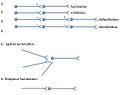
an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This...
9 KB (1,100 words) - 04:03, 7 February 2025
inhibitory postsynaptic potential is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), which is a synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron more...
22 KB (2,705 words) - 04:12, 7 February 2025
action potential at its axon hillock, thus transmitting the information to yet another cell. This phenomenon is known as an excitatory postsynaptic potential...
22 KB (2,547 words) - 13:04, 6 August 2024
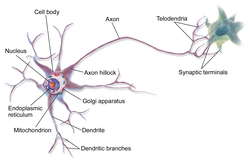
Postsynaptic potentials are changes in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic terminal of a chemical synapse. Postsynaptic potentials are graded potentials...
16 KB (1,656 words) - 04:54, 13 February 2025
Chemical synapse (redirect from Postsynaptic)
cases the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) will not reach the threshold for eliciting an action potential. When action potentials from multiple...
36 KB (4,277 words) - 19:24, 23 March 2025
mitigate the effects of an excitatory neurotransmitter. This depolarization is called an EPSP, or an excitatory postsynaptic potential, and the hyperpolarization...
19 KB (2,354 words) - 03:09, 20 January 2025
called excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs). Depolarizing local potentials sum together, and if the voltage reaches the threshold potential, an action...
6 KB (736 words) - 18:59, 17 November 2023
inhibition, is a form of postsynaptic potential inhibition that can be represented mathematically as reducing the excitatory potential by division, rather...
5 KB (553 words) - 02:06, 20 January 2025
plate potentials (EPPs) are the voltages which cause depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane...
21 KB (2,781 words) - 23:59, 22 February 2025
any synapse is to produce either an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) or an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP), which generate or repress the...
17 KB (2,047 words) - 04:37, 7 April 2025
In neuroscience, a silent synapse is an excitatory glutamatergic synapse whose postsynaptic membrane contains NMDA-type glutamate receptors but no AMPA-type...
13 KB (1,613 words) - 20:11, 12 November 2023
are two forms of synaptic potential: excitatory and inhibitory. The type of potential produced depends on both the postsynaptic receptor, more specifically...
11 KB (1,541 words) - 09:24, 18 September 2023
opposite effect. Whether a postsynaptic potential is considered excitatory or inhibitory depends on the reversal potential for the ions of that current...
65 KB (8,286 words) - 00:30, 22 April 2025
circuitry. Its inputs are analogous to excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials at neural dendrites, or activation. Its...
31 KB (3,602 words) - 17:55, 8 February 2025
— An enzyme in plants, bacteria, fungi, and some protists Excitatory postsynaptic potential — A characteristic of neurons This disambiguation page lists...
240 bytes (57 words) - 19:15, 7 May 2022
the onset of the excitatory postsynaptic potential and the postsynaptic action potential. LTP is induced by a series of action potentials which cause a variety...
23 KB (2,711 words) - 04:55, 28 April 2025
this depolarization can occur. Action potentials are most commonly initiated by excitatory postsynaptic potentials from a presynaptic neuron. Typically...
149 KB (16,451 words) - 05:32, 8 May 2025
understand their differing functions. AMPA generates fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP). AMPA activates AMPA receptors that are non-selective...
4 KB (274 words) - 19:25, 10 February 2025
potentials. This slow release is detectable and produces micro-inhibitory or micro-excitatory effects on the postsynaptic neuron. An action potential...
23 KB (2,723 words) - 04:20, 21 April 2025
Neurotransmitter (redirect from Excitatory neurotransmitter)
Anthony-Samuel; McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark (2001), "Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials", Neuroscience. 2nd edition, Sinauer Associates, retrieved...
99 KB (8,911 words) - 10:54, 22 April 2025
negative charge. Electrotonic potentials that increase the membrane potential are called excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs). This is because they...
11 KB (1,299 words) - 12:29, 2 March 2024
very powerful, excitatory input to the cerebellum which results in the generation of complex spike excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in Purkinje...
7 KB (689 words) - 21:28, 1 June 2024
will become permeable. In excitatory postsynaptic potentials, an excitatory response is generated. This is caused by an excitatory neurotransmitter, normally...
30 KB (3,965 words) - 22:08, 22 April 2025
short-term facilitation may increase the second spike's excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) amplitude, thereby giving that spike pair a greater...
61 KB (7,388 words) - 15:43, 1 May 2025
Castillo showed that the amplitude of the depolarization (excitatory postsynaptic potential) depended on the proximity of the micropipette releasing the...
35 KB (4,084 words) - 07:09, 9 March 2025
Nonsynaptic plasticity (category Articles containing potentially dated statements from January 2010)
specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification...
47 KB (5,507 words) - 09:48, 16 January 2025
one will see a sustained increase of the amplitude of the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) following tetanus. This response is interesting because...
75 KB (8,581 words) - 14:22, 3 May 2025
Glutamate receptor (redirect from Excitatory amino acid receptor)
responsible for the rapid depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that underlies the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). AMPA receptors are also involved...
64 KB (6,959 words) - 14:22, 3 May 2025
Orexin (section Other potential uses)
orexin: orexin-A and orexin-B (hypocretin-1 and hypocretin-2). They are excitatory neuropeptides with approximately 50% sequence identity, produced by cleavage...
54 KB (6,133 words) - 15:53, 28 April 2025
event in the neuron which occurs when an excitatory postsynaptic potential and an inhibitory postsynaptic potential are occurring close to each other on a...
999 bytes (128 words) - 01:28, 18 September 2022