, 26 May 2025
non-coding DNA fraction include regulatory sequences that control gene expression; scaffold attachment regions; origins of DNA replication; centromeres;...
42 KB (4,774 words) - 17:56, 3 November 2024
has been widely studied as a model eukaryotic virus, leading to many early discoveries in eukaryotic DNA replication and transcription. Following contamination...
21 KB (2,521 words) - 00:17, 7 May 2025
Replication timing refers to the order in which segments of DNA along the length of a chromosome are duplicated. In eukaryotic cells (cells that package...
13 KB (1,612 words) - 19:13, 21 May 2025
Origin recognition complex (category DNA-binding proteins)
component for eukaryotic DNA replication, and remains bound to chromatin at replication origins throughout the cell cycle. ORC directs DNA replication throughout...
21 KB (2,339 words) - 22:38, 18 March 2025
while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-polymerase or by helicase in front of the progressing replication fork. It is the only known...
15 KB (1,873 words) - 03:31, 25 November 2024
Replisome (category DNA replication)
complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the...
32 KB (3,700 words) - 00:38, 1 January 2024
eukaryotic organisms, but were first discovered in yeast and bacteria origins, by Huang Kowalski. The DNA unwinding allows for access of replication machinery...
18 KB (2,304 words) - 09:30, 17 April 2025
These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of...
78 KB (9,148 words) - 19:21, 26 May 2025
The replication factor C, or RFC, is a five-subunit protein complex that is required for DNA replication. The subunits of this heteropentamer are named...
6 KB (866 words) - 13:30, 2 July 2024
Intergenic region (redirect from Eukaryotic intergenic DNA)
origins of replication, scaffold attachment regions, and transposons and viruses. Non-functional DNA elements such as pseudogenes and repetitive DNA, both...
7 KB (616 words) - 14:06, 14 September 2024
cause aging. (Also see DNA damage theory of aging.) In replicating cells, such as cells lining the colon, errors occur upon replication of past damages in...
81 KB (10,123 words) - 19:07, 23 May 2025
separated, including DNA replication, recombination and DNA repair. These binding proteins seem to stabilize single-stranded DNA and protect it from forming...
22 KB (2,637 words) - 06:01, 3 April 2025
Bauerschmidt C, Kremmer E, Nasheuer HP (2003). "Regulation of eukaryotic DNA replication at the initiation step". Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31 (Pt 1): 266–9...
6 KB (787 words) - 03:58, 2 December 2024
polyadenylation site. dsDNA viruses make use of several mechanisms to replicate their genome. Bidirectional replication, in which two replication forks are established...
25 KB (2,893 words) - 17:54, 1 April 2025
geneticist and structural biologist. Tye's pioneering work on eukaryotic DNA replication led to the discovery of the minichromosome maintenance (MCM) genes...
10 KB (1,154 words) - 22:10, 16 March 2025
cruciform DNA while regulating the replication of DNA in eukaryotic cells. B-DNA can form transient structures of cruciform DNA that act as recognition signals...
28 KB (3,447 words) - 16:00, 30 March 2024
dividing cells, unrepaired DNA damage that does not kill the cell by blocking replication will tend to cause replication errors and thus mutation. The...
132 KB (16,177 words) - 11:20, 23 April 2025