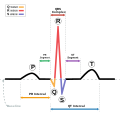
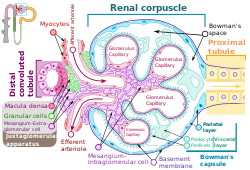
The myogenic mechanism is how arteries and arterioles react to an increase or decrease of blood pressure to keep the blood flow constant within the blood...
9 KB (1,119 words) - 07:47, 17 October 2024
Tubuloglomerular feedback (redirect from Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism)
increasing glomerular capillary pressure. Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Kidney Myogenic Mechanism Renal corpuscle Transforming growth factor Arulkumaran N, Turner CM...
21 KB (2,605 words) - 03:42, 24 July 2025
Renin–angiotensin system Vasoconstrictors Vasodilators Autoregulation Myogenic mechanism Tubuloglomerular feedback Cerebral autoregulation Paraganglia Aortic...
10 KB (946 words) - 02:21, 6 April 2024
Juxtaglomerular cell tumor Hyperaldosteronism Tubuloglomerular feedback Myogenic mechanism "Dictionary.com". Retrieved 11 June 2015. Gonzalez-Vicente, Agustin;...
8 KB (831 words) - 13:44, 28 June 2025
Smooth muscle (section Other contractile mechanisms)
Atherosclerosis. Atromentin has been shown to be a smooth muscle stimulant. Myogenic mechanism List of distinct cell types in the adult human body Betts, J. Gordon;...
37 KB (4,737 words) - 17:18, 22 January 2025
Ptosis (eyelid) (section Mechanism)
ptosis. Different trauma can cause and induce many different mechanisms. For example, myogenic ptosis results from a direct injury to the levator muscle...
30 KB (3,547 words) - 19:18, 31 March 2025
Myogenesis (redirect from Myogenic cells)
Myf5 are members of the myogenic bHLH (basic helix-loop-helix) proteins transcription factor family. Cells that make myogenic bHLH transcription factors...
24 KB (2,799 words) - 18:01, 16 July 2025
MYF6 (redirect from Myogenic factor 6)
Myogenic factor 6 (also known as Mrf4 or herculin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYF6 gene. This gene is also known in the biomedical literature...
9 KB (1,166 words) - 18:37, 22 August 2024
Vasoconstriction (section General mechanism)
circulating hormones, and intrinsic mechanisms inherent to the vasculature itself (also referred to as the myogenic response).[citation needed] Exposure...
19 KB (1,681 words) - 22:03, 18 February 2025
MYF5 (redirect from Myogenic factor 5)
Myogenic factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYF5 gene. It is a protein with a key role in regulating muscle differentiation or myogenesis...
18 KB (2,355 words) - 11:57, 21 June 2022
YK-11 (section Mechanism of action)
Inouye Y (2013). "Selective androgen receptor modulator, YK11, regulates myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by follistatin expression". Biological...
4 KB (398 words) - 19:21, 25 June 2025
MyoD (redirect from Myogenic differentiation 1)
proteins known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs). These bHLH (basic helix loop helix) transcription factors act sequentially in myogenic differentiation...
27 KB (3,389 words) - 17:32, 17 July 2025
concentration of potassium ions. The mechanisms of vasodilation are predominantly local metabolites and myogenic effects. Increased metabolic activity...
8 KB (952 words) - 18:10, 14 May 2025
Phosphoglucomutase (section Reaction mechanism)
glucose 6-phosphate. There are two forms of PGM1-CDG: 1.) exclusively myogenic, and 2.) multi-system (including muscles). The usual pathway for glycogen...
21 KB (2,346 words) - 01:07, 24 March 2024
(published February 1999), pp. 22–6, PMID 10377602 Folkow, B (1989), "Myogenic mechanisms in the control of systemic resistance. Introduction and historical...
14 KB (1,601 words) - 07:12, 13 July 2025
veins from other areas of the skin, facial veins responded with an active myogenic contraction to passive stretch and, therefore, were able to develop an...
10 KB (1,178 words) - 18:02, 18 June 2025
Edition, Campbell, 1999 Perry R, Rudnick M (2000). "Molecular mechanisms regulating myogenic determination and differentiation". Front Biosci. 5: D750–67...
37 KB (4,496 words) - 01:03, 18 July 2025
Cerebral autoregulation (section Myogenic regulation)
outcome. Three different mechanisms are thought to contribute to the process of cerebral autoregulation. These are metabolic, myogenic and neurogenic. Metabolic...
6 KB (688 words) - 19:05, 15 September 2023
Unlike skeletal muscle, the contractions of smooth and cardiac muscles are myogenic (meaning that they are initiated by the smooth or heart muscle cells themselves...
62 KB (7,391 words) - 08:47, 18 July 2025
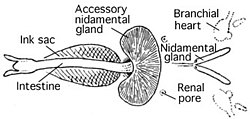
supplement the action of the systemic heart in a cephalopod's body. They are myogenic in nature. Branchial hearts are always in pairs located at the base of...
3 KB (317 words) - 15:10, 7 November 2023
Hitting the wall (section Mechanisms)
Excessive use of the myokinase reaction and purine nucleotide cycle leads to myogenic hyperuricemia. In muscle glycogenoses (muscle GSDs), an inborn error of...
13 KB (1,482 words) - 23:42, 17 July 2025
posture maintenance. Contractions in cardiac muscle tissue are due to a myogenic response of the heart's pacemaker cells. These cells respond to signals...
8 KB (925 words) - 13:29, 28 May 2025
patterns during development. Perry R, Rudnick M (2000). "Molecular mechanisms regulating myogenic determination and differentiation". Front Biosci. 5: D750–67...
3 KB (403 words) - 08:40, 25 July 2024
pair of somites. The interaction of other signaling molecules, such as myogenic regulatory factors, with this gradient promotes the development of other...
12 KB (1,405 words) - 16:53, 18 July 2025
Uterine contraction (section Mechanism)
pattern as the labour progresses. This transition is governed by various myogenic, neurogenic, and hormonal factors working together. As labour progresses...
15 KB (1,720 words) - 02:13, 31 July 2025
most mammals. The avian circulatory system is driven by a four-chambered, myogenic heart contained in a fibrous pericardial sac. This pericardial sac is filled...
59 KB (7,253 words) - 03:53, 29 July 2025
meat and seafood and inversely associated with dairy food consumption. Myogenic hyperuricemia, as a result of the myokinase (adenylate kinase) reaction...
28 KB (3,155 words) - 16:57, 17 July 2025
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (section Mechanism)
suggested skeletal muscle plays an important role in SBMA pathophysiology. Myogenic abnormalities in patient muscle include atrophic and morphologically abnormal...
44 KB (4,954 words) - 18:26, 17 July 2025
Metabolic myopathy (section Mechanism)
exercise (dyspnea/tachypnea/hyperpnea and tachycardia), Exercise-induced myogenic hyperuricemia (exercise-induced accelerated breakdown of purine nucleotides...
51 KB (5,293 words) - 03:06, 9 June 2025
abnormal intestinal motility. Normal colonic motility requires integration of myogenic, neural, and hormonal influences. The enteric nervous system is independent...
11 KB (1,106 words) - 14:12, 23 July 2025